Related Research Articles

The astronomical unit is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and equal to about 150 million kilometres or ~8 light minutes. The actual distance varies by about 3% as Earth orbits the Sun, from a maximum (aphelion) to a minimum (perihelion) and back again once each year. The AU was originally conceived as the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion; however, since 2012 it has been defined as exactly 149597870700 m.

The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the derived unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) and is defined as one cycle per second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (103 Hz, kHz), megahertz (106 Hz, MHz), gigahertz (109 Hz, GHz), terahertz (1012 Hz, THz), petahertz (1015 Hz, PHz), exahertz (1018 Hz, EHz), and zettahertz (1021 Hz, ZHz).

ISO 4217 is a standard published by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual currencies and their minor units. This data is published in three tables:

The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial units replaced the Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement, but imperial units are still used in the United Kingdom, Canada and some other countries formerly part of the British Empire. The imperial system developed from what were first known as English units, as did the related system of United States customary units.
The joule is a derived unit of energy in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy transferred to an object when a force of one newton acts on that object in the direction of the force's motion through a distance of one metre. It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second. It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule (1818–1889).

The kilogram is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), the current metric system, having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo in everyday speech.
1 is a number and a numerical digit used to represent that number in numerals. It represents a single entity, the unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of unit length is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0.
The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in the imperial, United States customary and other systems of measurement. Various definitions have been used; the most common today is the international avoirdupois pound, which is legally defined as exactly 0.45359237 kilograms, and which is divided into 16 avoirdupois ounces. The international standard symbol for the avoirdupois pound is lb; an alternative symbol is lbm, #, and ℔ or ″̶.
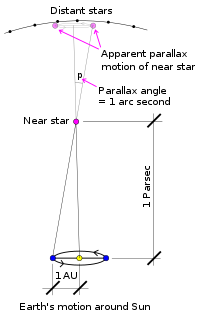
The parsec is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to 3.26 light-years or 206,000 astronomical units, i. e. 30.9 trillion kilometres. Parsec is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and is defined as the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one arcsecond. This corresponds to 648000/π astronomical units, i.e. 1 pc = 1/tan(1″) au. The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about 1.3 parsecs from the Sun. Most of the stars visible to the unaided eye in the night sky are within 500 parsecs of the Sun.

The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system. It is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world. It comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second, metre, kilogram, ampere, kelvin, mole, and candela. The system allows for an unlimited number of additional units, called derived units, which can always be represented as products of powers of the base units. Twenty-two derived units have been provided with special names and symbols. The seven base units and the 22 derived units with special names and symbols may be used in combination to express other derived units, which are adopted to facilitate measurement of diverse quantities. The SI system also provides twenty prefixes to the unit names and unit symbols that may be used when specifying power-of-ten multiples and sub-multiples of SI units. The SI is intended to be an evolving system; units and prefixes are created and unit definitions are modified through international agreement as the technology of measurement progresses and the precision of measurements improves.

The tonne is a metric unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is commonly referred to as a metric ton in the United States. It is equivalent to approximately 2,204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons (US) or approximately 0.984 long tons (UK). The official SI unit is the megagram, a less common way to express the same mass.

A metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the International System of Units (SI), under the oversight of an international standards body.

The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is defined as one newton per square metre and is equivalent to 10 barye (Ba) in the CGS system. The unit of measurement called standard atmosphere (atm) is defined as 101,325 Pa.
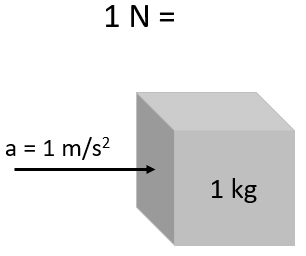
The newton is the International System of Units (SI) derived unit of force. It is named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his work on classical mechanics, specifically Newton's second law of motion.

Law & Order: Special Victims Unit is an American crime drama television series created by Dick Wolf for NBC. It stars Mariska Hargitay as onetime lead detective and later Captain Olivia Benson, the commanding officer of the Special Victims Unit in a fictionalized version of the New York City Police Department. Christopher Meloni played the other SVU lead detective, Elliot Stabler, until departing from the series in 2011 after 12 seasons. Meloni will return to star as Stabler in 2021 in the spin-off series Law & Order: Organized Crime. Law & Order: Special Victims Unit follows the style of the original Law & Order in that some episodes are loosely based on real crimes that have received media attention; these episodes are referred to as having been "ripped from the headlines".

Unit 731, short for Manshu Detachment 731 and also known as Kamo Detachment, Ishii Unit, was a covert biological and chemical warfare research and development unit of the Imperial Japanese Army that undertook lethal human experimentation during the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) of World War II. It was responsible for some of the most notorious war crimes carried out by Imperial Japan. Unit 731 was based at the Pingfang district of Harbin, the largest city in the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo, and had active branch offices throughout China and Southeast Asia.
The watt is a unit of power or radiant flux. In the International System of Units (SI), it is defined as a derived unit of 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3 or, equivalently, 1 joule per second. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt, an 18th-century Scottish inventor.

The hectare is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about 0.405 hectare and one hectare contains about 2.47 acres.
Real estate is property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals or water; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this (also) an item of real property, buildings or housing in general.
References
- ↑ Olędzki, Marek (2011). Wojny markomańskie (in Polish). Bellona. pp. 169–171. ISBN 9788311120358.