
Limburg is the southernmost of the 12 provinces of the Netherlands. The province is in the southern part of the country, stretched out from the north, where it touches the province of Gelderland. Its northern part has the province of North Brabant to its west. Its long eastern boundary is the international border with the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Much of the west border runs along the River Maas, bordering the Flemish province which is also named Limburg. On the south end it borders the Walloon province of Liège. The Vaalserberg is on the extreme south-eastern point, marking the tripoint of the Netherlands, Germany and Belgium.

The County Palatine of the Rhine, later the Electorate of the Palatinate or simply Electoral Palatinate, was a territory in the Holy Roman Empire administered by the count palatine of the Rhine. Its rulers served as prince-electors from "time immemorial", were noted as such in a papal letter of 1261, and were confirmed as electors by the Golden Bull of 1356.

The Duchy of Lorraine, originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy.

The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands and historically called the Netherlands, Flanders, or Belgica, refers to a coastal lowland region in northwestern Europe forming the lower basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting of Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. Geographically and historically, the area includes also parts of France and Germany such as the French Flanders and the German regions of East Frisia and Cleves. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were divided in numerous semi-independent principalities.

The Rhineland is the name used for a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.

The Ardennes, also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges. Geologically, the range is a western extension of the Eifel, and both were raised during the Givetian age of the Devonian, as were several other named ranges of the same greater range.

Arlon is a Walloon municipality of Belgium located in and capital of the province of Luxembourg in the Ardennes. With a population of just over 28,000, it is the smallest provincial capital in Belgium. Arlon is also the capital of its cultural region: the Arelerland.

Lotharingia was a medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire and a later duchy of the Ottonian Empire, comprising the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Rhineland-Palatinate (Germany), Saarland (Germany), and Lorraine (France). It was named after King Lothair II who received this territory after the kingdom of Middle Francia of his father Lothair I was divided among his sons in 855.
Alma or ALMA may refer to:

Longwy is a commune in the Meurthe-et-Moselle department in northeastern France.

A stem duchy was a constituent duchy of the Kingdom of Germany at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dynasty and through the transitional period leading to the formation of the Holy Roman Empire later in the 10th century. The Carolingians had dissolved the original tribal duchies of the Frankish Empire in the 8th century. As the Carolingian Empire declined in the late 9th century, the old tribal areas assumed new identities as subdivisions of the realm. The five stem duchies were: Bavaria, Franconia, Lotharingia (Lorraine), Saxony and Swabia (Alemannia). The Salian emperors retained the stem duchies as the major divisions of Germany, but they became increasingly obsolete during the early high-medieval period under the Hohenstaufen, and Frederick Barbarossa finally abolished them in 1180 in favour of more numerous territorial duchies.

The Duchy of Limburg or Limbourg was an imperial estate of the Holy Roman Empire. Its chief town was Limbourg-sur-Vesdre, is today located within the Belgian province of Liège, with a small part in the neighbouring province of Belgian Limburg, within the east of Voeren.

Lorraine is a cultural and historical region in north-eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Lorraine's name stems from the medieval kingdom of Lotharingia, which in turn was named for either Emperor Lothair I or King Lothair II. It later was ruled as the Duchy of Lorraine before the Kingdom of France annexed it in 1766.

The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine, was a stem duchy established in 959, of the medieval Kingdom of Germany, which encompassed almost all of the modern Netherlands, central and eastern Belgium, Luxemburg, the northern part of the German Rhineland province and the eastern parts of France's Nord-Pas de Calais region.

The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt.

The Duchy of Luxemburg was a state of the Holy Roman Empire, the ancestral homeland of the noble House of Luxembourg. The House of Luxembourg, now Duke of Limburg, became one of the most important political forces in the 14th century, competing against the House of Habsburg for supremacy in Central Europe. They would be the heirs to the Přemyslid dynasty in the Kingdom of Bohemia, succeeding the Kingdom of Hungary and contributing four Holy Roman Emperors until their own line of male heirs came to an end and the House of Habsburg got the pieces that the two Houses had originally agreed upon in the Treaty of Brünn in 1364.
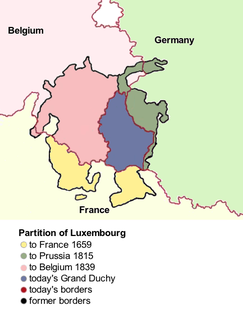
There have been three Partitions of Luxembourg between 1659 and 1839. Together, the three partitions reduced the territory of Luxembourg from 10,700 km2 (4,100 sq mi) to the present-day area of 2,586 km2 (998 sq mi) over a period of 240 years. The remainder forms parts of modern day Belgium, France, and Germany.
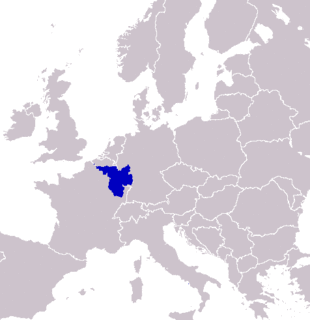
SaarLorLux or Saar-Lor-Lux, a portmanteau of Saarland, Lorraine and Luxembourg, is a euroregion of five regional authorities located in four European states. The term has also been applied to cooperations of several of these authorities or of their subdivisions, administrations, organisations, clubs and people. Member regions represent different political structures: the sovereign state of Luxembourg; Belgium's Walloon region, comprising the French and German speaking parts of Belgium; Lorraine, a region of France; the French départements Moselle and Meurthe-et-Moselle; and the German federated states of Saarland and Rhineland-Palatinate.

Hettange-Grande is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.

Meuse is a department in northeast France, named after the River Meuse. Meuse is part of the current region of Grand Est and is surrounded by the French departments of Ardennes, Marne, Haute-Marne, Vosges, Meurthe-et-Moselle, and has a short border with Belgium on the north. Parts of Meuse belong to Parc naturel régional de Lorraine. Front lines in trench warfare during World War I ran varying courses through the department and it hosted an important battle/offensive in 1916 in and around Verdun.


















