Related Research Articles

A safety data sheet (SDS), material safety data sheet (MSDS), or product safety data sheet (PSDS) is a document that lists information relating to occupational safety and health for the use of various substances and products. SDSs are a widely used type of fact sheet used to catalogue information on chemical species including chemical compounds and chemical mixtures. SDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product, along with spill-handling procedures. The older MSDS formats could vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements; however, the newer SDS format is internationally standardized.

Hazard symbols are recognizable symbols designed to warn about hazardous or dangerous materials, locations, or objects, including electromagnetic fields, electric currents; harsh, toxic or unstable chemicals ; and radioactivity. The use of hazard symbols is often regulated by law and directed by standards organizations. Hazard symbols may appear with different colors, backgrounds, borders, and supplemental information in order to specify the type of hazard and the level of threat. Warning symbols are used in many places in place of or in addition to written warnings as they are quickly recognized and more universally understood, as the same symbol can be recognized as having the same meaning to speakers of different languages.

Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006, amended on 16 December 2008 by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008. REACH addresses the production and use of chemical substances, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment. Its 849 pages took seven years to pass, and it has been described as the most complex legislation in the Union's history and the most important in 20 years. It is the strictest law to date regulating chemical substances and will affect industries throughout the world. REACH entered into force on 1 June 2007, with a phased implementation over the next decade. The regulation also established the European Chemicals Agency, which manages the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of REACH.
Risk and Safety Statements, also known as R/S statements, R/S numbers, R/S phrases, and R/S sentences, is a system of hazard codes and phrases for labeling dangerous chemicals and compounds. The R/S statement of a compound consists of a risk part (R) and a safety part (S), each followed by a combination of numbers. Each number corresponds to a phrase. The phrase corresponding to the letter/number combination has the same meaning in different languages—see 'languages' in the menu on the left.

The Dangerous Substances Directive was one of the main European Union laws concerning chemical safety, until its full replacement by the new regulation CLP Regulation (2008), starting in 2016. It was made under Article 100 of the Treaty of Rome. By agreement, it is also applicable in the EEA, and compliance with the directive will ensure compliance with the relevant Swiss laws. The Directive ceased to be in force on 31 May 2015 and was repealed by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006.

The European Community number is a unique seven-digit identifier that was assigned to substances for regulatory purposes within the European Union by the European Commission. The EC Inventory comprises three individual inventories, EINECS, ELINCS and the NLP list.

The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods relevant information with consistent organization. The system acts as a complement to the UN numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world. This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards.
The European Chemicals Bureau (ECB) was the focal point for the data and assessment procedure on dangerous chemicals within the European Union (EU). The ECB was located in Ispra, Italy, within the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission. In 2008 the ECB completed its mandate. Some of its activities were taken over by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA); others remained within the Joint Research Centre. The history of the ECB has been published as a JRC technical report.

The CLP Regulation is a European Union regulation from 2008, which aligns the European Union system of classification, labelling and packaging of chemical substances and mixtures to the Globally Harmonised System (GHS). It is expected to facilitate global trade and the harmonised communication of hazard information of chemicals and to promote regulatory efficiency. It complements the 2006 Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) Regulation and replaces an older system contained in the Dangerous Substances Directive (67/548/EEC) and the Dangerous Preparations Directive (1999/45/EC).

The Dangerous Preparations Directive was a European Union directive in the field of occupational safety and health and consumer protection that came into force in 30 July 1999. It complemented the Dangerous Substances Directive (67/548/EEC) and replaced a previous Dangerous Preparations Directive (88/379/EEC). The European Court of Justice had ruled in 1985 that Dangerous Substances Directive (67/548/EEC) applies only to pure substances, not preparations. It was repealed on 1 June 2015, as part of the European Union's adoption of Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals, as part of CLP Regulation.
Hazard statements form part of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). They are intended to form a set of standardized phrases about the hazards of chemical substances and mixtures that can be translated into different languages. As such, they serve the same purpose as the well-known R-phrases, which they are intended to replace.
Precautionary statements form part of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). They are intended to form a set of standardized phrases giving advice about the correct handling of chemical substances and mixtures, which can be translated into different languages. As such, they serve the same purpose as the well-known S-phrases, which they are intended to replace.
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). Two sets of pictograms are included within the GHS: one for the labelling of containers and for workplace hazard warnings, and a second for use during the transport of dangerous goods. Either one or the other is chosen, depending on the target audience, but the two are not used together for the same hazard. The two sets of pictograms use the same symbols for the same hazards, although certain symbols are not required for transport pictograms. Transport pictograms come in wider variety of colors and may contain additional information such as a subcategory number.
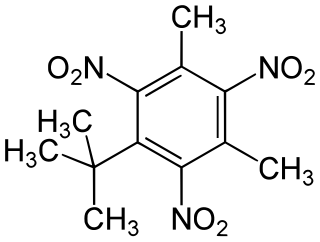
Musk xylene is a synthetic musk fragrance which mimics natural musk. It has been used as a perfume fixative in a wide variety of consumer products, and is still used in some cosmetics and fragrances.

n-Hexyllithium, C6H13Li, sometimes abbreviated to HxLi or NHL, is an organolithium compound used in organic synthesis as a strong base or as a lithiation reagent. It is usually encountered as a colorless or pale yellow solution in hexanes. Such solutions are highly sensitive to air and can ignite when treated with water.
European hazard symbols for chemicals are pictograms defined by the European Union for labelling chemical packaging and containers. They are standardised currently by the CLP/GHS classification.

Methyl eugenol (allylveratrol) is a natural chemical compound classified as a phenylpropene, a type of phenylpropanoid. It is the methyl ether of eugenol and is important to insect behavior and pollination. It is found in various essential oils.
Technical Guidance WM2: Hazardous Waste: Interpretation of the definition and classification of hazardous waste is a guidance document developed and jointly published by the English Environment Agency, Natural Resources Wales, Scottish Environment Protection Agency and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency to provide guidance on the assessment and classification of hazardous waste based on the revised Waste Framework Directive definition of hazardous waste. Waste producers, consultants, contractors and waste management companies use the guidance to a) identify the correct waste code for their waste and b) determine whether the waste is hazardous or not based on its chemical composition.
The Machinery Directive, Directive 2006/42/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 May 2006 is a European Union directive concerning machinery and certain parts of machinery. Its main intent is to ensure a common safety level in machinery placed on the market or put in service in all member states and to ensure freedom of movement within the European Union by stating that "member states shall not prohibit, restrict or impede the placing on the market and/or putting into service in their territory of machinery which complies with [the] Directive".
References
- 1 2 3 4 Consolidated text: Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006
- ↑ Commission Directive 2001/59/EC of 6 August 2001 adapting to technical progress for the 28th time Council Directive 67/548/EEC on the approximation of the laws, regulations and administrative provisions relating to the classification, packaging and labelling of dangerous substances. No longer in force, Date of end of validity: 31/05/2015; Implicitly repealed by 32008R1272. [1]
- ↑ Council Directive 2006/102/EC of 20 November 2006 adapting Directive 67/548/EEC on the classification, packaging and labelling of dangerous substances, by reason of the accession of Bulgaria and Romania: Annex IV - Safety advice concerning dangerous substances and preparations. No longer in force, Date of end of validity: 31/05/2015; Implicitly repealed by 32008R1272. [1]
- ↑ United Nations (2021). "Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS)" (PDF). unece.org. United Nations. pp. 263–378. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 November 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
Annex 3 - Codification of Hazard Statements, Codification, and Use of Precautionary Statements, Codification of Hazard Pictograms and Examples of Precautionary Pictograms