
List of retired BC Ferries:

List of retired BC Ferries:
Since the 1960s, BC Ferries has retired the following ferries: [1]
| Name | Built (rebuilt) | Years in service | Class | Auto capacity | Passenger capacity | Notes | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MV Quillayute | 1927 | 1961-1963 | None | 35 | 600 | Acquired in Black Ball purchase | [2] |
| SS Smokwa | 1946 | 1961-1966 | None | 46 | 473 | Acquired in Black Ball purchase; named Scotian when built | [3] |
| MV Jervis Queen | 1928 | 1961-1966 | None | 45 | 600 | Acquired in Black Ball purchase, formerly named Bainbridge | [4] |
| MV George S. Pearson | 1925 | 1961-1966 | None | 18 | 134 | Acquired in Gulf Island Ferry Company purchase, previously named Fox Island and Wollochet | [5] |
| MV Cy Peck | 1913 (1930) | 1961-1966 | None | 18 | 135 | Acquired in Gulf Island Ferry Company purchase; formerly named Island Princess and Daily | [6] |
| MV Sunshine Coast Queen | 1952 | 1967-1976 | None | 180+ | 973 | Originally named Vacationland and later Père Nouvel Sank while being towed for scrap December 3, 1987 | |
| MV Sechelt Queen | 1947 | 1961-1976 | None | 83 | 670 | Acquired in Black Ball purchase, originally named Chinook | [7] |
| MV Langdale Queen | 1903 (1919/1926/1952) | 1961-1976 | None | 80 | 600 | Acquired in Black Ball purchase, formerly named Kahloke, City of Sacramento, and Asbury Park; scrapped in 2009 | [8] |
| MV Dogwood Princess | 1969 | 1969-1979 | None | 0 | 30 | ||
| MV Dogwood Princess II | 1979 (1985) | 1979-2003 | None | 0 | 38 | Received an engine upgrade in 1985 | |
| MV Pender Queen | 1923 (1956) | 1961-1980 | None | 40 | 250 | Acquired in Gulf Island Ferry Company purchase, formerly named Motor Princess. Sunk and scrapped in 2003 | [9] |
| MV Princess of Vancouver | 1955 | 1985-1987 | Princess class | 150 | 984 | Formerly part of the Ministry of Transportation and Highways' saltwater ferry fleet and the Canadian Pacific Railway | |
| MV Queen of the Islands | 1963 | 1963-1991 | None | 40 | 400 | Sold in 1991, permanently moored in Mosquito Creek Marina in North Vancouver since 2009 | |
| MV Salt Spring Queen | 1949 | 1961-1996 | None | 36 | 187 | Acquired in Gulf Island Ferry Company purchase, formerly named Delta Princess. Sold and renamed Golden Queen. | |
| MV Vesuvius Queen | 1950 | 1962-1998 | None | 35 | 184 | Originally named Lloyd Jones and sailed on Okanagan Lake, sold to R & G Importadora & Exportadora of the Dominican Republic in 1998 | [10] |
| MV Queen of Sidney | 1960 | 1960-2000 | Sidney | 138 | 989 | First vessel built by BC Ferries, abandoned in 2000 | |
| MV Queen of Victoria | 1962 (1970/1981) | 1962-2000 | V | 286 | 1360 | Stretched in 1970, upper deck added in 1981 to increase capacity; sold to R & G Importadora & Exportadora of the Dominican Republic in 2001 | [11] |
| MV PacifiCat Explorer | 1998 | 1998-2000 | PacifiCat | 235 | 1000 | Video documentary filmed about the ship's construction | |
| MV PacifiCat Discovery | 1999 | 1999-2000 | PacifiCat | 235 | 1000 | ||
| MV PacifiCat Voyager | 2000 | Never | PacifiCat | 235 | 1000 | Would have entered service in 2000 | |
| MV Albert J. Savoie | 1961 | 1985-2002 | N | 16 | 133 | Formerly part of the Ministry of Transportation and Highways' saltwater ferry fleet | |
| MV Garibaldi II | 1964 (1977) | 1985-2006 | N | Originally 16, later reduced to 7 | 133+ | Formerly part of the Ministry of Transportation and Highways' saltwater ferry fleet, sold to Harbour Cruises via Woodfibre Pulp Mill in 2006. | |
| MV Queen of the North | 1969 | 1974-2006 | None | 115 | 650 | Purchased from Stena Line in 1974; formerly named Queen of Surrey and Stena Danica; sank in Wright Sound on March 22, 2006 | |
