
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that designs and develops central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), system-on-chip (SoC), and high-performance compute solutions. AMD serves a wide range of business and consumer markets, including gaming, data centers, artificial intelligence (AI), and embedded systems.

Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualized computing. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California, on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the technology and systems involved, or a specialized device built for such functionality.

Xilinx, Inc. was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company is renowned for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA). It also pioneered the first fabless manufacturing model.
NetApp, Inc. is an American data infrastructure company that provides unified data storage, integrated data services, and cloud operations (CloudOps) solutions to enterprise customers. The company is based in Cork City, Ireland. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012 to 2021. Founded in 1992 with an initial public offering in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.

A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. Unlike a rack-mount server, a blade server fits inside a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers, providing services such as power, cooling, networking, various interconnects and management. Together, blades and the blade enclosure form a blade system, which may itself be rack-mounted. Different blade providers have differing principles regarding what to include in the blade itself, and in the blade system as a whole.
Utility computing, or computer utility, is a service provisioning model in which a service provider makes computing resources and infrastructure management available to the customer as needed, and charges them for specific usage rather than a flat rate. Like other types of on-demand computing, the utility model seeks to maximize the efficient use of resources and/or minimize associated costs. Utility is the packaging of system resources, such as computation, storage and services, as a metered service. This model has the advantage of a low or no initial cost to acquire computer resources; instead, resources are essentially rented.

The PowerEdge (PE) line is Dell's server computer product line. PowerEdge machines come configured as tower, rack-mounted, or blade servers. Dell uses a consistent chip-set across servers in the same generation regardless of packaging, allowing for a common set of drivers and system-images.
SAP IQ is a column-based, petabyte scale, relational database software system used for business intelligence, data warehousing, and data marts. Produced by Sybase Inc., now an SAP company, its primary function is to analyze large amounts of data in a low-cost, highly available environment. SAP IQ is often credited with pioneering the commercialization of column-store technology.
The IBM Intelligent Cluster was a cluster solution for x86-based high-performance computing composed primarily of IBM components, integrated with network switches from various vendors and optional high-performance InfiniBand interconnects.
AMD FireStream was AMD's brand name for their Radeon-based product line targeting stream processing and/or GPGPU in supercomputers. Originally developed by ATI Technologies around the Radeon X1900 XTX in 2006, the product line was previously branded as both ATI FireSTREAM and AMD Stream Processor. The AMD FireStream can also be used as a floating-point co-processor for offloading CPU calculations, which is part of the Torrenza initiative. The FireStream line has been discontinued since 2012, when GPGPU workloads were entirely folded into the AMD FirePro line.

In computing, virtualization (v12n) is a series of technologies that allows dividing of physical computing resources into a series of virtual machines, operating systems, processes or containers.

Fabric computing or unified computing involves constructing a computing fabric consisting of interconnected nodes that look like a weave or a fabric when seen collectively from a distance.
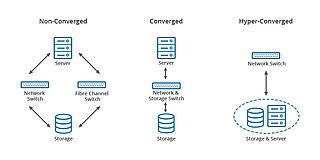
Converged infrastructure is a way of structuring an information technology (IT) system which groups multiple components into a single optimized computing package. Components of a converged infrastructure may include servers, data storage devices, networking equipment and software for IT infrastructure management, automation and orchestration.

The Open Compute Project (OCP) is an organization that facilitates the sharing of data center product designs and industry best practices among companies. Founded in 2011, OCP has significantly influenced the design and operation of large-scale computing facilities worldwide.

Virtual Computing Environment Company (VCE) was a division of EMC Corporation that manufactured converged infrastructure appliances for enterprise environments. Founded in 2009 under the name Acadia, it was originally a joint venture between EMC and Cisco Systems, with additional investments by Intel and EMC subsidiary VMware. EMC acquired a 90% controlling stake in VCE from Cisco in October 2014, giving it majority ownership. VCE ended in 2016 after an internal division realignment, followed by the sale of EMC to Dell.

HP Cloud was a set of cloud computing services available from Hewlett-Packard. It was the combination of the previous HP Converged Cloud business unit and HP Cloud Services, an OpenStack-based public cloud. It was marketed to enterprise organizations to combine public cloud services with internal IT resources to create hybrid clouds, or a mix of private and public cloud environments, from around 2011 to 2016.
MiTAC Holdings Corporation was formed on September 12, 2013, through a stock swap from MiTAC International Corp. As part of a restructuring aimed at future operational objectives, the Group established MiTAC Computing Technology Corporation on September 1, 2014, to focus on designs and manufactures servers for data centers and enterprises, offering solutions from edge to cloud computing, including hyperscale data centers, AI/HPC systems, and energy-efficient technologies like liquid cooling.

The Nvidia DGX represents a series of servers and workstations designed by Nvidia, primarily geared towards enhancing deep learning applications through the use of general-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU). These systems typically come in a rackmount format featuring high-performance x86 server CPUs on the motherboard.
Inspur Server Series is a series of server computers introduced in 1993 by Inspur, an information technology company, and later expanded to the international markets. The servers were likely among the first originally manufactured by a Chinese company. It is currently developed by Inspur Information and its San Francisco-based subsidiary company - Inspur Systems, both Inspur's spinoff companies. The product line includes GPU Servers, Rack-mounted servers, Open Computing Servers and Multi-node Servers.













