Related Research Articles
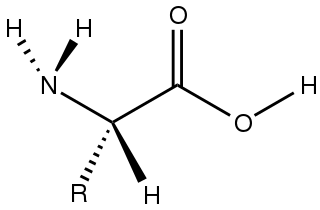
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life.

Cysteine is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula HOOC−CH(−NH2)−CH2−SH. The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. Cysteine is chiral, but both D and L-cysteine are found in nature. L‑Cysteine is a protein monomer in all biota, and D-cysteine acts as a signaling molecule in mammalian nervous systems. Cysteine is named after its discovery in urine, which comes from the urinary bladder or cyst, from Greek κύστη kýsti, "bladder".

Dehydroalanine is a dehydroamino acid. It does not exist in its free form, but it occurs naturally as a residue found in peptides of microbial origin. As an amino acid residue, it is unusual because it has an unsaturated backbone.
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.
Native Chemical Ligation (NCL) is an important extension of the chemical ligation concept for constructing a larger polypeptide chain by the covalent condensation of two or more unprotected peptides segments. Native chemical ligation is the most effective method for synthesizing native or modified proteins of typical size.
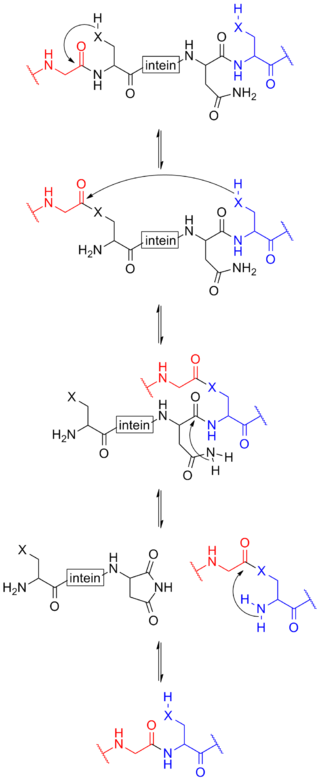
Protein splicing is an intramolecular reaction of a particular protein in which an internal protein segment is removed from a precursor protein with a ligation of C-terminal and N-terminal external proteins on both sides. The splicing junction of the precursor protein is mainly a cysteine or a serine, which are amino acids containing a nucleophilic side chain. The protein splicing reactions which are known now do not require exogenous cofactors or energy sources such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or guanosine triphosphate (GTP). Normally, splicing is associated only with pre-mRNA splicing. This precursor protein contains three segments—an N-extein followed by the intein followed by a C-extein. After splicing has taken place, the resulting protein contains the N-extein linked to the C-extein; this splicing product is also termed an extein.
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad.
A carboxypeptidase is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes (cleaves) a peptide bond at the carboxy-terminal (C-terminal) end of a protein or peptide. This is in contrast to an aminopeptidases, which cleave peptide bonds at the N-terminus of proteins. Humans, animals, bacteria and plants contain several types of carboxypeptidases that have diverse functions ranging from catabolism to protein maturation. At least two mechanisms have been discussed.

Cyclic peptides are polypeptide chains which contain a circular sequence of bonds. This can be through a connection between the amino and carboxyl ends of the peptide, for example in cyclosporin; a connection between the amino end and a side chain, for example in bacitracin; the carboxyl end and a side chain, for example in colistin; or two side chains or more complicated arrangements, for example in alpha-amanitin. Many cyclic peptides have been discovered in nature and many others have been synthesized in the laboratory. Their length ranges from just two amino acid residues to hundreds. In nature they are frequently antimicrobial or toxic; in medicine they have various applications, for example as antibiotics and immunosuppressive agents. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) is a convenient method to detect cyclic peptides in crude extract from bio-mass.

