This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2008) |
| Pannonia Inferior | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||||||
| 103–3rd century | |||||||||||
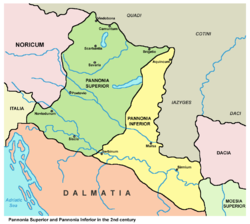
 Pannonia Inferior (125 AD) | |||||||||||
| Capital | Aquincum and Sirmium [1] | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 103 | ||||||||||
• Reorganized | 3rd century | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Bosnia and Herzegovina Croatia Hungary Serbia | ||||||||||
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east (across the Danube) by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east.