Contents
- Medieval Times
- Sosso Empire
- Mali Empire
- Songhai Empire
- Modern Times
- Massina Empire
- Toucouleur Empire
- Wassoulou Empire
- Republic of Mali
- See also









The Mali Empire was an empire in West Africa from c. 1226 to 1670. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa. At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of its language, laws, and customs.

The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its largest ethnic group and ruling elite, the Songhai people. Sonni Ali established Gao as the empire's capital, although a Songhai state had existed in and around Gao since the 11th century. Other important cities in the kingdom were Timbuktu and Djenné, where urban-centred trade flourished; they were conquered in 1468 and 1475, respectively. Initially, the Songhai Empire was ruled by the Sonni dynasty, but it was later replaced by the Askia dynasty (1493–1591).

The Songhai people are an ethnolinguistic group in West Africa who speak the various Songhai languages. Their history and lingua franca is linked to the Songhai Empire which dominated the western Sahel in the 15th and 16th century. Predominantly adherents of Islam, the Songhai are primarily located in Niger and Mali. Historically, the term "Songhai" did not denote an ethnic or linguistic identity but referred to the ruling caste of the Songhay Empire known as the Songhaiborai. However, the correct term used to refer to this group of people collectively by the natives is "Ayneha". Although some speakers in Mali have also adopted the name Songhay as an ethnic designation, other Songhay-speaking groups identify themselves by other ethnic terms such as Zarma or Isawaghen. The dialect of Koyraboro Senni spoken in Gao is unintelligible to speakers of the Zarma dialect of Niger, according to at least one report. The Songhay languages are commonly taken to be Nilo-Saharan but this classification remains controversial: Dimmendaal (2008) believes that for now it is best considered an independent language family.

Askia Muhammad Ture I (1443–1538), born Muhammad ibn Abi Bakr al-Turi or Muhammad Ture, was the first ruler of the Askia dynasty of the Songhai Empire, reigning from 1493 to 1528. He is also known as Askia the Great, and his name in modern Songhai is Mamar Kassey. Askia Muhammad strengthened his empire and made it the largest empire in West Africa's history. At its peak under his reign, the Songhai Empire encompassed the Hausa states as far as Kano and much of the territory that had belonged to the Songhai empire in the east. His policies resulted in a rapid expansion of trade with Europe and Asia, the creation of many schools, and the establishment of Islam as an integral part of the empire.
Sunni Ali, also known as Si Ali, Sunni Ali Ber, reigned from about 1464 to 1492 as the 15th ruler of the Sunni dynasty of the Songhai Empire. He transformed the relatively small state into an empire by conquering Timbuktu, Massina, the Inner Niger Delta, and Djenne.

Gao, or Gawgaw/Kawkaw, is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, 320 km (200 mi) east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.

Azawad, or Azawagh, was a short-lived unrecognised state lasting between 2012 and 2013. Azawagh (Azawaɣ) is the generic Tuareg Berber name for all Tuareg Berber areas, especially the northern half of Mali and northern and western Niger. The Azawadi declaration of independence was declared unilaterally by the National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad (MNLA) in 2012, after a Tuareg rebellion drove the Malian Armed Forces from the region.
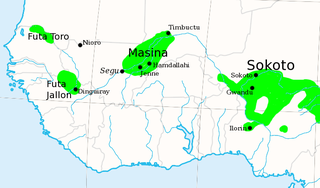
The Caliphate of Hamdullahi, commonly known as the Massina empire, was an early nineteenth-century Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa centered in the Inner Niger Delta of what is now the Mopti and Ségou Regions of Mali. It was founded by Seku Amadu in 1818 during the Fulani jihads after defeating the Bambara Empire and its allies at the Battle of Noukouma. By 1853, the empire had fallen into decline and was ultimately destroyed by Omar Saidou Tall of Toucouleur.

The Iwellemmedan (Iwəlləmədǎn), also spelled Iullemmeden, Aulliminden, Ouilliminden, Lullemmeden, and Iwellemmeden, are one of the seven major Tuareg tribal or clan confederations. Their communities are historically nomadic and intermixed with other ethnic groups. The Iwellemmeden inhabit a wide area ranging from east and north central Mali, through the Azawagh valley, into northwestern Niger and south into northern Nigeria. While once a single confederation of dozens of Tuareg clans, subject peoples, and allied groups, since the 18th century they have been divided into Kel Ataram (west) and Kel Dinnik (east) confederations.
Goundam is a commune and town in north central Mali, in the Tombouctou Region. It is the capital of Goundam Cercle, one of five subdivisions of the Region. In the 2009 census the commune had a population of 16,253. The main ethnic groups are Songhay, Tuareg and Fulani.
The Twelve Doors of Mali were the possessions of the Mansa (emperor) of the medieval Mali Empire which was established in c.. 1235 following The Battle of Kirina. These lands were either allied to or conquered by Sundiata Keita on his campaign to free the Mandinka heartland from the Sosso kingdom of Kaniaga.
The Sonni dynasty, Sunni dynasty or Si dynasty was a dynasty of rulers of the Songhai Empire of medieval West Africa. The origins of the dynasty lies in its predecessor Za Dynasty. The last ruler, Sonni Baru, ruled until 1493 when the throne was usurped by the Askiya Muhammad I, the founder of the Askiya dynasty.
The Arma people are an ethnic group of the middle Niger River valley, descended from Moroccan invaders of the 16th century. The name, applied by other groups, derives from the word ar-rumah "fusiliers".
The military history of the Mali Empire is that of the armed forces of the Mali Empire, which dominated Western Africa from the mid 13th to the late 15th century. The military culture of the empire's driving force, Mandinka people, influenced many later states in West Africa including break-away powers such as the Songhay and Jolof empires. Institutions from the Mali Empire also survived in the 19th century army of Samory Ture who saw himself as the heir to Old Mali's legacy.
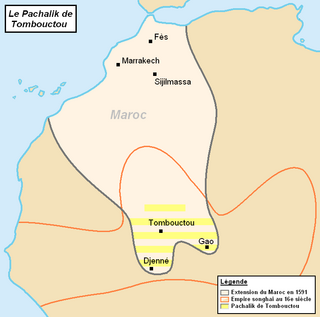
The Battle of Jenné was a military engagement between forces of the Mali Empire and the Moroccan Pashalik of Timbuktu.

The Pashalik of Timbuktu, also known as the Pashalik of Sudan, was a West African political entity that existed between the 16th and the 19th century. It was formed after the Battle of Tondibi, when a military expedition sent by Saadian sultan Ahmad al-Mansur of Morocco defeated the Songhai Empire and established control over a territory centered on Timbuktu. Following the decline of the Saadi Sultanate in the early 17th century, Morocco retained only nominal control of the Pashalik.
Tenguella was a Fula silatigi or chief who founded a short-lived state in the upper Senegal river valley, a precursor of the Empire of Great Fulo. He was referred to as the Great Fulo or Great king of the Fulos in Portuguese documents of the time.

Manding, Manden or even Mandé is a region located in West Africa, a space between southern Mali and eastern Guinea. It is the historic home of the Mandinka community.
The history of the Mali Empire begins when the first Mande people entered the Manding region during the period of the Ghana Empire. After its fall, the various tribes established independent chiefdoms. In the 12th century, these were briefly conquered by the Sosso Empire under Soumaoro Kante. He was in turn defeated by a Mande coalition led by Sundiata Keita, who founded the Mali Empire.