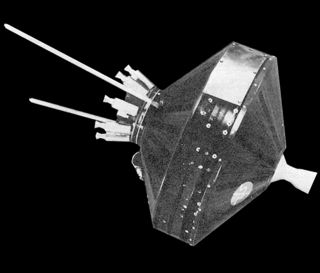
Pioneer 1 was an American space probe, the first under the auspices of NASA, which was launched by a Thor-Able rocket on 11 October 1958. It was intended to orbit the Moon and make scientific measurements, but due to a guidance error failed to achieve lunar orbit and was ultimately destroyed upon reentering Earth's atmosphere. The flight, which lasted 43 hours and reached an apogee of 113,800 km, was the second and most successful of the three Thor-Able space probes.

The PGM-17A Thor was the first operational ballistic missile of the United States Air Force (USAF). Named after the Norse god of thunder, it was deployed in the United Kingdom between 1959 and September 1963 as an intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) with thermonuclear warheads. Thor was 65 feet (20 m) in height and 8 feet (2.4 m) in diameter. It was later augmented in the U.S. IRBM arsenal by the Jupiter.

Delta is an American versatile family of expendable launch systems that has provided space launch capability in the United States since 1960. Japan also launched license-built derivatives from 1975 to 1992. More than 300 Delta rockets have been launched with a 95% success rate. Only the Delta IV Heavy rocket remains in use as of November 2020. Delta rockets are currently manufactured and launched by the United Launch Alliance.

The Thor-Able was an American expendable launch system and sounding rocket used for a series of re-entry vehicle tests and satellite launches between 1958 and 1960. It was a two-stage rocket, consisting of a Thor IRBM as a first stage and a Vanguard-derived Able second stage. On some flights, an Altair solid rocket motor was added as a third stage. It was a member of the Thor family and an early predecessor of the Delta.

The Graphite-Epoxy Motor (GEM) is a family of solid rocket boosters first developed in the late 1980s and used from 1990 to the present day. GEM motors are manufactured with carbon-fibre-reinforced polymer casings and a fuel consisting of HTPB-bound ammonium perchlorate composite propellant. GEM is currently produced by Northrop Grumman Space Systems. GEM boosters were previously used on the Delta II, Delta III, and Delta IV launch vehicles, and are currently used on the Atlas V. A new variant, the GEM 63XL, is slated to fly as part of the Vulcan Centaur launch vehicle as early as 2022.

Long March 5, or Changzheng 5 (CZ-5), and also by its nickname "Pang-Wu", is a Chinese heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT). It is the first Chinese launch vehicle designed to use exclusively non-hypergolic liquid propellants. It is the fifth iteration of the Long March rocket family.

Thor-Agena was a series of orbital launch vehicles. The launch vehicles used the Douglas-built Thor first stage and the Lockheed-built Agena second stages. They are thus cousins of the more-famous Thor-Deltas, which founded the Delta rocket family. The first attempted launch of a Thor-Agena was in January 1959. The first successful launch was on 28 February 1959, launching Discoverer 1. It was the first two-stage launch vehicle to place a satellite into orbit.

The Proton-M, (Протон-М) GRAU index 8K82M or 8K82KM, is an expendable Russian heavy-lift launch vehicle derived from the Soviet-developed Proton. It is built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81 and 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Commercial launches are marketed by International Launch Services (ILS), and generally use Site 200/39. The first Proton-M launch occurred on 7 April 2001.

The Thor-Ablestar, or Thor-Able-Star, also known as Thor-Epsilon was an early American expendable launch system consisting of a PGM-17 Thor missile, with an Ablestar upper stage. It was a member of the Thor family of rockets, and was derived from the Thor-Able.

The Delta 0100 series, also Delta 100, 0300 or 300 series, was an American expendable launch system which conducted orbital launches between 1968 and 1972. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets, and the first to be designated using a four digit numerical code. Two variants were flown, individually designated Delta 0300 and Delta 0900.

The Delta 1000 series was an American expendable launch system which was used to conduct eight orbital launches between 1972 and 1975. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets. Several variants existed, differentiated by a four digit numerical code. Delta 1000 was developed by McDonnell Douglas company in 1972.

Astra is an American launch vehicle company based in Alameda, California. Astra was incorporated in October 2016 by Chris Kemp and Adam London. Formerly known in media as "Stealth Space Company", the company formally came out as Astra Space, Inc. in a Bloomberg L.P. article by Ashlee Vance. Investors include BlackRock, Advance, ACME, Airbus Ventures, Innovation Endeavors, Salesforce co-founder Marc Benioff, former Disney CEO Michael Eisner, and more.
The Blok DM-03, GRAU index 11S861-03, is a Russian upper stage used as an optional fourth stage on the Proton-M ICBM very heavy rocket. Three have been launched, the first in December 2010; the first two launches failed before fourth stage ignition, the first as a result of a problem with the Blok DM's fuel load.











