
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a transmission network. This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the electrical grid.

The National Grid is the high-voltage electric power transmission network serving Great Britain, connecting power stations and major substations, and ensuring that electricity generated anywhere on the grid can be used to satisfy demand elsewhere. The network serves the majority of Great Britain and some of the surrounding islands. It does not cover Northern Ireland, which is part of the Irish single electricity market.
The East–West Interconnector is a 500 MW high-voltage direct current submarine and subsoil power cable which connects the Irish and British electricity markets. The project was developed by the Irish national grid operator EirGrid.

EirGrid plc is the state-owned electric power transmission operator in Ireland. It is a public limited company registered under the Companies Acts; its shares are held by the Minister for the Environment, Climate and Communications. It is one of a number of Irish state-sponsored bodies and is regulated by the Commission for Regulation of Utilities.
NordBalt is a submarine power cable between Klaipėda in Lithuania and Nybro in Sweden. The purpose of the cable is to facilitate the trading of power between the Baltic and Nordic electricity markets, and to increase the supply and energy security in both markets.
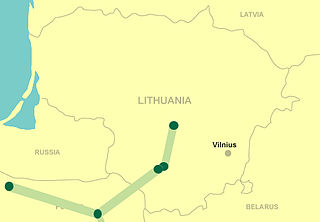
LitPol Link is an electricity link between Poland and Lithuania which connects the Baltic transmission system to the synchronous grid of Continental Europe. It has a capacity of 500 MW and since 2021 it can operate in a synchronous regime.

The synchronous grid of Continental Europe is the largest synchronous electrical grid in the world. It is interconnected as a single phase-locked 50 Hz mains frequency electricity grid that supplies over 400 million customers in 24 countries, including most of the European Union. In 2009, 667 GW of production capacity was connected to the grid, providing approximately 80 GW of operating reserve margin. The transmission system operators operating this grid formed the Union for the Coordination of Transmission of Electricity (UCTE), now part of the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E).
TenneT is a transmission system operator in the Netherlands and in a large part of Germany.
Unified National Smart Grid as well as Unified Solar is a proposal for a nationally interconnected grid relying on a backbone of electric power transmission lines linking the US' local grids that have been upgraded to smart grids. Europe's analogous project is sometimes referred to as the SuperSmart Grid.

A wide area synchronous grid is a three-phase electric power grid that has regional scale or greater that operates at a synchronized utility frequency and is electrically tied together during normal system conditions. Also known as synchronous zones, the most powerful is the Northern Chinese State Grid with 1,700 gigawatts (GW) of generation capacity, while the widest region served is that of the IPS/UPS system serving most countries of the former Soviet Union. Synchronous grids with ample capacity facilitate electricity trading across wide areas. In the ENTSO-E in 2008, over 350,000 megawatt hours were sold per day on the European Energy Exchange (EEX).
The Great Belt power link, also known as the Great Belt electricity link, is a high-voltage direct-current interconnection across the Great Belt between Funen and Zealand connecting two power transmission systems in Denmark.
The electricity sectors of the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland are integrated and supply 2.5 million customers from a combination of coal, peat, natural gas, wind and hydropower. In 2022, 34 TWh were generated. In 2018 natural gas produced 51.8%, while wind turbines generated 28.1%, coal 7%, and peat 6.8% of Ireland's average electricity demand. In 2020 wind turbines generated 36.3% of Ireland's electrical demand, one of the highest wind power proportions in the world. While the United Kingdom was one of the first countries in the world to deploy commercial nuclear power plants, the island of Ireland has never had a nuclear power plant built on either side of the Irish border. Nuclear power in Ireland was discussed in the 1960s and 1970s but ultimately never phased in, with legislation now in place explicitly forbidding its introduction.

The North Sea Link is a 1,400 MW high-voltage direct current submarine power cable between Norway and the United Kingdom.
Viking Link is a 1,400 MW HVDC submarine power cable between the United Kingdom and Denmark completed in 2023.

The electrical power grid that powers Northern America is not a single grid, but is instead divided into multiple wide area synchronous grids. The Eastern Interconnection and the Western Interconnection are the largest. Three other regions include the Texas Interconnection, the Quebec Interconnection, and the Alaska Interconnection. Each region delivers power at a nominal 60 Hz frequency. The regions are not usually directly connected or synchronized to each other, but there exist some HVDC interconnectors. The Eastern and Western grids are connected via seven links that allow 1.32 GW to flow between them. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that increasing these interconnections would save energy costs.

The Šiauliai–Jelgava power line is an electricity link (interconnector) in the Baltic transmission system between Lithuania and Latvia. The overhead power line is one of seven interconnections between the two countries and one of the four 330 kV power transmission lines between Lithuania and Latvia.
The high-voltage electricity substations in the United Kingdom are listed in the following tables. The substations provide entry points to, and exit points from, the National Grid (GB) or Northern Ireland Electricity Network. Entry points include power stations, major wind farms and inter-connectors from other countries and regions. Exit points are to lower voltage transmission and distribution substations which are also shown in the tables.








