
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.

A vehicle is a machine designed for self propulsion, usually to transport people or cargo, or both. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles, railed vehicles, watercraft, amphibious vehicles, aircraft and spacecraft.

Taxiing is the movement of an aircraft on the ground, under its own power, in contrast to towing or pushback where the aircraft is moved by a tug. The aircraft usually moves on wheels, but the term also includes aircraft with skis or floats.

The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine. The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s.

The Tupolev Tu-134 is a twin-engined, narrow-body jet airliner built in the Soviet Union for short and medium-haul routes from 1966 to 1989. The original version featured a glazed-nose design and, like certain other Russian airliners, it can operate from unpaved airfields.
In aviation, a go-around is an aborted landing of an aircraft that is on final approach or has already touched down. A go-around can either be initiated by the pilot flying or requested by air traffic control for various reasons, such as an unstabilized approach or an obstruction on the runway.

The Tupolev Tu-110 was a jet airliner designed and built in the USSR, which saw its maiden flight in 1957.

Thrust reversal, also called reverse thrust, is the temporary diversion of an aircraft engine's thrust for it to act against the forward travel of the aircraft, providing deceleration. Thrust reverser systems are featured on many jet aircraft to help slow down just after touch-down, reducing wear on the brakes and enabling shorter landing distances. Such devices affect the aircraft significantly and are considered important for safe operations by airlines. There have been accidents involving thrust reversal systems, including fatal ones.

In aeronautics, a spoiler is a device which intentionally reduces the lift component of an airfoil in a controlled way. Most often, spoilers are plates on the top surface of a wing that can be extended upward into the airflow to spoil the streamline flow. By so doing, the spoiler creates a controlled stall over the portion of the wing behind it, greatly reducing the lift of that wing section. Spoilers differ from airbrakes in that airbrakes are designed to increase drag without disrupting the lift distribution across the wing span, while spoilers disrupt the lift distribution as well as increasing drag.
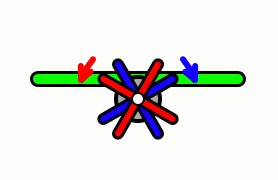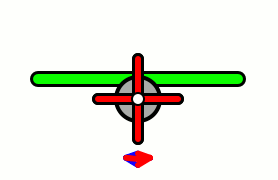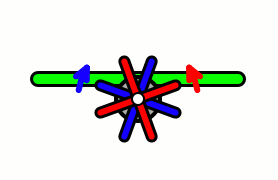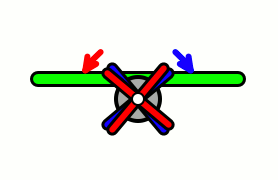
Aircraft equipped with contra-rotating propellers (CRP) coaxial contra-rotating propellers, or high-speed propellers, apply the maximum power of usually a single piston engine or turboprop engine to drive a pair of coaxial propellers in contra-rotation. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via a planetary gear or spur gear transmission. Contra-rotating propellers are also known as counter-rotating propellers, although the term counter-rotating propellers is much more widely used when referring to airscrews on separate non-coaxial shafts turning in opposite directions.

In aeronautics, air brakes or speed brakes are a type of flight control surface used on an aircraft to increase the drag on the aircraft. When extended into the airstream, air brakes cause an increase in the drag on the aircraft. When not in use, they conform to the local streamlined profile of the aircraft in order to help minimize drag.

The Sukhoi Su-9 was an early jet fighter built in the Soviet Union shortly after World War II. The design began in 1944 and was intended to use Soviet-designed turbojet engines. The design was heavily influenced by captured German jet fighters and it was subsequently redesigned to use a Soviet copy of a German turbojet. The Su-9 was slower than competing Soviet aircraft and it was cancelled as a result. A modified version with different engines and a revised wing became the Su-11, but this did not enter production either. The Su-13 was a proposal to re-engine the aircraft with Soviet copies of the Rolls-Royce Derwent turbojet as well as to modify it for night fighting, but neither proposal was accepted.

The Soloviev D-30 is a Soviet two-shaft low-bypass turbofan engine, officially referred to as a "bypass turbojet". It is one of the most powerful turbofan engines developed in the Soviet Union. Development of the turbofan spurred numerous growth versions with increased fan diameter and modified component arrangements. Developed in a short period of time, the D-30 turned out to be one of the most reliable engines in the history of Soviet engine development, and it was recognized with the USSR State Prize.
In aviation, a balanced field takeoff is a condition where the takeoff distance required (TODR) with one engine inoperative and the accelerate-stop distance are equal for the aircraft weight, engine thrust, aircraft configuration and runway condition. For a given aircraft weight, engine thrust, aircraft configuration, and runway condition, the shortest runway length that complies with safety regulations is the balanced field length.

S7 Airlines Flight 778(S7778/SBI778) was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from Moscow to Irkutsk, Russia. On 9 July 2006, at 06:44 local time, the Airbus A310-324 aircraft operating the route overran the runway during its landing in Irkutsk. The aircraft failed to stop and crashed through the airport's concrete perimeter fence, struck rows of private garages and burst into flames, killing 125 people.

In aeronautics, an aircraft propeller, also called an airscrew, converts rotary motion from an engine or other power source into a swirling slipstream which pushes the propeller forwards or backwards. It comprises a rotating power-driven hub, to which are attached several radial airfoil-section blades such that the whole assembly rotates about a longitudinal axis. The blade pitch may be fixed, manually variable to a few set positions, or of the automatically variable "constant-speed" type.
Red Wings Airlines is a Russian regional leisure airline based in Moscow Domodedovo Airport. The airline provides both scheduled passenger and cargo services.

Aircraft systems are those required to operate an aircraft efficiently and safely. Their complexity varies with the type of aircraft.

The Progress D-436 is a three-shaft high by-pass turbofan engine developed by the Ukrainian company Ivchenko-Progress, and manufactured by Motor Sich in Ukraine. It was initially developed to meet the requirements for late versions of the Yakovlev Yak-42 and the Antonov An-72 in the 1980s. The engine first ran in 1985 and was subsequently certified in 1987. Several variants have been developed and are currently in service with a variety of aircraft.

Red Wings Airlines Flight 9268 was a Tupolev Tu-204-100 passenger jet that on 29 December 2012 crashed on landing at Moscow Vnukovo Airport, Russia, following a repositioning flight from Pardubice Airport, Czech Republic. There were no passengers on board, but 5 of the 8 crew members were killed when the aircraft hit a ditch and highway structures after overrunning the runway.

