| MV Queen of Esquimalt | 1963 (1969/1982) | 1963-2008 | V | 376 | 1630 | Stretched in 1969, upper deck added in 1982 to increase capacity | [12] |
| MV Queen of Tsawwassen | 1960 | 1960-2008 | Sidney | 128 | 640 | [13] | |
| MV Queen of Saanich | 1962 (1972/1982) | 1962-2008 | V | 360 | 1672 | Stretched in 1972, upper deck added in 1982 to increase capacity | |
| MV Queen of Vancouver | 1962 (1972/1981) | 1962-2009 | V | 338 | 1670 | Stretched in 1972, upper deck added in 1981 to increase capacity | [14] |
| MV Queen of Prince Rupert | 1965 | 1965-2009 | None | 80 | 510 | Last BC Ferry built at Victoria Machinery Depot | |
| MV Mill Bay | 1956 | 1969-2011 | None | 16 | 136 | Acquired in 1969 purchase of Coast Ferries | |
| MV Queen of Chilliwack | 1978 | 1991-2015 | None | 115 | 400 | Acquired by Goundar Shipping in 2015 | |
| MV Tenaka | 1964 | 1985-2016 | None | 24 | 244 | Acquired by Lady Rose Marine Services in 2016 | |
| MV Queen of Burnaby | 1965 (1972) | 1965-1994; 2000-2017 | Burnaby | 168 | 904 | Stretched in 1972 to increase capacity | |
| MV Queen of Nanaimo | 1964 (1974) | 1964-2017 | Burnaby | 164 | 1163 | Stretched in 1974 to increase capacity | |
| MV Howe Sound Queen | 1964 | 1971-2019 | None | 52 | 300 | Purchased in 1971. Sold at an auction for CA$ 210,000 in 2019 | [15] |
| MV Nimpkish | 1973 | 1985-2020 | N | 12 | 95 | Transferred to BC Ferries in 1985 | |
| MV North Island Princess | 1958 (1971) | 1969-1977; 1985-2020 | None | 38 | 150 | Acquired in 1969 purchase of Coast Ferries; Transferred to Ministry of Transportation & Highways in 1977 and back to BC Ferries in 1985; currently for sale. | [16] [17] |
| MV Bowen Queen | 1965 (1979) | 1965-2022 | Powell River | 61 | 400 | Stretched in 1979 to increase capacity | |
| MV Mayne Queen | 1965 (1979) | 1965-2022 | Powell River | 58 | 400 | Stretched in 1979 to increase capacity. Last full day of service on route 5 was November 19, 2022. | |
| MV Powell River Queen | 1965 (1979) | 1965-2023 | Powell River | 59 | 408 | Stretched in 1979 to increase capacity. Currently for sale. |
BC Ferries has plans to retire the Queen of New Westminster as well as the five C-class vessels, starting in 2029. These will be replaced by up to seven of the "New Major Vessel" ships. [18]
British Columbia Ferry Services Inc., operating as BC Ferries (BCF), is a former provincial Crown corporation, now operating as an independently managed, publicly owned Canadian company. BC Ferries provides all major passenger and vehicle ferry services for coastal and island communities in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Set up in 1960 to provide a similar service to that provided by the Black Ball Line and the Canadian Pacific Railway, which were affected by job action at the time, BC Ferries has become the largest passenger ferry line in North America, operating a fleet of 41 vessels with a total passenger and crew capacity of over 27,000, serving 47 locations on the B.C. coast.
The Inside Passage is a coastal route for ships and boats along a network of passages which weave through the islands on the Pacific Northwest coast of the North American Fjordland. The route extends from southeastern Alaska in the United States, through western British Columbia in Canada, to northwestern Washington state in the United States. Ships using the route can avoid some of the bad weather in the open ocean and may visit some of the many isolated communities along the route. The Inside Passage is heavily travelled by cruise ships, freighters, tugs with tows, fishing craft, pleasure craft, and ships of the Alaska Marine Highway, BC Ferries, and Washington State Ferries systems. Coast Guard vessels of both Canada and the United States patrol and transit in the Passage.

