Related Research Articles

An encyclopedia or encyclopædia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on factual information concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.

The Encyclopædia Britannica is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia.

Imam is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide religious guidance. Thus for Sunnis, anyone can study the basic Islamic sciences and become an Imam.
June 6 is the 157th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 208 days remain until the end of the year.

Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the greater category of wind instruments. Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and reed instruments. The main distinction between these instruments and other wind instruments is the way in which they produce sound. All woodwinds produce sound by splitting the air blown into them on a sharp edge, such as a reed or a fipple. Despite the name, a woodwind may be made of any material, not just wood. Common examples include brass, silver, cane, as well as other metals such as gold and platinum. The saxophone, for example, though made of brass, is considered a woodwind because it requires a reed to produce sound. Occasionally, woodwinds are made of earthen materials, especially ocarinas.

Pope Cornelius was the bishop of Rome from 6th or 13th March 251 until his martyrdom in June 253. He was pope during and following a period of persecution of the church, while a schism occurred over how repentant church members who had practiced pagan sacrifices to protect themselves could be readmitted to the church. He agreed with Cyprian of Carthage that those who had lapsed could be restored to communion after varying forms of Reinitiation and Penance. This position was in contrast to the Novatianists, who held that those who failed to maintain their confession of faith under persecution would not be received again into communion with the church. This resulted in a short-lived schism in the Church of Rome that spread as each side sought to gather support. Cornelius held a synod that confirmed his election and excommunicated Novatian, but the controversy regarding lapsed members continued for years.

The Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition (1910–1911) is a 29-volume reference work, an edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica. It was developed during the encyclopaedia's transition from a British to an American publication. Some of its articles were written by the best-known scholars of the time. This edition of the encyclopaedia, containing 40,000 entries, has entered the public domain and is easily available on the Internet. Its use in modern scholarship and as a reliable source has been deemed problematic due to the outdated nature of some of its content. Modern scholars have deemed some articles as cultural artifacts of the 19th and early 20th centuries.

Encyclopedia Americana is a general encyclopedia written in American English. It was the first major multivolume encyclopedia that was published in the United States. With Collier's Encyclopedia and Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopedia Americana became one of the three major English-language general encyclopedias; the three were sometimes collectively called "the ABCs". Following the acquisition of Grolier in 2000, the encyclopedia has been produced by Scholastic.
Online encyclopedias, also called Internet encyclopedias, are digital encyclopedias accessible through the Internet. Examples include Wikipedia, the Encyclopædia Britannica since 2016 and Encyclopedia.com.

The Timurid dynasty, self-designated as Gurkani, was a Sunni Muslim dynasty or clan of Turco-Mongol origin descended from the warlord Timur. The word "Gurkani" derives from "Gurkan", a Persianized form of the Mongolian word "Kuragan" meaning "son-in-law". This was an honorific title used by the dynasty as the Timurids were in-laws of the line of Genghis Khan, founder of the Mongol Empire, as Timur had married Saray Mulk Khanum, a direct descendant of Genghis Khan. Members of the Timurid dynasty signaled the Timurid Renaissance, and they were strongly influenced by Persian culture and established two significant empires in history, the Timurid Empire (1370–1507) based in Persia and Central Asia, and the Mughal Empire (1526–1857) based in the Indian subcontinent.
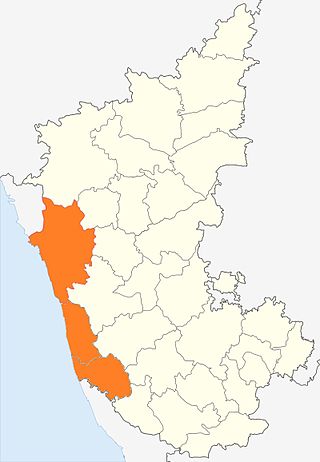
Kanara or Canara, also known as Karavali is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka. The subregion comprises three civil districts, namely: Uttara Kannada, Udupi, and Dakshina Kannada. Kassergode was included prior to the States Reorganisation Act.

Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. is a British company known for publishing the Encyclopædia Britannica, the world's oldest continuously published encyclopaedia. The company also owns the American dictionary publisher Merriam-Webster.

An inland port is a port on an inland waterway, such as a river, lake, or canal, which may or may not be connected to the sea. The term "inland port" is also used to refer to a dry port.
Pabbajjā literally means "to go forth" and refers to when a layperson leaves home to live the life of a Buddhist renunciate among a community of bhikkhus. This generally involves preliminary ordination as a novice. It is sometimes referred to as "lower ordination". After a period or when the novice reaches 20 years of age, the novice can be considered for the upasampadā ordination whereby the novice becomes a monk (bhikkhu) or nun (bhikkhuni).

Volcán Tajumulco is a large stratovolcano in the department of San Marcos in western Guatemala. It is the highest mountain in Central America at 4,203 metres (13,789 ft). It is part of the mountain range of the Sierra Madre de Chiapas, which begins in Mexico's southernmost state of Chiapas.

Wittelsbach-Hapsburg aristocrat Ernest of Bavaria was Prince-Elector-Archbishop of the Archbishopric of Cologne and, as such, Archchancellor of the Holy Roman Empire and Duke of Westphalia, from 1583 to 1612 as successor of the expelled Archbishop Gebhard Truchsess von Waldburg.
A colorimeter is a device used in colorimetry that measures the absorbance of particular wavelengths of light by a specific solution. It is commonly used to determine the concentration of a known solute in a given solution by the application of the Beer–Lambert law, which states that the concentration of a solute is proportional to the absorbance.

The leaders of the Central Powers of World War I were the political or military figures who commanded or supported the Central Powers.
References
- ↑ "K2". Encyclopaedia Britannica (Online). 2019.
- ↑ "Tirich-Mir". Encyclopaedia Britannica (Online). 2013.