Related Research Articles
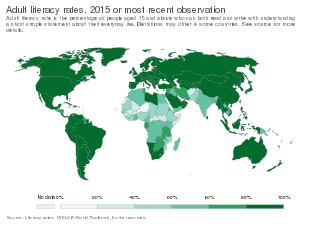
Literacy is the ability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was understood solely as alphabetical literacy ; and the period after 1950, when literacy slowly began to be considered as a wider concept and process, including the social and cultural aspects of reading and writing and functional literacy.

Phonics is a method for teaching reading and writing to beginners. To use phonics is to teach the relationship between the sounds of the spoken language (phonemes), and the letters (graphemes) or groups of letters or syllables of the written language. Phonics is also known as the alphabetic principle or the alphabetic code. It can be used with any writing system that is alphabetic, such as that of English, Russian, and most other languages. Phonics is also sometimes used as part of the process of teaching Chinese people to read and write Chinese characters, which are not alphabetic, using pinyin, which is alphabetic.

The International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA) is an independent, international cooperative of national research institutions and governmental research agencies. It conducts large-scale comparative studies of educational achievement and other aspects of education.

The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) is a worldwide study by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in member and non-member nations intended to evaluate educational systems by measuring 15-year-old school pupils' scholastic performance on mathematics, science, and reading. It was first performed in 2000 and then repeated every three years. Its aim is to provide comparable data with a view to enabling countries to improve their education policies and outcomes. It measures problem solving and cognition.
The National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) is the part of the United States Department of Education's Institute of Education Sciences (IES) that collects, analyzes, and publishes statistics on education and public school district finance information in the United States. It also conducts international comparisons of education statistics and provides leadership in developing and promoting the use of standardized terminology and definitions for the collection of those statistics. NCES is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System.

The education system in Switzerland is very diverse, because the constitution of Switzerland delegates the authority for the school system mainly to the cantons. The Swiss constitution sets the foundations, namely that primary school is obligatory for every child and is free in state schools and that the confederation can run or support universities.

The National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) is the largest continuing and nationally representative assessment of what U.S. students know and can do in various subjects. NAEP is a congressionally mandated project administered by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), within the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the United States Department of Education. The first national administration of NAEP occurred in 1969. The National Assessment Governing Board (NAGB) is an independent, bipartisan board that sets policy for NAEP and is responsible for developing the framework and test specifications.The National Assessment Governing Board, whose members are appointed by the U.S. Secretary of Education, includes governors, state legislators, local and state school officials, educators, business representatives, and members of the general public. Congress created the 26-member Governing Board in 1988.
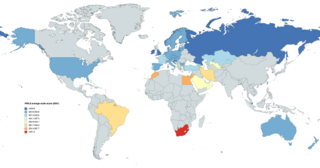
The IEA's Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS) is an international study of reading (comprehension) achievement in 9-10 year olds. It has been conducted every five years since 2001 by the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA). It is designed to measure children's reading literacy achievement, to provide a baseline for future studies of trends in achievement, and to gather information about children's home and school experiences in learning to read.
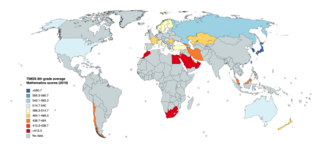
The International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA)'s Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) is a series of international assessments of the mathematics and science knowledge of students around the world. The participating students come from a diverse set of educational systems in terms of economic development, geographical location, and population size. In each of the participating educational systems, a minimum of 4,000 to 5,000 students is evaluated. Contextual data about the conditions in which participating students learn mathematics and science are collected from the students and their teachers, their principals, and their parents via questionnaires.

The Australian Council for Educational Research (ACER), established in 1930, is an independent educational research organisation based in Camberwell, Victoria (Melbourne) and with offices in Adelaide, Brisbane, Cyberjaya, Dubai, Jakarta, London, New Delhi, Perth and Sydney. ACER develops and manages a range of testing and assessment services and conducts research and analysis in the education sector.

