Oriental Mindoro, officially the Province of Oriental Mindoro, is a province in the Philippines located on the island of Mindoro under Mimaropa region in Luzon, about 140 kilometres (87 mi) southwest of Manila. The province is bordered by the Verde Island Passage and the rest of Batangas to the north, by Marinduque, Maestre de Campo Island, Tablas Strait and the rest of Romblon to the east, by Semirara and the rest of Caluya Islands, Antique to the south, and by Occidental Mindoro to the west. Calapan, the only city in the island, is the provincial capital and Mimaropa's regional center.

Antique, officially the Province of Antique, is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is San Jose de Buenavista, the most populous town in Antique. The province is situated in the western section of Panay Island and borders Aklan, Capiz and Iloilo to the east, while facing the Sulu Sea to the west.

Capiz, officially the Province of Capiz, is a province in the Philippines located in the central section of Western Visayas region. Its capital is the city of Roxas. It is located at the northeastern portion of Panay Island, bordering Aklan to the north, Antique to the west, and Iloilo to the south. Capiz faces the Sibuyan Sea to the north.

Western Visayas is an administrative region in the Philippines, numerically designated as Region VI. It consists of six provinces and two highly urbanized cities. The regional center is Iloilo City. The region is dominated by the native speakers of four Visayan languages: Hiligaynon, Kinaray-a, Aklanon and Capiznon. The land area of the region is 20,794.18 km2 (8,028.68 sq mi), and with a population of 7,954,723 inhabitants, it is the second most populous region in the Visayas after Central Visayas.

San Jose, officially the Municipality of San Jose, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Occidental Mindoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 153,267, representing a third of the provincial population, and is the largest among cities and municipalities in the Mimaropa region.

Malay, officially the Municipality of Malay, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Aklan, Philippines. It is the richest municipality in the province in terms of revenue. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 60,077 people making it the second most populated town in Aklan.
Caluya, officially the Municipality of Caluya, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Antique, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 38,908 people, making it the sixth most populous municipality in the province.

Panay, officially the Municipality of Panay, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Capiz, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 48,890 people.

Banton, officially the Municipality of Banton, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Romblon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 5,737 people.

Concepcion, officially the Municipality of Concepcion, is a 6th class municipality in the province of Romblon, Philippines. The municipality is coextensive with Maestre de Campo Island, which is also known as Sibale Island. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 3,561 people.

Ferrol, officially the Municipality of Ferrol, is a 6th class municipality in the province of Romblon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 8,005 people.

Lubang, officially the Municipality of Lubang, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Occidental Mindoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,437 people.

Magsaysay, officially the Municipality of Magsaysay, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Occidental Mindoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 39,767 people.

Bulalacao, officially the Municipality of Bulalacao, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Oriental Mindoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 44,366 people.

Calapan, officially the City of Calapan, is a 3rd class component city in the province of Oriental Mindoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 145,786 people. The city is the capital of the province of Oriental Mindoro.

Roxas, officially the Municipality of Roxas, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Oriental Mindoro, Philippines. It has a population of 58,849 according to the 2020 census.
Mindoro was a province of the Philippines from 1902 until 1950 when it was split into two provinces, Occidental Mindoro and Oriental Mindoro. It is located on Mindoro island, Philippines.
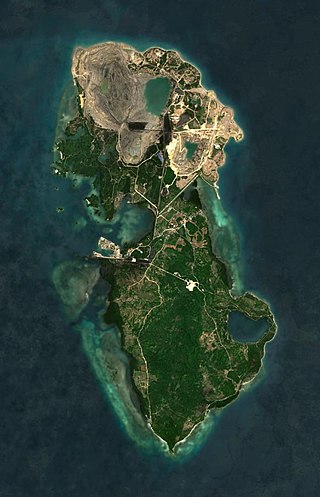
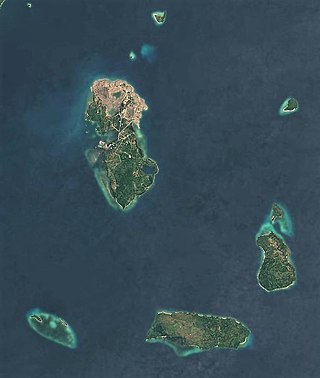
Semirara is an island in the Philippines located at in the Caluya archipelago which is situated south of Mindoro Island. It is under the jurisdiction of the town of Caluya of the province of Antique. It is a major site of coal mining in the Philippines. Other economic activities in the island include fishing, seashell gathering, and farming.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Mimaropa is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus reached Mimaropa on March 20, 2020, when the first case of the disease was confirmed in Puerto Princesa.

On the morning of February 28, 2023, MT Princess Empress sank off Naujan, Oriental Mindoro, Philippines, causing an oil spill in the waters of the provinces of Antique, Batangas, Oriental Mindoro, and Palawan. En route from Bataan to Iloilo, the oil tanker was carrying 900,000 liters of industrial fuel oil before it sank.