
The Thirteen Colonies were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America during the 17th and 18th centuries. Grievances against the imperial government led the 13 colonies to begin uniting in 1774, and expelling British officials by 1775. Assembled at the Second Continental Congress in Philadelphia, they appointed George Washington as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army to fight the American Revolutionary War. In 1776, Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence as the United States of America. Defeating British armies with French help, the Thirteen Colonies gained sovereignty with the Treaty of Paris in 1783.
In the United States, a county or county equivalent is an administrative or political subdivision of a U.S. state or other territories of the United States which consists of a geographic area with specific boundaries and usually some level of governmental authority. The term "county" is used in 48 states, while Louisiana and Alaska have functionally equivalent subdivisions called parishes and boroughs, respectively. The specific governmental powers of counties vary widely between the states, with many providing some level of services to civil townships, municipalities, and unincorporated areas. Certain municipalities are in multiple counties; New York City is uniquely partitioned into five counties, referred to at the city government level as boroughs. Some municipalities have been consolidated with their county government to form consolidated city-counties, or have been legally separated from counties altogether to form independent cities. Conversely, counties in Connecticut, Rhode Island, eight of Massachusetts's 14 counties, and Alaska's Unorganized Borough have no government power, existing only as geographic distinctions.

The United States is a country primarily located in North America. Demographics of the United States concern matters of population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects regarding the population.

The Mid-Atlantic is a region of the United States located in the overlap between the Northeastern and Southeastern states of the United States. Its exact definition differs upon source, but the region typically includes Delaware, the District of Columbia, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia with other sources including or excluding other states or areas in the Northeast and Southeast. The region has its origin in the Middle Colonies of the 18th century when its states were among the Thirteen Colonies of pre-revolutionary British America. As of the 2020 census, the region had a population of 60,783,913, representing slightly over 18% of the nation's population.

Slavery in the colonial history of the United States refers to the institution of slavery that existed in the European colonies in North America which eventually became part of the United States of America. Slavery developed due to a combination of factors, primarily the labor demands for establishing and maintaining European colonies, which had resulted in the Atlantic slave trade. Slavery existed in every European colony in the Americas during the early modern period, and both Africans and indigenous peoples were targets of enslavement by European colonists during the era.

The United States census is a census that is legally mandated by the Constitution of the United States. It takes place every ten years. The first census after the American Revolution was taken in 1790 under Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson. There have been 23 federal censuses since that time. The census includes territories of the United States. The United States Census Bureau is responsible for conducting the census.

The Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations was one of the original Thirteen Colonies established on the east coast of America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean. It was founded by Roger Williams. It was an English colony from 1636 until 1707, and then a colony of Great Britain until the American Revolution in 1776, when it became the State of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations.

The Province of Maine refers to any of the various English colonies established in the 17th century along the northeast coast of North America, within portions of the present-day U.S. states of Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec and New Brunswick. It existed through a series of land patents made by the kings of England during this era, and included New Somersetshire, Lygonia, and Falmouth. The province was incorporated into the Massachusetts Bay Colony during the 1650s, beginning with the formation of York County, Massachusetts, which extended from the Piscataqua River to just east of the mouth of the Presumpscot River in Casco Bay. Eventually, its territory grew to encompass nearly all of present-day Maine.

The Eastern United States, often abbreviated as simply the East, is a macroregion of the United States located to the east of the Mississippi River. It includes 17–26 states and Washington, D.C., the national capital.

British Americans usually refers to Americans whose ancestral origin originates wholly or partly in the United Kingdom. It is primarily a demographic or historical research category for people who have at least partial descent from peoples of Great Britain and the modern United Kingdom, i.e. English, Scottish, Irish, Welsh, Scotch-Irish, Orcadian, Manx, Cornish Americans and those from the Channel Islands and Gibraltar.

The 1850 United States census was the seventh decennial United States Census Conducted by the Census Office, it determined the resident population of the United States to be 23,191,876—an increase of 35.9 percent over the 17,069,453 persons enumerated during the 1840 census. The total population included 3,204,313 enslaved people.

Caribbean Americans or West Indian Americans are Americans who trace their ancestry to the Caribbean. Caribbean Americans are a multi-ethnic and multi-racial group that trace their ancestry further in time mostly to Africa, as well as Asia, the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, and to Europe. As of 2016, about 13 million — about 4% of the total U.S. population — have Caribbean ancestry.

Slavery was practiced in Massachusetts bay by Native Americans before European settlement, and continued until its abolition in the 1700s. Although slavery in the United States is typically associated with the Caribbean and the Antebellum American South, enslaved people existed to a lesser extent in New England: historians estimate that between 1755 and 1764, the Massachusetts enslaved population was approximately 2.2 percent of the total population; the slave population was generally concentrated in the industrial and coastal towns. Unlike in the American South, enslaved people in Massachusetts had legal rights, including the ability to file legal suits in court.
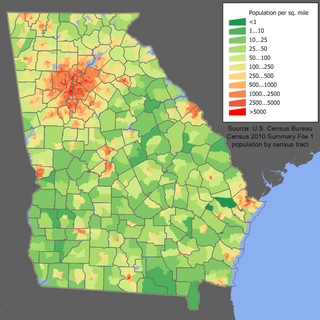
Georgia is a South Atlantic U.S. state with a population of 10,711,908 according to the 2020 United States census, or just over 3% of the U.S. population. The majority of the state's population is concentrated within Metro Atlanta, although other highly populated regions include: West Central and East Central Georgia; West, Central, and East Georgia; and Coastal Georgia; and their Athens, Columbus, Macon and Warner Robins, Augusta, Savannah, Hinesville, and Brunswick metropolitan statistical areas.

Washington County, known locally as South County, is a county located in the U.S. state of Rhode Island. As of the 2020 census, the population was 129,839. Rhode Island counties have no governmental functions other than as court administrative boundaries, which are part of the state government.

Freedom suits were lawsuits in the Thirteen Colonies and the United States filed by slaves against slaveholders to assert claims to freedom, often based on descent from a free maternal ancestor, or time held as a resident in a free state or territory.
The racial and ethnic demographics of the United States have changed dramatically throughout its history.















