Related Research Articles

Halberstadt is a town in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, the capital of Harz district. Located north of the Harz mountain range, it is known for its old town center, which was largely destroyed by Allied bombings in the late stages of World War II after local Nazi leaders refused to surrender. The town was rebuilt in the following decades.
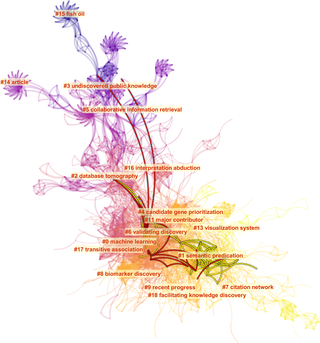
Bibliometrics is the use of statistical methods to analyse books, articles and other publications, especially in scientific contents. Bibliometric methods are frequently used in the field of library and information science. Bibliometrics is closely associated with scientometrics, the analysis of scientific metrics and indicators, to the point that both fields largely overlap.

Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes peer-reviewed online academic journals and books, conference papers, theses and dissertations, preprints, abstracts, technical reports, and other scholarly literature, including court opinions and patents.
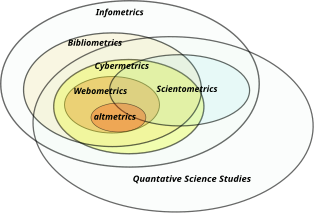
Informetrics is the study of quantitative aspects of information, it is an extension and evolution of traditional bibliometrics and scientometrics. Informetrics uses bibliometrics and scientometrics methods to study mainly the problems of literature information management and evaluation of science and technology. Informetrics is an independent discipline that uses quantitative methods from mathematics and statistics to study the process, phenomena, and law of informetrics. Informetrics has gained more attention as it is a common scientific method for academic evaluation, research hotspots in discipline, and trend analysis.

Jorge Eduardo Hirsch is an Argentine American professor of physics at the University of California, San Diego. Hirsch received a PhD in physics from the University of Chicago in 1980 and completed his postdoctoral research at the Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics at the University of California, Santa Barbara in 1983. He is known for inventing the h-index in 2005, an index for quantifying a scientist's publication productivity and the basis of several scholar indices.
Börde is a district in Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. Its seat is the town Haldensleben. It takes its name from the natural region Magdeburg Börde. It is the site of the Morsleben radioactive waste repository. The disposal of waste into the facility ended in 1998.
Harz is a district in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Its area is 2,104.9 km2 (812.7 sq mi).

YouTube Creator Awards, commonly known as YouTube Play Buttons or YouTube Plaques, are a series of awards from the American video platform YouTube that aim to recognize its most popular channels. They are based on a channel's subscriber count but are offered at the sole discretion of YouTube. Each channel is reviewed before an award is issued, to ensure that the channel follows the YouTube community guidelines. YouTube reserves the right to refuse to hand out a Creator Award, which it has done for channels featuring horror or extremist political content.

Altmetric, or altmetric.com, is a data science company that tracks where published research is mentioned online, and provides tools and services to institutions, publishers, researchers, funders and other organisations to monitor this activity, commonly referred to as altmetrics. Altmetric was recognized by European Commissioner Máire Geoghegan-Quinn in 2014 as a company challenging the traditional reputation systems.
Author-level metrics are citation metrics that measure the bibliometric impact of individual authors, researchers, academics, and scholars. Many metrics have been developed that take into account varying numbers of factors.
Bibliometrix is a package for the R statistical programming language for quantitative research in scientometrics and bibliometrics.

Microsoft Academic was a free internet-based academic search engine for academic publications and literature, developed by Microsoft Research in 2016 as a successor of Microsoft Academic Search. Microsoft Academic was shut down in 2022. Both OpenAlex and The Lens claim to be successors to Microsoft Academic.

Serbian Citation Index is a combination of an online multidisciplinary bibliographic database, a national citation index, an Open Access full-text journal repository and an electronic publishing platform. It is produced and maintained by the Centre for Evaluation in Education and Science (CEON/CEES), based in Belgrade, Serbia. In July 2017, it indexed 230 Serbian scholarly journals in all areas of science and contained more than 80,000 bibliographic records and more than one million bibliographic references.
Dr. Alan D. Swain III was a human factors engineer who specialized in weapons systems and nuclear power plants. He was a Distinguished Member of Technical Staff at Sandia National Laboratories, where he developed the technique for human error-rate prediction (THERP). According to a bibliometrics analysis performed in 2020, Swain is the most highly cited author in the field of human reliability analysis.
References
- ↑ "BibExcel". homepage.univie.ac.at. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- ↑ "Bibliometrix - Home". www.bibliometrix.org. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- ↑ "Biblioshiny". Bibliometrix. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- ↑ Batagelj, Vladamir; Mrvar, Andrej. "Networks / Pajek". vlado.fmf.uni-lj.si. Retrieved 2022-08-12.
- ↑ Harzing, Anne-Wil. "Publish or Perish". Harzing.com. Retrieved 2022-08-12.
- ↑ Van Eck, Nees Jan; Waldman, Ludo (31 December 2009). "VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping". Scientometrics. 84: 523–538. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3 . PMC 2883932 . Retrieved 23 September 2023.
- ↑ "VOSviewer - Visualizing scientific landscapes". VOSviewer. Retrieved 2022-06-02.