MV Queen of Nanaimo is a Burnaby-class passenger vessel that was operated by BC Ferries from the time it entered service in 1964 until 2017. Queen of Nanaimo was used to ferry passengers and vehicles from mainland British Columbia, Canada to the islands off its coast. In 2017, the vessel was sold to Goundar Shipping Ltd. and renamed MV Lomaiviti Princess V for service in Fiji.

The V-class ferries, also known as the Victoria class, originally included seven ferries operated by BC Ferries built between 1962 and 1965. The V class were a continuation of the previous Sidney-class design with some cosmetic changes and different engines. These vessels were the backbone of service on the Tsawwassen – Swartz Bay route prior to the arrival of MV Spirit of British Columbia in 1993. Four of these vessels underwent vehicle capacity increases three times. The lead ship of the class, Queen of Victoria suffered significant damage in a collision in 1970.

MV Queen of Alberni is a C-class ferry that operates between Tsawwassen and Duke Point in British Columbia as part of the BC Ferries fleet.

BC Ferries operates two T-class ferries for use on small inter-island routes. They have raised bows, which make it easier for the ships to travel in the rough seas often found on British Columbia's central coast. The ferries carry 30 cars and 150 passengers. Both were built in 1969. They were originally owned and operated by the British Columbia Ministry of Transportation until 1985, when the Ministry's saltwater ferries and routes were transferred to BC Ferries, including the T class. The two T-class ferries are Tachek and Quadra Queen II.

MV Coastal Celebration is the third and final Coastal-class ship to be delivered to BC Ferries. The class comprises some of the largest double-ended ferries in the world. The vessel completed construction in 2008 and entered service the same year. Unlike her sister ships, Coastal Renaissance and Coastal Inspiration, Coastal Celebration was equipped with a Pacific Buffet for service on the Swartz Bay to Tsawwassen route, until it was discontinued during the COVID-19 pandemic, and then closed permanently in June 2023.

The Sidney class consisted of two roll-on/roll-off ferries, Queen of Sidney and Queen of Tsawwassen, built for the British Columbia Ferry Corporation in service from 1960 to 2008. The design for the ships was based on the ferry MV Coho with changes made to accommodate loading of vehicles through the bow of the vessel. Both vessels serviced different routes throughout their service lives.

MV Queen of Prince Rupert was a roll-on/roll-off (RORO) ferry operated by BC Ferries that provided the main surface transport link between the Queen Charlotte Islands and mainland British Columbia, connecting Skidegate with Prince Rupert across the Hecate Strait. The vessel also ran on the Prince Rupert–Port Hardy Inside Passage route during the low season.

MV Malaspina Sky is an Intermediate-class ferry in the BC Ferries fleet built in 2008.

Spirit of Vancouver Island is an S-class ferry, part of the BC Ferries fleet. Along with MV Spirit of British Columbia, it is the largest in the BC Ferries fleet. The ship was completed in 1994 and serves the Swartz Bay – Tsawwassen route. In 2018, Spirit of Vancouver Island began a mid-life refit in Poland, where it was converted to a dual-fuel system to allow liquefied natural gas propulsion. The vessel returned to service in 2019.

