The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.
This article talks about transportation in the Bahamas, a North American archipelagic state in the Atlantic Ocean.

Search and rescue (SAR) is the search for and provision of aid to people who are in distress or imminent danger. The general field of search and rescue includes many specialty sub-fields, typically determined by the type of terrain the search is conducted over. These include mountain rescue; ground search and rescue, including the use of search and rescue dogs ; urban search and rescue in cities; combat search and rescue on the battlefield and air-sea rescue over water.
Lieutenant commander is a commissioned officer rank in many navies. The rank is superior to a lieutenant and subordinate to a commander. The corresponding rank in most armies and air forces is major, and in the Royal Air Force and other Commonwealth air forces is squadron leader.

RFA Mounts Bay is a Bay-class auxiliary landing ship dock of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary. She is named after Mount's Bay in Cornwall.

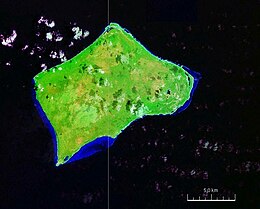
Inagua is the southernmost district of the Bahamas, comprising the islands of Great Inagua and Little Inagua. The headquarters for the district council are in Matthew Town.

United States Coast Guard Air Station Clearwater is the United States Coast Guard's largest air station. It is located at the St. Petersburg-Clearwater International Airport in Clearwater, Florida and is home to nearly 700 USCG aviation and support personnel. As of March 2021, there are ten MH-60T Jayhawk helicopters and four HC-130H Hercules aircraft assigned to CGAS Clearwater. Also on static display is USCG 1023, a restored Grumman HU-16 Albatross.

The Bell 412 is a utility helicopter of the Huey family manufactured by Bell Helicopter. It is a development of the Bell 212, with the major difference being the composite four-blade main rotor.

USCGC Tahoma (WMEC-908) is a United States Coast Guard medium endurance cutter. Her keel was laid on June 28, 1983 at Robert Derecktor Shipyard Incorporated, Middletown, Rhode Island. She was delivered August 12, 1987 and commissioned April 6, 1988. She is the third cutter to bear the name Tahoma, which is the Northwest Pacific Indian word that refers to the Cascade Range mountain peak now known as Mount Rainier. Her nickname, Mighty T, was selected because it was the nickname of her predecessor, Tahoma (WPG-80), during World War II.

The Royal Bahamas Defence Force (RBDF) is the military of The Bahamas. Since The Bahamas does not have an army or an air force, its navy composes the entirety of its armed forces. Under The Defence Act, the Royal Bahamas Defence Force has been mandated to defend The Bahamas, protect its territorial integrity, patrol its waters, provide assistance in times of disaster, maintain order in conjunction with the law enforcement agencies of The Bahamas, and carry out any such duties as determined by the National Security Council. The Defence Force is also a member of CARICOM's Regional Security Task Force. The task force has seen action in the United Nations mandate in Haiti 1994.

USCGC Confidence (WMEC-619) is a United States Coast Guard medium endurance cutter.

The Ukrainian patrol vessel Starobilsk (P191) is an Island-class patrol boat of the Naval Forces of Armed Forces of Ukraine.
The Bahamas National Trust is a non-profit organisation in the Bahamas that manages the country's 32 national parks. Its headquarters is located in New Providence in the Bay Street Business Centre, East Bay Street. Its office was formally located at The Retreat Gardens on Village Road. The Bahamas National Trust was created by an Act of Parliament in 1959, through the efforts of two groups of conservationists.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Commonwealth of The Bahamas.
Inagua National Park is a national park on the island of Great Inagua in The Bahamas. It was established in 1965 and has an area of 220,000 acres (890 km2).

USCGC Bernard C. Webber (WPC-1101) is the first of the United States Coast Guard's 58 Sentinel-class cutters. Like most of her sister ships, she replaced a 110-foot (34 m) Island-class patrol boat. Bernard C. Webber, and the next five vessels in the class, Richard Etheridge, William Flores, Robert Yered, Margaret Norvell, and Paul Clark, are all based in Miami, Florida.
HMBS Lignum Vitae is the first of four Damen Stan 3007 patrol vessels commissioned by the Royal Bahamas Defence Force. She was projected to be ready for delivery to the Bahamas in June 2015.
The HBMS Cascarilla is the second of four Damen Stan 3007 patrol vessels commissioned by the Royal Bahamas Defence Force.
Little Inagua National Park is a national park on and around Little Inagua, the Bahamas. The reserve was established in 2002 and has an area of 62,800 acres (254 km2), including the island and its surrounding waters.
Fox Hill Prison is the only prison in the Bahamas. Located in Nassau, the capital, it is operated by the Bahamas Department of Correctional Services. Fox Hill Prison has minimum, medium, and maximum security facilities for male prisoners. It also has one block for female prisoners as well as a medical block.