The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world by discharge volume, following the Amazon and Ganges rivers. It is the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths of around 220 m (720 ft). The Congo–Lualaba–Luvua–Luapula–Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,900 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,100 mi).

Sir Henry Morton Stanley was a Welsh-American explorer, journalist, soldier, colonial administrator, author and politician who was famous for his exploration of Central Africa and his search for missionary and explorer David Livingstone. Besides his discovery of Livingstone, he is mainly known for his search for the sources of the Nile and Congo rivers, the work he undertook as an agent of King Leopold II of the Belgians which enabled the occupation of the Congo Basin region, and his command of the Emin Pasha Relief Expedition. He was knighted in 1897, and served in Parliament as a Liberal Unionist member for Lambeth North from 1895 to 1900.

The Congo Free State, also known as the Independent State of the Congo, was a large state and absolute monarchy in Central Africa from 1885 to 1908. It was privately owned by King Leopold II, the constitutional monarch of the Kingdom of Belgium. In legal terms, the two separate nations were in a personal union. The Congo Free State was not a part of, nor did it belong to Belgium. Leopold was able to seize the region by convincing other European states at the Berlin Conference on Africa that he was involved in humanitarian and philanthropic work and would not tax trade. Via the International Association of the Congo, he was able to lay claim to most of the Congo Basin. On 29 May 1885, after the closure of the Berlin Conference, the king announced that he planned to name his possessions "the Congo Free State", an appellation which was not yet used at the Berlin Conference and which officially replaced "International Association of the Congo" on 1 August 1885. The Free State was privately controlled by Leopold from Brussels; he never visited it.
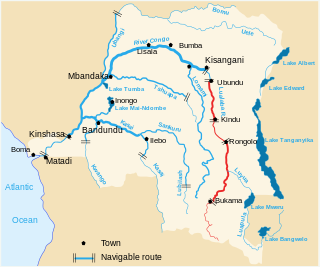
The Lualaba River flows entirely within the eastern part of Democratic Republic of the Congo. It provides the greatest streamflow to the Congo River, while the source of the Congo is recognized as the Chambeshi. The Lualaba is 1,800 kilometres (1,100 mi) long. Its headwaters are in the country's far southeastern corner near Musofi and Lubumbashi in Katanga Province, next to the Zambian Copperbelt.

The Pool Malebo, formerly Stanley Pool, also known as Mpumbu, Lake Nkunda or Lake Nkuna by local indigenous people in pre-colonial times, is a lake-like widening in the lower reaches of the Congo River. The river serves as the border between the Republic of the Congo to the north and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south.

The Emin Pasha Relief Expedition of 1887 to 1889 was one of the last major European expeditions into the interior of Africa in the nineteenth century. Led by Henry Morton Stanley, its goal was ostensibly the relief of Emin Pasha, the besieged Egyptian governor of Equatoria, who was threatened by Mahdist forces.
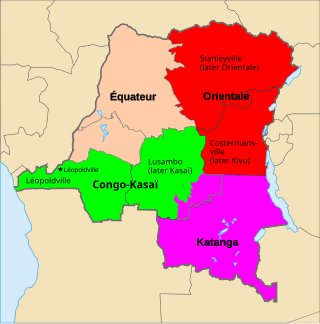
Orientale Province is one of the former provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and its predecessors the Congo Free State and the Belgian Congo. It went through a series of boundary changes between 1898 and 2015, when it was divided into smaller units.

The Kasai River is a left bank tributary of the Congo River, located in Central Africa. The river begins in central Angola and flows to the east until it reaches the border between Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it turns north and serves as the border until it flows into the DRC. From Ilebo, between the confluences with Lulua river and Sankuru river, the Kasai river turns to a westerly direction. The lower stretch of the river from the confluence with Fimi river, is known as the Kwa(h) River, before it joins the Congo at Kwamouth northeast of Kinshasa. The Kasai basin consists mainly of equatorial rainforest areas, which provide an agricultural land in a region noted for its infertile, sandy soil. It is a tributary of Congo river and diamonds are found in it. Around 60% of diamonds in Belgium go from Kasai river for cutting and shaping.

The Republic of the Congo is an African nation with close musical ties to its neighbor, the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Democratic Republic of the Congo's homegrown pop music, soukous, is popular across the border, and musicians from both countries have fluidly travelled throughout the region playing similarly styled music, including Nino Malapet and Jean Serge Essous. Brazzaville had a major music scene until unrest in the late 1990s, and produced popular bands like Extra Musica and Bantous de la Capitale that played an integral role in the development of soukous and other styles of Congolese popular music. The Hip-Hop group "Bisso na Bisso" also hails from Congo-Brazzaville.
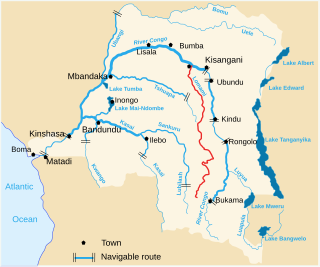
The Lomami River is a major tributary of the Congo River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The river is approximately 1,280 km (800 mi) long. It flows north, west of and parallel to the upper Congo.
Colonization of the Congo Basin refers to the European colonization of the Congo Basin of tropical Africa. It was the last part of the continent to be colonized. By the end of the 19th century, the Basin had been carved up by European colonial powers, into the Congo Free State, the French Congo and the Portuguese Congo.

Boma is a port town on the Congo River, some 100 kilometres (62 mi) upstream from the Atlantic Ocean, in the Kongo Central Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), adjacent to the border with Angola. It had an estimated population of 162,521 in 2012.

The International Association of the Congo, also known as the International Congo Society, was an association founded on 17 November 1879 by Leopold II of Belgium to further his interests in the Congo. It replaced the Belgian Committee for Studies of the Upper Congo which was part of the International African Association front organisation created for the exploitation of the Congo. The goals of the International Congo Society was to establish control of the Congo Basin and to exploit its economic resources. The Berlin Conference recognised the society as sovereign over the territories it controlled and on August 1, 1885, i.e. four and half months after the closure of the Berlin Conference, King Leopold's Vice-Administrator General in the Congo, announced that the society and the territories it occupied were henceforth called "the Congo Free State".

Richard Dorsey Loraine Mohun was an American explorer, diplomat, mineral prospector and mercenary. Mohun worked for the United States government as a commercial agent in Angola and the Congo Free State. During his time as commercial agent, he volunteered to command a unit of Belgian artillery in a campaign to force Arab slavers from the colony.

The Congo Arab war or Arab war was a colonial war fought between the Congo Free State and Arab-Swahili warlords associated with the Arab slave trade in the eastern regions of the Congo basin between 1892 and 1894.
Bena Kamba is a community on the Lomami River in Maniema province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Louis-Napoléon Chaltin (1857–1933) was a Belgian career soldier and colonial official notable for his service in the Congo Free State during the late 19th century.
The Livingstone Inland Mission (LIM) was an evangelical missionary society that operated in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1878 and 1884.
Relations between the Congo Free State and the United States began after recognition between the two states in 1885 when the Congo Free State was established. After Belgium under Leopold II annexed the Congo Free State in 1908, later becoming Belgian Congo, relations ceased between the two nations.

James Sligo Jameson was a Scottish naturalist and traveller in Africa. He identified the black honey-buzzard in 1877. Jameson's antpecker, Jameson's firefinch, and Jameson's wattle-eye are named after him. However, he is most remembered for his role in causing a slave girl to be killed and eaten by cannibals.