
Orogeny is a mountain-building process that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An orogenic belt or orogen develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere. A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny.
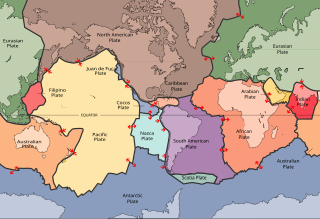
A lithosphere is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy.

Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subsidence creates a regional depression that provides accommodation space for accumulation of sediments. Over millions or tens or hundreds of millions of years the deposition of sediment, primarily gravity-driven transportation of water-borne eroded material, acts to fill the depression. As the sediments are buried, they are subject to increasing pressure and begin the processes of compaction and lithification that transform them into sedimentary rock.
Isostasy or isostatic equilibrium is the state of gravitational equilibrium between Earth's crust and mantle such that the crust "floats" at an elevation that depends on its thickness and density. This concept is invoked to explain how different topographic heights can exist at Earth's surface. Although originally defined in terms of continental crust and mantle, it has subsequently been interpreted in terms of lithosphere and asthenosphere, particularly with respect to oceanic island volcanoes, such as the Hawaiian Islands.

In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems.

Post-glacial rebound is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are phases of glacial isostasy, the deformation of the Earth's crust in response to changes in ice mass distribution. The direct raising effects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in parts of Northern Eurasia, Northern America, Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through the processes of ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.

Mountain formation refers to the geological processes that underlie the formation of mountains. These processes are associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust. Folding, faulting, volcanic activity, igneous intrusion and metamorphism can all be parts of the orogenic process of mountain building. The formation of mountains is not necessarily related to the geological structures found on it.

Tectonic uplift is the geologic uplift of Earth's surface that is attributed to plate tectonics. While isostatic response is important, an increase in the mean elevation of a region can only occur in response to tectonic processes of crustal thickening, changes in the density distribution of the crust and underlying mantle, and flexural support due to the bending of rigid lithosphere.
Flexural rigidity is defined as the force couple required to bend a fixed non-rigid structure by one unit of curvature, or as the resistance offered by a structure while undergoing bending.

The outer trench swell, outer trench high, or outer rise is a subtle ridge on the seafloor near an oceanic trench, where a descending plate begins to flex and fault in preparation for its descent into the mantle at a subduction zone. The lithosphere is bent upwards by plate stresses, and is not in isostatic equilibrium.

A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting forms new ocean basins. Eventually the continental rift forms a mid-ocean ridge and the locus of extension moves away from the continent-ocean boundary. The transition between the continental and oceanic lithosphere that was originally formed by rifting is known as a passive margin.

A foreland basin is a structural basin that develops adjacent and parallel to a mountain belt. Foreland basins form because the immense mass created by crustal thickening associated with the evolution of a mountain belt causes the lithosphere to bend, by a process known as lithospheric flexure. The width and depth of the foreland basin is determined by the flexural rigidity of the underlying lithosphere, and the characteristics of the mountain belt. The foreland basin receives sediment that is eroded off the adjacent mountain belt, filling with thick sedimentary successions that thin away from the mountain belt. Foreland basins represent an endmember basin type, the other being rift basins. Space for sediments is provided by loading and downflexure to form foreland basins, in contrast to rift basins, where accommodation space is generated by lithospheric extension.
In geology, epeirogenic movement is upheavals or depressions of land exhibiting long wavelengths and little folding apart from broad undulations. The broad central parts of continents are called cratons, and are subject to epeirogeny. The movement may be one of subsidence toward, or of uplift from, the center of Earth. The movement is caused by a set of forces acting along an Earth radius, such as those contributing to isostasy and faulting in the lithosphere.

Isostatic depression is the sinking of large parts of the Earth's crust into the asthenosphere caused by a heavy weight placed on the Earth's surface, often glacial ice during continental glaciation. Isostatic depression and isostatic rebound occur at rates of centimeters per year. Greenland is an example of an isostatically depressed region.

In geodynamics, delamination refers to the loss and sinking (foundering) of the portion of the lowermost lithosphere from the tectonic plate to which it was attached.
In geology and geophysics, thermal subsidence is a mechanism of subsidence in which conductive cooling of the mantle thickens the lithosphere and causes it to decrease in elevation. This is because of thermal expansion: as mantle material cools and becomes part of the mechanically rigid lithosphere, it becomes denser than the surrounding material. Additional material added to the lithosphere thickens it and further causes a buoyant decrease in the elevation of the lithosphere. This creates accommodation space into which sediments can deposit, forming a sedimentary basin.
Tectonic subsidence is the sinking of the Earth's crust on a large scale, relative to crustal-scale features or the geoid. The movement of crustal plates and accommodation spaces produced by faulting brought about subsidence on a large scale in a variety of environments, including passive margins, aulacogens, fore-arc basins, foreland basins, intercontinental basins and pull-apart basins. Three mechanisms are common in the tectonic environments in which subsidence occurs: extension, cooling and loading.

Devana Chasma is a weak extensional rift zone on Venus, with a length of 4000 km, a width of 150–250 km, and a depth reaching 5 km. Most of the faults are facing north–south. The rift is located in Beta Regio, a 3000 km rise created by volcanic activity. Mantle plumes rising from the bottom are the reason behind the formation of the rift zone. The slow extension rates in the rift may be driven by the same reason.

Anthony Brian Watts FRS is a British marine geologist and geophysicist and Professor of Marine Geology and Geophysics in the Department of Earth Sciences, at the University of Oxford.

The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary represents a mechanical difference between layers in Earth's inner structure. Earth's inner structure can be described both chemically and mechanically. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary lies between Earth's cooler, rigid lithosphere and the warmer, ductile asthenosphere. The actual depth of the boundary is still a topic of debate and study, although it is known to vary according to the environment.