Education in the State of Palestine refers to the educational system in the Gaza Strip and the West Bank, which is administered by the Palestinian Ministry of Education and Higher Education. Enrollment rates amongst Palestinians are relatively high by regional and global standards. According to a youth survey in 2003, 60% between the ages 10–24 indicated that education was their first priority. Youth literacy rate was 98.2%, while the national literacy rate was 91.1% in 2006. The literacy rate ages 15-24 was 99.4% in 2016. Enrollment ratios for higher education were 45% in 2022. In 2016 Hanan Al Hroub was awarded the Varkey Foundation Global Teacher Prize for her work in teaching children how to cope with violence.
Education in Lebanon is regulated by the Ministry of Education and Higher Education (MEHE). In Lebanon, the main three languages, English and/or French with Arabic are taught from early years in schools. English or French are the mandatory media of instruction for mathematics and sciences for all schools. Education is compulsory from age 3 to 14.

The most recent comprehensive data on adult literacy in the United States come from the Program for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies (PIAAC) study conducted in stages from 2012 to 2017 by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES). English literacy test results from 2014 suggest that 21% of U.S. adults ages 16 to 65 score at or below PIAAC literacy level 1, meaning they have difficulty "[completing] tasks that require comparing and contrasting information, paraphrasing, or making low-level inferences." Included in that 21% is the 4.2% of respondents who were unable to be assessed due to language barriers, cognitive disability, or physical disability. A 2020 study by the Gallup analysis company funded by the Barbara Bush Foundation for Family Literacy estimated that getting all U.S. adults to at least PIAAC literacy level 3 proficiency would raise American's incomes by $2.2 trillion.

Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of symbols, often specifically those of a written language, by means of sight or touch.
The Programme for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies (PIAAC) is a worldwide study by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 24 countries of cognitive and workplace skills. The main aim is to be able to assess the skills of literacy, numeracy and problem solving in technology-rich environments, and use the collected information to help countries develop ways to further improve these skills. The focus is on the working-age population. The first data was released on October 8, 2013. A first round of the Second Cycle of survey took place in 2022-2023 with results to be released on 10 December 2024.
The Programme for International Student Assessment has had several runs before the most recent one in 2012. The first PISA assessment was carried out in 2000. The results of each period of assessment take about one year and a half to be analysed. First results were published in November 2001. The release of raw data and the publication of technical report and data handbook only took place in spring 2002. The triennial repeats follow a similar schedule; the process of seeing through a single PISA cycle, start-to-finish, always takes over four years. 470,000 15-year-old students representing 65 nations and territories participated in PISA 2009. An additional 50,000 students representing nine nations were tested in 2010.
PR1ME Mathematics teaching programme (PR1ME) is created for the primary or elementary grades and was first introduced in 2014 by Scholastic. It is adopted by schools in multiple countries such as Philippines, Australia, New Zealand and Mexico. PR1ME is a programme based on the Mathematics teaching and learning practices of Singapore, Hong Kong and Republic of Korea, which have consistently performed strongly in international mathematics studies such as the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) and Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development's Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA). This programme was developed in collaboration with the Ministry of Education (MOE), Singapore and is adapted from the Primary Mathematics Project developed by MOE.

Female education in STEM refers to child and adult female representation in the educational fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). In 2017, 33% of students in STEM fields were women.
Matthias von Davier is a psychometrician, academic, inventor, and author. He is the executive director of the TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center at the Lynch School of Education and Human Development and the J. Donald Monan, S.J., University Professor in Education at Boston College.
References
- 1 2 "The Civic Education Study (CivEd) - Countries" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "Civics Education Study 1999 (CD-ROM)". 4 June 2004. Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "EDAT : Home - National Center for Education Statistics" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "Education Longitudinal Study of 2002 (ELS:2002) - Available Data and Related Products" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- 1 2 3 Download microdata
- ↑ "NAEP Data Explorer.net" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "National Longitudinal Study of 1972 (NLS -72) - Overview: Purpose" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "Program for the International Assessment for Adult Competencies (PIAAC) - Participating Countries" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "Program for the International Assessment for Adult Competencies (PIAAC) - Schedule and Plans" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS) - Countries" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS) - Data Files" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ list of PISA countries Archived 2015-09-08 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "PISA products - PISA" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) - TIMSS Participating Countries" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ "Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) - Data Files" . Retrieved 14 March 2017.