
List of Ships of the Victorian Naval Forces, 1855–1901:

List of Ships of the Victorian Naval Forces, 1855–1901:
| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albert | Gunboat | 1884–1897 | ||
| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batman | Auxiliary gunboat | 1884–unknown | ||
| Burrumbeet | Auxiliary armed steamer | |||

| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerberus | Turret ship (monitor) | 1869–1924 | ||
| Childers | 1st class Torpedo boat | 1884–1918 | ||
| Commissioner | Auxiliary torpedo boat | |||
| Countess of Hopetoun | 1st class Torpedo Boat | 1891–1924 | ||
| Courier | Auxiliary armed steamer | |||
| Customs Number 1 | Auxiliary torpedo boat | |||
| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elingamite | Auxiliary armed steamer | |||
| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fawker | Auxiliary gunboat | 1883–unknown | ||
| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gannet | Auxiliary gunboat | 1884–1893 | ||
| Gordon | Torpedo boat | 1884–1914 | ||
| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lady Loch | Gunboat | 1886–unknown | ||
| Lion | Auxiliary armed launch | |||
| Lonsdale | Torpedo boat | 1884–1912-1913 | ||

| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nelson | Training ship | 1867–1898 | ||
| Nepean | Torpedo boat | 1884–1912-1913 | ||
| Name | Type | Class | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Victoria (I) | Steam sloop | 1855–1880 | ||
| Victoria (II) | Gunboat | 1884–1896 | ||
| Vulcan | Auxiliary | 1889–unknown | ||

In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn . Many writers begin the sequence with 0 and 1, although some authors start it from 1 and 1 and some from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the sequence begins

Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.
Hinduism is an umbrella-term for a broad range of Indian religions and traditions, unified by the concept of dharma, a universal order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living. The word Hindu is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described as Sanātana Dharma, a modern usage, based on the belief that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym for Hinduism is Vaidika Dharma.

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier that is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase or receive ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.

JPEG is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality. Since its introduction in 1992, JPEG has been the most widely used image compression standard in the world, and the most widely used digital image format, with several billion JPEG images produced every day as of 2015.
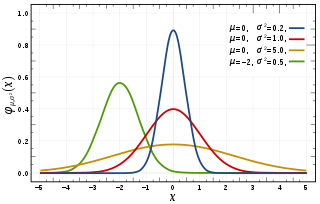
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is The parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution, while the parameter is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is (sigma). A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate.
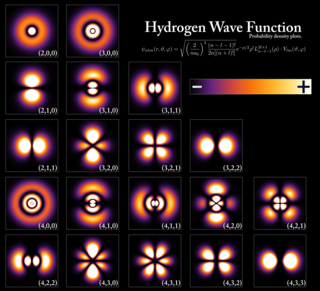
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory that describes the behavior of nature at and below the scale of atoms. It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.

The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. The Sun has been an object of veneration in many cultures. It has been a central subject for astronomical research since antiquity.

Sexual intercourse is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion and thrusting of the male penis inside the female vagina for sexual pleasure, reproduction, or both. This is also known as vaginal intercourse or vaginal sex. Sexual penetration has been known by humans since the dawn of time, and has been an instinctive form of sexual behaviour and psychology among humans. Other forms of penetrative sexual intercourse include anal sex, oral sex, fingering and penetration by use of a dildo, and vibrators. These activities involve physical intimacy between two or more people and are usually used among humans solely for physical or emotional pleasure. They can contribute to human bonding.

William Shakespeare was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon". His extant works, including collaborations, consist of some 39 plays, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. Shakespeare remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted.

World War II or the Second World War was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Axis powers. Nearly all the world's countries—including all the great powers—participated, with many investing all available economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities in pursuit of total war, blurring the distinction between military and civilian resources. Tanks and aircraft played major roles, with the latter enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and delivery of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was the deadliest conflict in history, resulting in 70 to 85 million fatalities, more than half of which were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust of European Jews, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. Following the Allied powers' victory, Germany, Austria, Japan, and Korea were occupied, and war crimes tribunals were conducted against German and Japanese leaders.

Yahweh was an ancient Levantine deity, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Though no consensus exists regarding the deity's origins, scholars generally contend that Yahweh is associated with Seir, Edom, Paran and Teman, and later with Canaan. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age, if not somewhat earlier. Although the religion of Israelites was polytheistic prior to the Babylonian captivity, the deity of Yahweh later evolved into the concepts of God in Judaism and Samaritanism, which are strictly monotheistic.
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. Adding 0 to any number leaves that number unchanged. In mathematical terminology, 0 is the additive identity of the integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and complex numbers, as well as other algebraic structures. Multiplying any number by 0 has the result 0, and consequently, division by zero has no meaning in arithmetic.
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure, is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere is a unit of pressure defined as 101,325 Pa (1,013.25 hPa), which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inches Hg, or 14.696 psi. The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm.

The Greece national football team represents Greece in men's international football matches, and is controlled by the Hellenic Football Federation, the governing body for football in Greece. Greece is one of only ten national teams to have been crowned UEFA European Champions.

Jesus, also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe Jesus to be the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited messiah, or Christ, a descendant from the Davidic line that is prophesied in the Old Testament.

Philosophy is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its own methods and assumptions.

Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the origin and nature of the world; the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself.

Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology, is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period. The northernmost extension of Germanic mythology and stemming from Proto-Germanic folklore, Norse mythology consists of tales of various deities, beings, and heroes derived from numerous sources from both before and after the pagan period, including medieval manuscripts, archaeological representations, and folk tradition. The source texts mention numerous gods such as the thunder-god Thor, the raven-flanked god Odin, the goddess Freyja, and numerous other deities.