
The Alþingi, anglicised as Althingi or Althing, is the supreme national parliament of Iceland. It is one of the oldest surviving parliaments in the world. The Althing was founded in 930 at Þingvellir, about 45 kilometres (28 mi) east of what later became the country's capital, Reykjavík. After Iceland's union with Norway in 1262, the Althing lost its legislative power, which was not restored until 1904 when Iceland gained home rule from Denmark. For 641 years, the Althing did not serve as the parliament of Iceland; ultimate power rested with the Norwegian, and subsequently the Danish throne. Even after Iceland's union with Norway in 1262, the Althing still held its sessions at Þingvellir until 1800, when it was discontinued. It was restored in 1844 by royal decree and moved to Reykjavík. The restored unicameral legislature first came together in 1845 and after 1874 operated in two chambers with an additional third chamber taking on a greater role as the decades passed until 1991 when Althing became once again unicameral. The present parliament building, the Alþingishús, was built in 1881, made of hewn Icelandic stone. The unicameral parliament has 63 members, and is elected every four years based on party-list proportional representation. The current speaker of the Althing is Birgir Ármannsson.
An electoraldistrict, sometimes called a constituency, riding, or ward, is a subdivision of a larger state created to provide its population with representation in the larger state's legislature. That body, or the state's constitution or a body established for that purpose, determines each district's boundaries and whether each will be represented by a single member or multiple members. Generally, only voters (constituents) who reside within the district are permitted to vote in an election held there. District representatives may be elected by a first-past-the-post system, a proportional representative system, or another voting method. They may be selected by a direct election under universal suffrage, an indirect election, or another form of suffrage.

An electoral district in Canada is a geographical constituency upon which Canada's representative democracy is based. It is officially known in Canadian French as a circonscription but frequently called a comté (county). In Canadian English it is also colloquially and more commonly known as a riding or constituency.
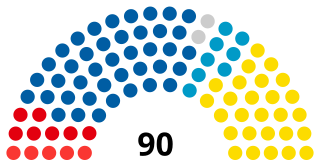
The National Assembly is the general representative body of Slovenia. According to the Constitution of Slovenia and the Constitutional Court of Slovenia, it is the major part of the distinctively incompletely bicameral Slovenian Parliament, the legislative branch of the Republic of Slovenia. It has 90 members, elected for a four-year term. 88 members are elected using the party-list proportional representation system and the remaining two, using the Borda count, by the Hungarian and Italian-speaking ethnic minorities, who have an absolute veto in matters concerning their ethnic groups.

The Assembly of the Republic, commonly referred to as simply Parliament, is the unicameral parliament of Portugal. According to the Constitution of Portugal, the parliament "is the representative assembly of all Portuguese citizens". The constitution names the assembly as one of the country's organs of supreme authority.

There are three types of elections in Nepal: elections to the federal parliament, elections to the provincial assemblies and elections to the local government. Within each of these categories, there may be by-elections as well as general elections. Currently three electoral systems are used: parallel voting for the House of Representatives and provincial assemblies, single transferable vote for the National Assembly, and first-past-the-post for local elections.
Elections in Hungary are held at two levels: general elections to elect the members of the National Assembly and local elections to elect local authorities. European Parliament elections are also held every 5 years.

In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons.
General elections were held in South Africa on 22 April 1970 to elect members of the 166-seat House of Assembly. Parliament was dissolved on 2 March and the deadline for the submission of candidates was 13 March.
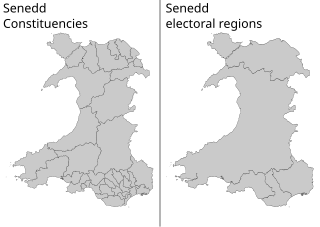
The Senedd constituencies and electoral regions are the electoral districts used to elect members of the Senedd to the Senedd, and have been used in some form since the first election of the then National Assembly for Wales in 1999. New boundaries were introduced for the 2007 elections and currently consist of forty constituencies and five regions. The five electoral regions are: Mid and West Wales, North Wales, South Wales Central, South Wales East, and South Wales West, with the forty constituencies listed below. Voting last took place in all districts in the 2021 Senedd election, and is not used for local government.
Electoral districts go by different names depending on the country and the office being elected.

State elections were held in South Australia on 27 March 1915. All 46 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal Union government led by Premier of South Australia Archibald Peake was defeated by the opposition United Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Crawford Vaughan. Each district elected multiple members, with voters casting multiple votes.
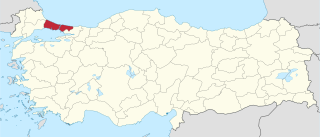
Istanbul is a Turkish province divided into three electoral districts of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey. It elects ninety-eight members of parliament (deputies) to represent the province of the same name for a five-year term by the D'Hondt method, a party-list proportional representation system.

Ankara is a Turkish province divided into three electoral districts of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey. It elects thirty-six members of parliament (deputies) to represent the province of the same name for a four-year term by the D'Hondt method, a party-list proportional representation system.
The electoral system of Turkey varies for general, presidential and local elections that take place in Turkey every five years. Turkey has been a multi-party democracy since 1950, with the first democratic election held on 14 May 1950 leading to the end of the single-party rule established in 1923. The current electoral system for electing Members of Parliament to the Grand National Assembly has a 7% election threshold.

National remnant is an apportionment scheme used in some party-list proportional representation systems that have multi-member electoral districts. The system uses a Largest remainder method to determine some of the seats in each electoral district. However, after the integer part of the seats in each district is allocated to the parties, the seats left unallocated will then be allocated not in each electoral district in isolation, but in a larger division, such as nationwide or in large separate regions that each encompass multiple electoral districts.

Parliamentary elections were held in Slovenia on 3 June 2018. The elections were originally expected to be held later in June 2018, but after the resignation of Prime Minister Miro Cerar on 14 March 2018 all parties called for snap elections. They were the third consecutive snap elections after 2011 and 2014.
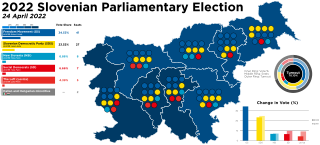
Parliamentary elections were held in Slovenia on 24 April 2022 to elect all 90 members of the National Assembly.
Parliamentary elections are to be held in Slovenia no later than 24 April 2026.












