
macOS, originally Mac OS X, previously shortened as OS X, is an operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and laptop computers, it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of all Linux distributions, including ChromeOS.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Darwin is the core Unix operating system of macOS, iOS, watchOS, tvOS, iPadOS, visionOS, and bridgeOS. It previously existed as an independent open-source operating system, first released by Apple Inc. in 2000. It is composed of code derived from NeXTSTEP, FreeBSD, BSD, Mach, and other free software projects' code, as well as code developed by Apple.

A personal firewall is an application which controls network traffic to and from a computer, permitting or denying communications based on a security policy. Typically it works as an application layer firewall.

XNU is the computer operating system (OS) kernel developed at Apple Inc. since December 1996 for use in the Mac OS X operating system and released as free and open-source software as part of the Darwin OS, which in addition to macOS is also the basis for the Apple TV Software, iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, visionOS, and tvOS OSes.
Mac OS X Tiger is the 5th major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Mac computers. Tiger was released to the public on April 29, 2005 for US$129.95 as the successor to Mac OS X 10.3 Panther. Included features were a fast searching system called Spotlight, a new version of the Safari web browser, Dashboard, a new 'Unified' theme, and improved support for 64-bit addressing on Power Mac G5s. Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger also had a number of additional features that Microsoft had spent several years struggling to add to Windows with acceptable performance, such as fast file searching and improved graphics processing.
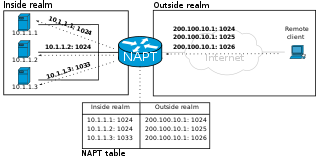
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.
Internet security is a branch of computer security. It encompasses the Internet, browser security, web site security, and network security as it applies to other applications or operating systems as a whole. Its objective is to establish rules and measures to use against attacks over the Internet. The Internet is an inherently insecure channel for information exchange, with high risk of intrusion or fraud, such as phishing, online viruses, trojans, ransomware and worms.
An application firewall is a form of firewall that controls input/output or system calls of an application or service. It operates by monitoring and blocking communications based on a configured policy, generally with predefined rule sets to choose from. The application firewall can control communications up to the application layer of the OSI model, which is the highest operating layer, and where it gets its name. The two primary categories of application firewalls are network-based and host-based.

Apple Remote Desktop (ARD) is a Macintosh application produced by Apple Inc., first released on March 14, 2002, that replaced a similar product called Apple Network Assistant. Aimed at computer administrators responsible for large numbers of computers and teachers who need to assist individuals or perform group demonstrations, Apple Remote Desktop allows users to remotely control or monitor other computers over a network. Mac Pro (2019), Mac mini with a 10Gb Ethernet card, and Mac Studio (2022) have Lights Out Management function and are able to power-on by Apple Remote Desktop.

Mac OS X Leopard is the sixth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. Leopard was released on October 26, 2007 as the successor of Mac OS X Tiger, and is available in two editions: a desktop version suitable for personal computers, and a server version, Mac OS X Server. It retailed for $129 for the desktop version and $499 for Server. Leopard was superseded by Mac OS X Snow Leopard in 2009. Mac OS X Leopard is the last version of macOS that supports the PowerPC architecture as its successor, Mac OS X Snow Leopard, functions solely on Intel based Macs.
There are a number of security and safety features new to Windows Vista, most of which are not available in any prior Microsoft Windows operating system release.
The Mac OS nanokernel is an operating system kernel serving as the basis of most PowerPC based system software versions 7 through 9 of the classic Mac OS, predating Mac OS X.

Mac OS X Snow Leopard is the seventh major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers.

iOS is a mobile operating system based on macOS and on components of the Mach microkernel and FreeBSD, a Unix-like operating system, developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its smartphones. It was unveiled in January 2007 for the first-generation iPhone, launched in June 2007.

Junos OS is a FreeBSD-based network operating system used in Juniper Networks routing, switching and security devices.

System Integrity Protection is a security feature of Apple's macOS operating system introduced in OS X El Capitan (2015). It comprises a number of mechanisms that are enforced by the kernel. A centerpiece is the protection of system-owned files and directories against modifications by processes without a specific "entitlement", even when executed by the root user or a user with root privileges (sudo).

macOS Sierra is the thirteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. The name "macOS" stems from the intention to unify the operating system's name with that of iOS, watchOS and tvOS. Sierra is named after the Sierra Nevada mountain range in California and Nevada. Its major new features concern Continuity, iCloud, and windowing, as well as support for Apple Pay and Siri.
macOS Catalina is the sixteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. It is the successor to macOS Mojave and was announced at WWDC 2019 on June 3, 2019 and released to the public on October 7, 2019. Catalina is the first version of macOS to support only 64-bit applications and the first to include Activation Lock. It is also the last version of macOS to have the major version number of 10; its successor, Big Sur, released on November 12, 2020, is version 11. In order to increase web compatibility, Safari, Chromium and Firefox have frozen the OS in the user agent running in subsequent releases of macOS at 10.15.7 Catalina.














