Contents
- Medieval Times
- Mali Empire
- Songhai Empire
- Modern Times
- Kingdom of Waalo
- French West Africa
- Notes
- See also





Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is a country in West Africa, on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. Senegal is bordered by Mauritania to the north, Mali to the east, Guinea to the southeast and Guinea-Bissau to the southwest. Senegal nearly surrounds The Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. Senegal also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's economic and political capital is Dakar.
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era.
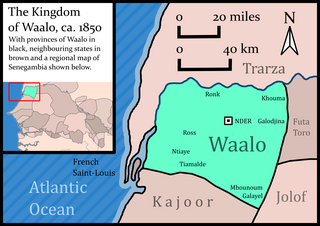
Waalo was a kingdom on the lower Senegal River in West Africa, in what is now Senegal and Mauritania. It included parts of the valley proper and areas north and south, extending to the Atlantic Ocean. To the north were Moorish emirates; to the south was the kingdom of Cayor; to the east was Jolof.
The Senegambia is, in the narrow sense, a historical name for a geographical region in West Africa, which lies between the Senegal River in the north and the Gambia River in the south. However, there are also text sources which state that Senegambia is understood in a broader sense and equated with the term the Western region. This refers to the coastal areas between Senegal and Sierra Leone, where the inland border in the east was not further defined.
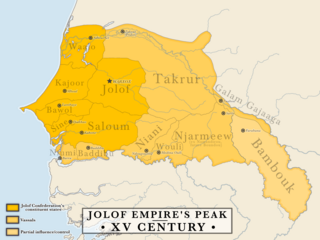
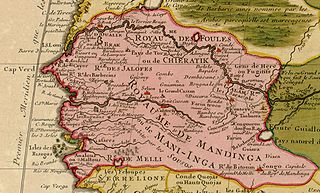
The Jolof Empire, also known as Great Jolof, or the WolofEmpire, was a Wolof and Sereer confederacy state that ruled parts of West Africa, most precisely modern-day Senegal, Mali, Gambia and Mauritania from around the 12th century to 1549. Following the 1549 battle of Danki, its vassal states were fully or de facto independent; in this period it is known as the Jolof Kingdom.

The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a lingua franca in much of West Africa. Virtually all of Mandinka people are adherent to Islam, mostly based on the Maliki jurisprudence. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali.
Sundiata Keita was a prince and founder of the Mali Empire. He was also the great-uncle of the Malian ruler Mansa Musa, who is usually regarded as the wealthiest person of all time, although there are no reliable ways to accurately calculate his wealth.

Senegambia, officially the Senegambia Confederation or Confederation of Senegambia, was a loose confederation in the late 20th century between the West African countries of Senegal and its neighbour the Gambia, which is almost completely surrounded by Senegal. The confederation was founded on 1 February 1982 following an agreement between the two countries signed on 12 December 1981. It was intended to promote cooperation between the two countries, but was dissolved by Senegal on 30 September 1989 after the Gambia refused to move closer toward union. The Senegambia Confederation should not be confused with the historic Senegambia region, generally shortened to the Senegambia.

Hadji Oumarûl Foutiyou Tall, born in Futa Tooro, present day Senegal, was a West African Tijani sufi Toucouleur Islamic scholar and military commander who founded the short-lived Toucouleur Empire, which encompassed much of what is now Senegal, Guinea, Mauritania and Mali.

Kaarta, or Ka'arta, was a Bambara kingdom that arose after the fall of the Songhai Empire in what is today the western half of Mali and lasted until its destruction by Umar Tall in the 1850s.
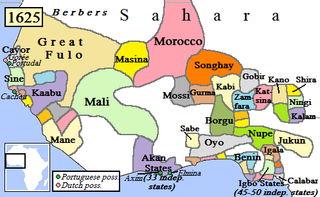
The Empire of Great Fulo, also known as the Denanke Kingdom or Denianke Kingdom, was a Pulaar kingdom of Senegal, which dominated the Futa Toro region. Its population dominated its neighbors through wars against the Mali and Songhai empires.
Mamadu Diakhou Bâ, also known as Maba Jahou Bah, Ma Ba Diakhu, Ma Ba Diakho Ba, Ma Ba Jaaxu, Mabba Jaxu Ba, was a Muslim leader in West Africa during the 19th century. He was a disciple of the Tijaniyya Sufi brotherhood and became the Almami of Saloum.
Tiramakhan Traore was a 13th-century general in the Mali Empire who served under Sundiata Keita. Traore expanded the power of Mali westward and set up the Kabu Empire. In his conquest of the region, he is reported to have defeated the Bainuk king Kikikor and annexed his state. The Guelowar royal family, including the royal family of Kaabu prior to their defeat at the Battle of Kansala, claimed descent from Tiramakhan Traore.
The military history of the Mali Empire is that of the armed forces of the Mali Empire, which dominated Western Africa from the mid 13th to the late 15th century. The military culture of the empire's driving force, Mandinka people, influenced many later states in West Africa including break-away powers such as the Songhay and Jolof empires. Institutions from the Mali Empire also survived in the 19th century army of Samory Ture who saw himself as the heir to Old Mali's legacy.
The French conquest of Senegal started in 1659 with the establishment of Saint-Louis, Senegal, followed by the French capture of the island of Gorée from the Dutch in 1677, but would only become a full-scale campaign in the 19th century.

The Kingdom of Jolof, also known as Wolof and Wollof, was a West African rump state located in what is today the nation of Senegal. For nearly two hundred years, the Wolof rulers of the Jolof Empire collected tribute from vassal kings states who voluntarily agreed to the confederacy. At the 1549 Battle of Danki, however, the Buurba Jolof was defeated by the lord of Kayor, resulting in the rapid disintegration of the empire. Jolof survived as a rump state, unable to access the Atlantic trade between its former vassal territories and the Portuguese.
This is a timeline of the history and development of Serer religion and the Serer people of Senegal, The Gambia and Mauritania. This timeline merely gives an overview of their history, consisting of calibrated archaeological discoveries in Serer countries, Serer religion, politics, royalty, etc. Dates are given according to the Common Era. For a background to these events, see Roog, Serer religion, Serer creation myth, Serer prehistory, Lamane, States headed by Serer Lamanes, Serer history and Serer people.
Maad a Sinig Maysa Wali Jaxateh Manneh was a king described in the oral tradition of the Serer pre-colonial Kingdom of Sine and the first of the Guelowar maternal dynasty to rule in Serer country. He reigned as Maad a Sinig from c. 1350 to 1370.
Tenguella was a Fula silatigi or chief who founded a short-lived state in the upper Senegal river valley, a precursor of the Empire of Great Fulo. He was named Great Fulo or Great king of the Fulos in Portuguese documents of the time.