
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands—called coal forests—that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. However, many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras.

A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed underground from the remains of dead plants and animals that humans extract and burn to release energy for use. The main fossil fuels are coal, petroleum and natural gas, which humans extract through mining and drilling. Fossil fuels may be burnt to provide heat for use directly, to power engines, or to generate electricity.

Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United Kingdom and South Africa, a coal mine and its structures are a colliery, a coal mine is called a 'pit', and the above-ground structures are a 'pit head'. In Australia, "colliery" generally refers to an underground coal mine.

The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and public understanding of energy and its interaction with the economy and the environment. EIA programs cover data on coal, petroleum, natural gas, electric, renewable and nuclear energy. EIA is part of the U.S. Department of Energy.
The energy policy of India is to increase energy in India and reduce energy poverty, with more focus on developing alternative sources of energy, particularly nuclear, solar and wind energy. India attained 63% overall energy self-sufficiency in 2017.

The petroleum industry in Russia is one of the largest in the world. Russia has the largest reserves and is the largest exporter of natural gas. It has the second largest coal reserves, the sixth largest oil reserves, and is one of the largest producers of oil. It is the fourth largest energy user.
Peak coal is the peak consumption or production of coal by a human community. Global coal consumption peaked in 2013, and had dropped slightly by the end of the 2010s. The peak of coal's share in the global energy mix was in 2008, when coal accounted for 30% of global energy production. The decline in coal use is largely driven by consumption declines in the United States and Europe, as well as developed economies in Asia. In 2019, production increases in countries such as China, Indonesia, India, Russia and Australia compensated for the falls in the United States and Europe. However, coal's structural decline continued in the 2020s.
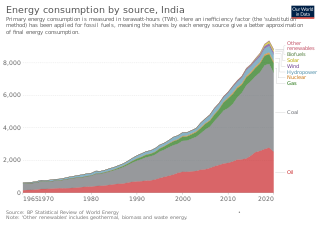
Since 2013, total primary energy consumption in India has been the third highest in the world after China and United States. India is the second-top coal consumer in the year 2017 after China. India ranks third in oil consumption with 22.1 crore tons in 2017 after United States and China. India is net energy importer to meet nearly 47% of its total primary energy in 2019.
Energy in Kazakhstan describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Kazakhstan. Energy policy of Kazakhstan describes the politics of Kazakhstan related to energy.

Energy in Mexico describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Mexico.

Energy in Germany is sourced predominantly by fossil fuels, followed by wind, nuclear power, solar, biomass and hydro.

Coal in India has been mined since 1774, and India is the second largest producer and consumer of coal after China, mining 716 million metric tons in 2018. Coal supplies over 40% of energy in India. Around 30% of coal is imported. Due to high demand and poor average quality, India imports coking coal to meet the requirements of its steel plants. Dhanbad, the largest coal producing city, has been called the coal capital of India. State-owned Coal India had a monopoly on coal mining between its nationalisation in 1973 and 2018.

South Korea is a major energy importer, importing nearly all of its oil needs and ranking as the second-largest importer of liquefied natural gas in the world. Electricity generation in the country mainly comes from conventional thermal power, which accounts for more than two thirds of production, and from nuclear power.

Energy in Australia is the production in Australia of energy and electricity, for consumption or export. Energy policy of Australia describes the politics of Australia as it relates to energy.

South Africa produces in excess of 255 million tonnes of coal and consumes almost three-quarters of that domestically. As of 2018, South Africa was the seventh largest producer and consumer of coal in the world. This large industry, means that as of 2015 about 80,000 workers, or .5% of total employment, was from the coal industry, down from a peak in 1981 of 135,000 workers. The coal industry is South Africa's largest contribution to the greenhouse gases that cause climate change.
Energy in the Czech Republic describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in the Czech Republic.

World energy supply and consumption is global production and preparation of fuel, generation of electricity, energy transport and energy consumption. It is a basic part of economic activity. It does not include energy from food.