The steamboat Daily operated in the early 1900s as part of the Puget Sound Mosquito Fleet. In later years, Daily was renamed Island Princess and later Cy Peck.

Asbury Park was a high-speed coastal steamer built in Philadelphia, and intended to transport well-to-do persons from New York to summer homes on the New Jersey shore. This vessel was sold to West Coast interests in 1918, and later converted to an automobile ferry, serving on various routes San Francisco Bay, Puget Sound and British Columbia. This vessel was known by a number of other names, including City of Sacramento, Kahloke, Langdale Queen, and Lady Grace.

MV Spirit of British Columbia is an S-class ferry, part of the BC Ferries fleet active along the British Columbia coast. It and Spirit of Vancouver Island represent the two largest ships in the fleet. The ship was completed in 1993 and serves the Tsawwassen–Swartz Bay route. In 2018, it underwent a mid-life refit that included conversion to a dual-fuel system that allows it to use either marine diesel oil or liquefied natural gas.

MV Nicola is an N-class ferry, owned, but not operated by BC Ferries. It is also known as Spirit of Lax Kw' Alaams, a British Columbia First Nations name. Spirit of Lax Kw' Alaams currently runs between Prince Rupert and Port Simpson, a British Columbia First Nations community on British Columbia's North Coast. Overnight the vessel is kept at the Smit tugboat dock in Prince Rupert Harbour.

N-class ferries are a class of RORO ferries, of which one remaining example is owned by BC Ferries and has the distinction of being the smallest vessel in their fleet.

Princess Beatrice was a steamship built for and owned by the marine division of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR). The ship served from 1903 to 1928 in the coastal waters of British Columbia. The ship also operated on Puget Sound on a route from Victoria, British Columbia to Seattle, Washington. Princess Beatrice was the first ship to operate in the year-round steamship service between Seattle and Victoria that was run by CPR from 1904 to 1959. This ship should not be confused with an earlier Princess Beatrice, built in Scotland in 1874, which served on the Atlantic coast of Canada.

Princess Marguerite, Princess Marguerite II, and Princess Marguerite III was a series of Canadian coastal passenger vessels that operated along the west coast of British Columbia and into Puget Sound in Washington state almost continuously from 1925 to 1999. Known locally as "the Maggie", they saw the longest service of any vessel that carried passengers and freight between Victoria, Vancouver, and Seattle. The vessels were owned and operated by a series of companies, primarily Canadian Pacific Railway Company (CPSS) and British Columbia Steamships Corporation. The first two were part of the CPR "Princess fleet," which was composed of ships having names which began with the title "Princess". These were named after Marguerite Kathleen Shaughnessy, who was not a princess but was the daughter of Baron Thomas Shaughnessy, then chairman of the board of CPSS's parent, the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR).
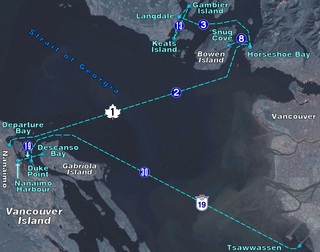
The Bowen Island ferry travels between Snug Cove on Bowen Island, and Horseshoe Bay in the District of West Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, a trip of three nautical miles across Queen Charlotte Channel. A scheduled ferry has been in operation since 1921, when Bowen Island was a popular holiday destination. Prior to that year, transportation to the island was by steamship from Vancouver, with only one trip daily. The Bowen Island ferry used a fleet of small passenger vessels until 1956, when a single car ferry began passenger service, and that ferry began carrying vehicles in 1958. In 2022 the route carried in excess of 1.2 million passengers plus 570,000 vehicles.

MV Chinook was a luxury automobile ferry designed by William Francis Gibbs, that operated between Seattle, Port Angeles and Victoria under the ownership of Puget Sound Navigation Company.