Dermcidin is a protein with 110 amino acids that in humans is encoded by the DCD gene. The full-length protein produces derived peptides as proteolysis-inducing factor (PIF) and other anti-microbial peptides, secreted by human eccrine sweat glands onto the skin as a part of the innate host defense of the immune system. PIF is involved in muscular proteolysis.
Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) is an antimicrobial peptide encoded in the human by the CAMP gene. The active form is LL-37. In humans, CAMP encodes the peptide precursor CAP-18, which is processed by proteinase 3-mediated extracellular cleavage into the active form LL-37.
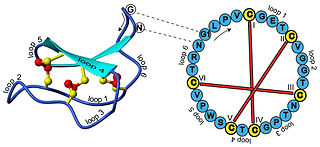
In biochemistry, cyclotides are small, disulfide-rich peptides isolated from plants. Typically containing 28-37 amino acids, they are characterized by their head-to-tail cyclised peptide backbone and the interlocking arrangement of their three disulfide bonds. These combined features have been termed the cyclic cystine knot (CCK) motif. To date, over 100 cyclotides have been isolated and characterized from species of the families Rubiaceae, Violaceae, and Cucurbitaceae. Cyclotides have also been identified in agriculturally important families such as the Fabaceae and Poaceae.
Dermaseptins are a family of peptides isolated from skin of the frog genus Phyllomedusa. The sequence of the dermaseptins varies greatly but due to the presence of lysine residues all are cationic and most have the potential to form amphipathic helices in water or when integrated with the lipid bilayer of the bacterial membrane. Clear separation of two lobes of positive and negative intramolecular electrostatic potential is thought to be important in cytotoxic activity. Dermaseptins are typically 27-34 amino acid residues in length and were the first vertebrate peptides demonstrated as having a lethal effect on the filamentous fungi implicated in severe opportunistic infections accompanying immunodeficiency syndrome and immunosuppressive drug therapy.

Alpha defensins are a family of mammalian defensin peptides of the alpha subfamily. They are also known as cryptdins and are produced within the small bowel. Cryptdin is a portmanteau of crypt and defensin.
Protegrins are small peptides containing 16-18 amino acid residues. Protegrins were first discovered in porcine leukocytes and were found to have antimicrobial activity against bacteria, fungi, and some enveloped viruses. The amino acid composition of protegrins contains six positively charged arginine residues and four cysteine residues. Their secondary structure is classified as cysteine-rich β-sheet antimicrobial peptides, AMPs, that display limited sequence similarity to certain defensins and tachyplesins. In solution, the peptides fold to form an anti-parallel β-strand with the structure stabilized by two cysteine bridges formed among the four cysteine residues. Recent studies suggest that protegrins can bind to lipopolysaccharide, a property that may help them to insert into the membranes of gram-negative bacteria and permeabilize them.
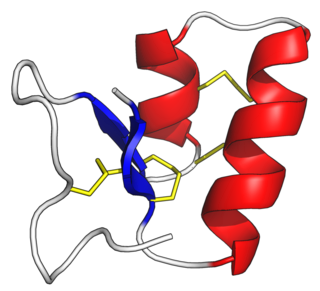
Thionins are a family of small proteins found solely in higher plants. Typically, a thionin consists of 45–48 amino acid residues. 6–8 of these are cysteine forming 3–4 disulfide bonds. They include phoratoxins and viscotoxins.
Myticin is a cysteine-rich peptide produced in three isoforms, A, B and C, by Mytilus galloprovincialis, which are found primarily in marine habitats. Myticin is also produced in other species of Mytilus, though the properties of Myticin in Mytilus galloprovincialis is understood to a greater extent. Isoforms A and B show antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, while isoform C is additionally active against the fungus Fusarium oxysporum and bacterium Escherichia coli. Myticin-prepro is the precursor peptide.
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs), also known as ribosomal natural products, are a diverse class of natural products of ribosomal origin. Consisting of more than 20 sub-classes, RiPPs are produced by a variety of organisms, including prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea, and they possess a wide range of biological functions.
Asparagine peptide lyase are one of the seven groups in which proteases, also termed proteolytic enzymes, peptidases, or proteinases, are classified according to their catalytic residue. The catalytic mechanism of the asparagine peptide lyases involves an asparagine residue acting as nucleophile to perform a nucleophilic elimination reaction, rather than hydrolysis, to catalyse the breaking of a peptide bond.

Papain-like proteases are a large protein family of cysteine protease enzymes that share structural and enzymatic properties with the group's namesake member, papain. They are found in all domains of life. In animals, the group is often known as cysteine cathepsins or, in older literature, lysosomal peptidases. In the MEROPS protease enzyme classification system, papain-like proteases form Clan CA. Papain-like proteases share a common catalytic dyad active site featuring a cysteine amino acid residue that acts as a nucleophile.
References
- ↑ Krause A, Sillard R, Kleemeier B, Klüver E, Maronde E, Conejo-GarcÃa JR, Forssmann WG, Schulz-Knappe P, Nehls MC, Wattler F, Wattler S, Adermann K (January 2003). "Isolation and biochemical characterization of LEAP-2, a novel blood peptide expressed in the liver". Protein Sci. 12 (1): 143–52. doi:10.1110/ps.0213603. PMC 2312392 . PMID 12493837.