
The Humber Forts are two large fortifications in the mouth of the Humber Estuary in northern England: Haile Sand Fort and Bull Sand Fort.

Limehouse Town Hall is a former town hall building on Commercial Road, in Limehouse, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets.
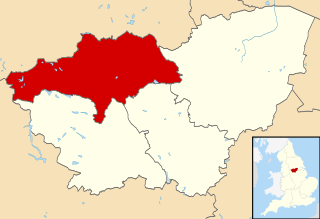
The Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley is a metropolitan borough of South Yorkshire, England; its main town is Barnsley.

High Hoyland is a village and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley in South Yorkshire, England, on the border with West Yorkshire. It lies to the west of Kexbrough, and is located at approximately 53°35′10″N1°35′30″W, at an elevation of around 200 metres above sea level. At the 2001 census it had a population of 142, reducing to 128 at the 2011 Census.

Hoyland is a town near Barnsley in Northern England. The town developed from the hamlets of Upper Hoyland, Hoyland and Hoyland Common.

St John the Evangelist and St Mary Magdalene Church is a parish church in the Church of England Diocese of Sheffield in Goldthorpe, near Barnsley, South Yorkshire, England.

Municipal Buildings is a Grade II* listed building on Dale Street, Liverpool, England.

Barnsley West and Penistone was a parliamentary constituency in South Yorkshire which returned one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, elected by the first-past-the-post voting system.

Beckfoot Bridge was historically a significant crossing point over Harden Beck in Bingley, West Yorkshire, England.

Carnaby is a small village and civil parish on the A614 road in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It is situated approximately 2 miles (3 km) south-west of Bridlington town centre.

Elsecar Heritage Centre is a living history centre in Elsecar, Barnsley, England.

The Wool Exchange Building in Bradford, West Yorkshire, England is a grade I-listed building built as a wool-trading centre in the 19th century. The grandeur of its Gothic Revival architecture is symbolic of the wealth and importance that wool brought to Bradford. Today it contains a small shopping centre.

Carlton Towers is a Grade I listed Victorian gothic country house in Carlton, North Yorkshire, England.

The 1st White Cloth Hall is a Grade II* listed building on Kirkgate, in the city centre of Leeds in West Yorkshire, England.

Bettison's Folly is a tower in Hornsea, East Riding of Yorkshire, England. Also referred to as Bettisons Tower and the Forgotten Folly, it was built some time between 1829 and 1853 by William Bettison.

Skidby Windmill is a Grade II* listed windmill at Skidby near Beverley, in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England.

St Thomas's Church is a Church of England church in the Diocese of Leeds. It is situated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, England and is a Grade II* listed building. The church was designed by Sir George Gilbert Scott and built between 1857 and 1859. It was consecrated in 1859 and celebrated its 150th anniversary in 2009.

The Leeds Club is a Grade II* listed Victorian building in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It is situated on Albion Place in the city centre.
There are over 9,000 Grade I listed buildings in England. This page is a list of these buildings in the district of Craven in North Yorkshire.

Lytham Windmill is situated on Lytham Green in the coastal town of Lytham St Annes, Lancashire, England. It is of the type known as a tower mill and was designed for grinding wheat and oats to make flour or bran. Since commercial milling on the site ceased in 1921 the mill has belonged to the town and is operated by Fylde Borough Council, who open it to the public during the summer. The mill also contains a museum run by the Lytham Heritage Trust which explains the history and practice of flour milling.























