Related Research Articles

The Spanish missions in California formed a series of 21 religious outposts or missions established between 1769 and 1833 in what is now the U.S. state of California. The missions were established by Catholic priests of the Franciscan order to evangelize indigenous peoples backed by the military force of the Spanish Empire. The missions were part of the expansion and settlement of New Spain through the formation of Alta California, expanding the empire into the most northern and western parts of Spanish North America. Civilian settlers and soldiers accompanied missionaries and formed settlements like the Pueblo de Los Ángeles.

Mission Santa Barbara is a Spanish mission in Santa Barbara, California. Often referred to as the ‘Queen of the Missions,’ it was founded by Padre Fermín Lasuén for the Franciscan order on December 4, 1786, the feast day of Saint Barbara, as the tenth mission of what would later become 21 missions in Alta California.

Mission Santa Cruz is a Spanish Californian mission. Located on Mission Hill, it was founded on August 28, 1791, by Father Fermín Francisco de Lasuén, the successor of Father Junipero Serra. The mission was dedicated that same year. The present mission chapel building is a replica located near the original site, on which Holy Cross Church now stands.

Mission San Luis Rey de Francia is a former Spanish mission in San Luis Rey, a neighborhood of Oceanside, California. This Mission lent its name to the Luiseño tribe of Mission Indians.
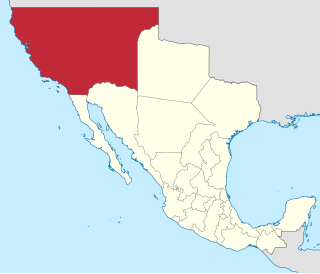
Alta California, also known as Nueva California among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of Las Californias, but was made a separate province in 1804. Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed Alta California in 1824.

New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain, or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish conquest of the Americas and having its capital in Mexico City. Its jurisdiction comprised a large area that included what is now Mexico, the Western and Southwestern United States in North America; Central America, the Caribbean, very northern parts of South America, and several territorial Pacific Ocean archipelagos.

The Nahuas are a group of the indigenous people of Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua. They comprise the largest indigenous group in Mexico and second largest in El Salvador. The Mexica (Aztecs) were of Nahua ethnicity, and the Toltecs are often thought to have been as well, though in the pre-Columbian period Nahuas were subdivided into many groups that did not necessarily share a common identity.

Bernardino de Sahagún, OFM was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain. Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, he journeyed to New Spain in 1529. He learned Nahuatl and spent more than 50 years in the study of Aztec beliefs, culture and history. Though he was primarily devoted to his missionary task, his extraordinary work documenting indigenous worldview and culture has earned him the title as “the first anthropologist." He also contributed to the description of Nahuatl, the imperial language of the Aztec Empire. He translated the Psalms, the Gospels, and a catechism into Nahuatl.

Californio is a term used to designate a Hispanic Californian, especially those descended from Spanish and Mexican settlers of the 17th through 19th centuries. California's Spanish-speaking community has resided there since 1683 and is made up of varying Spanish and Mexican origins, including criollos, Mestizos, Indigenous Californian peoples, and small numbers of Mulatos. Alongside the Tejanos of Texas and Neomexicanos of New Mexico and Colorado, Californios are part of the larger Spanish-American/Mexican-American/Hispano community of the United States, which has inhabited the American Southwest and the West Coast since the 16th century. Some may also identify as Chicanos, a term that came about in the 1960s.
Ida Louise Altman is an American historian of early modern Spain and Latin America. Her book Emigrants and Society: Extremadura and Spanish America in the Sixteenth Century received the 1990 Herbert E. Bolton Prize of the Conference on Latin American History. She is Professor Emerita of History at the University of Florida and served as Department Chair.

Aztec codices are Mesoamerican manuscripts made by the pre-Columbian Aztec, and their Nahuatl-speaking descendants during the colonial period in Mexico.

The Acjachemen are an Indigenous people of California. They historically lived south of what is known as Aliso Creek and north of the Las Pulgas Canyon in what are now the southern areas of Orange County and the northwestern areas of San Diego County.

The Awaswas, also known as the Santa Cruz people, were a group of the Indigenous peoples of California in North America, with subgroups historically numbering about 600 to 1,400. Academic research suggests that their ancestors had lived within the Santa Cruz Mountains region for approximately 12,000 years. The Awaswas maintained regular trade networks with regional cultures before the Spanish colonists began settling in the area from the 18th century.

The Colegio de Santa Cruz in Tlatelolco, Mexico City, is the first and oldest European school of higher learning in the Americas and the first major school of interpreters and translators in the New World. It was established by the Franciscans on January 6, 1536 with the intention, as is generally accepted, of preparing Native American boys for eventual ordination to the Catholic priesthood. Students trained in the Colegio were important contributors to the work of Franciscan Bernardino de Sahagún in the creation of his monumental twelve-volume General History of the Things of New Spain, often referred to as the Florentine Codex. The failure of the Colegio had long-lasting consequences, with scholar Robert Ricard saying that "[h]ad the College of Tlatelolco given the country even one [native] bishop, the history of the Mexican Church might have been profoundly changed."
James Lockhart was a U.S. historian of colonial Spanish America, especially the Nahua people and Nahuatl language.

Modesta Avila was a Californio ranchera and protester, best known for being the first convicted felon and first state prisoner in Orange County, California. Avila had only received a minor warning in 1889 for placing an obstruction on the tracks to protest against the Santa Fe Railroad being built through her property without adequate compensation, but she continued to taunt the authorities, and was eventually arrested four months later.

The California genocide was the killing of thousands of Indigenous peoples of California by United States government agents and private citizens in the 19th century. It began following the American Conquest of California from Mexico, and the influx of settlers due to the California Gold Rush, which accelerated the decline of the Indigenous population of California. Between 1846 and 1873, it is estimated that non-Natives killed between 9,492 and 16,094 California Natives. Hundreds to thousands were additionally starved or worked to death. Acts of enslavement, kidnapping, rape, child separation and displacement were widespread. These acts were encouraged, tolerated, and carried out by state authorities and militias.
Mocuachem, or alternatively spelled Mukwa'shish, Mocuache, Mocuachame, and Moquache, was a Payómkawichum village in San Diego County, California. At least 12 people were baptized by Spanish missionaries from the village as an act of Christian conversion carried out primarily at Mission San Juan Capistrano.

José de Grácia Cruz was a Acjachemen man who was born in 1848 at Mission San Juan Capistrano. He was known for his work as a bell ringer at the mission, as an artisan, a flutist in a native orchestra that would play at the mission, a sheep shearer, and for his knowledge of the Juaneño language and village sites, including Puvunga. He was also the source of the story of the mission's swallows in St. John O'Sullivan's Capistrano Nights (1930). He was referred to locally as "Acǘ," a nickname that was reportedly given to him as a child by his parents.

Monjeríos were gendered quarters within a colonial Spanish mission for overseeing, regulating, and disciplining unmarried Indigenous girls and single women. Girls were taken away from their parents to the monjeríos at around the age of seven until marriage. The quarters functioned as a form of social control at the missions for conversion to Catholicism, regulation of the sexuality of girls and women, and for the rearing of Indigenous children as a labor source.
References
- ↑ "Lisbeth Haas". University of California Santa Cruz. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
- ↑ Conquests and Historical Identities in California, 1769-1936. University of California Press. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
- ↑ Saints and Citizens: Indigenous Histories of Colonial Missions and Mexican California. University of California Press. Retrieved 8 August 2014.