Related Research Articles

The International Bureau of Weights and Measures is an intergovernmental organisation, through which its 59 member-states act on measurement standards in four areas: chemistry, ionising radiation, physical metrology, as well as Coordinated Universal Time. It is based in Saint-Cloud, near Paris, France. The organisation has been referred to as IBWM in older literature.
The Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) of the United States are a set of publicly announced standards that the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed for use in computer systems of non-military United States government agencies and contractors. FIPS standards establish requirements for ensuring computer security and interoperability, and are intended for cases in which suitable industry standards do not already exist. Many FIPS specifications are modified versions of standards the technical communities use, such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
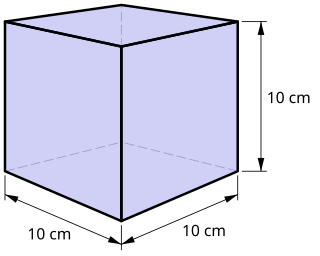
The litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metres (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical science laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards.

The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce.
The National Institute of Justice (NIJ) is the research, development and evaluation agency of the United States Department of Justice.

Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, abbreviated as IIEST Shibpur is a public university located at Shibpur, Howrah, West Bengal. Founded in 1856, it is recognised as an Institute of National Importance under MHRD by the Government of India. It is controlled by the Council of NITSER. It is the fourth oldest engineering institute in India after College of Engineering, Guindy, IIT Roorkee, College of Engineering, Pune.

The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is a cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. Its English name was Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications (MPHPT) prior to 2004. It is housed in the 2nd Building of the Central Common Government Office at 2-1-2 Kasumigaseki in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan.

The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program and the Federal Lands Highway Program. Its role had previously been performed by the Office of Road Inquiry, Office of Public Roads and the Bureau of Public Roads.

Lewis McAdory Branscomb was an American physicist, government policy advisor, and corporate research manager. He was best known for being head of the National Bureau of Standards and, later, chief scientist of IBM; and as a prolific writer on science policy issues.

William A. Jeffrey is the CEO of SRI International, a position he has held since September 2014. He is an astronomer and astrophysicist by education.

Russell A. Kirsch was an American engineer at the National Bureau of Standards. He was recognized as the developer of the first digital image scanner, and subsequently scanned the world's first digital photograph – an image of his infant son.

Arati Prabhakar is an American engineer and public official. Since October 3, 2022, she has served as the 12th director of the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy and Science Advisor to the President.
Li Tieying is a retired politician of the People's Republic of China. He held many positions since 1955, including Vice Chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress and President of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. He is an author of several books. For more than 20 years he served as Minister in charge of the State Commission for Economic Restructuring, and participated in major decision making and the implementation of China's economic reforms during that time.

Katharine Blodgett Gebbie was an American astrophysicist and civil servant. She was the founding Director of the Physical Measurement Laboratory of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and of its two immediate predecessors, the Physics Laboratory and the Center for Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, both for which she was the only Director. During her 22 years of management of these institutions, four of its scientists were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. In 2015, the NIST Katharine Blodgett Gebbie Laboratory Building in Boulder, Colorado was named in her honor.

Willie E. May is an American chemist who was director of the United States' National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the U.S. Under Secretary of Commerce for Standards and Technology. He has been active in international organizations, collaborating with others in Brazil, China, and the European Union.

Ernest Ambler was a British-American physicist who served as the Acting Under Secretary for Technology in the Department of Commerce (1988–89), as director of the United States' National Bureau of Standards, and as the first director of the United States' National Institute of Standards and Technology 1988–89.

Joan Raup Rosenblatt was an American statistician who became Director of the Computing and Applied Mathematics Laboratory of the National Institute of Standards and Technology. She was president of the Caucus for Women in Statistics in 1976.
Helen M. Wood is an American computer scientist who worked for many years at the National Bureau of Standards, directed the Office of Satellite Data Processing and Distribution in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and served as president of the IEEE Computer Society.