Calabria is a region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian Sea to the west. It has almost 2 million residents across a total area of 15,222 km2 (5,877 sq mi). Catanzaro is the region's capital.

Reggio di Calabria, commonly and officially referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the largest city in Calabria as well as the seat of the Regional Council of Calabria. It has an estimated population between 150,000 and 200,000 and is the twenty-first most populous city in Italy, after Modena and other Italian cities, and the 100th most populated city in Europe. Reggio Calabria is located near the center of the Mediterranean and is known for its climate, ethnic and cultural diversity. It is the third economic centre of mainland Southern Italy. About 560,000 people live in the metropolitan area, recognised in 2015 by Italy as a metropolitan city. Sadly, it holds the record of the worst city in terms of quality of life for environmental and cultural parameters, ranking among the worst Italian cities for quality of life.

Magna Graecia is a term that was used for the Greek-speaking areas of Southern Italy, in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these regions were extensively populated by Greek settlers starting from the 8th century BC.
Basilicata, also known by its ancient name Lucania, is an administrative region in Southern Italy, bordering on Campania to the west, Apulia to the north and east, and Calabria to the south. It has two coastlines: a 30-km stretch on the Tyrrhenian Sea between Campania and Calabria, and a longer coastline along the Gulf of Taranto between Calabria and Apulia. The region can be thought of as the "instep" of the "boot" of Italy, with Calabria functioning as the "toe" and Apulia the "heel".

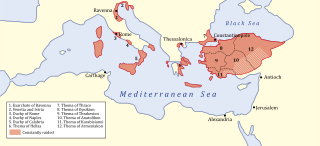
The Exarchate of Ravenna, also known as the Exarchate of Italy, was an administrative district of the Byzantine Empire comprising, between the 6th and 8th centuries, the territories under the jurisdiction of the exarch of Italy resident in Ravenna. The term is used in historiography in a double sense: "exarchate" in the strict sense denotes the territory under the direct jurisdiction of the exarch, i.e. the area of the capital Ravenna, but the term is mainly used to designate all the Byzantine territories in continental and peninsular Italy. According to the legal sources of the time, these territories constituted the so-called Provincia Italiae, on the basis of the fact that they too, until at least the end of the 7th century, fell under the jurisdiction of the exarch and were governed by duces or magistri militum under him.

Lucania was a historical region of Southern Italy, corresponding to the modern-day region of Basilicata. It was the land of the Lucani, an Oscan people. It extended from the Tyrrhenian Sea to the Gulf of Taranto. It bordered with Samnium and Campania in the north, Apulia in the east, and Bruttium in the south-west, and was at the tip of the peninsula which is now called Calabria. It comprised almost all the modern region of Basilicata, the southern part of the Province of Salerno, the western part of Province of Taranto and a northern portion of the Province of Cosenza.

The Catepanateof Italy was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 965 until 1071. At its greatest extent, it comprised mainland Italy south of a line drawn from Monte Gargano to the Gulf of Salerno. North of that line, Amalfi and Naples also maintained allegiance to Constantinople through the catepan. The Italian region of Capitanata derives its name from katepanikion.

Lauria is a town and comune of the province of Potenza, in Basilicata, southern Italy, situated near the borders of Calabria. It is a walled, medieval town on the steep side of a hill, with another portion of municipal territory in the plain below.

Longobardia was a Byzantine term for the territories controlled by the Lombards in the Italian Peninsula. In the ninth and tenth centuries, it was also the name of a Byzantine military-civilian province known as the Theme of Longobardia located in southeastern Italy.
Nicholas Epigingles, better known by his Latinized surname Picingli, was a Byzantine general active in southern Italy and the Balkans. As strategos of the thema of Longobardia, he led the Byzantine contingent of the Christian league in the Battle of Garigliano in 915. He was killed fighting against the Bulgarians, probably in the Battle of Acheloos on 20 August 917.

Tursi is an Italian comune of 4,712 inhabitants in the province of Matera in Basilicata, elevated to a city by decree of the President of the Republic Carlo Azeglio Ciampi on May 4, 2006. The municipality is home to the Basso Sinni mountain community.

Tricarico is a town and comune in the province of Matera, Basilicata, southern Italy.

Leoluca, also Leone Luca, Leo Luke of Corleone, Saint Leoluca, or Luke of Sicily was the abbot and wonderworker of the monastery of Mount Mula in Calabria, and a founder of Italo-Greek monasticism in southern Italy. He is venerated as a saint in the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches.

Greeks in Italy have been present since the migrations of traders and colonial foundations in the 8th century BC, continuing down to the present time. Nowadays, there is an ethnic minority known as the Griko people, who live in the Southern Italian regions of Calabria and Apulia, especially the peninsula of Salento, within the ancient Magna Graecia region, who speak a distinctive dialect of Greek called Griko. They are believed to be remnants of the ancient and medieval Greek communities, who have lived in the south of Italy for centuries. A Greek community has long existed in Venice as well, the current centre of the Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of Italy and Malta, which in addition was a Byzantine province until the 10th century and held territory in Morea and Crete until the 17th century. Alongside this group, a smaller number of more recent migrants from Greece lives in Italy, forming an expatriate community in the country. Today many Greeks in Southern Italy follow Italian customs and culture, experiencing assimilation.
Nikephoros Phokas, usually surnamed the Elder to distinguish him from his grandson, Emperor Nikephoros II Phokas, was one of the most prominent Byzantine generals of the late 9th century, and the first important member of the Phokas family. As a youth he was taken into the personal retinue of Emperor Basil I the Macedonian, rising quickly to the posts of protostrator and then governor of Charsianon, whence he fought with success against the Arabs. In c. 886 he led a major expedition in southern Italy, where his victories laid the foundation for the Byzantine resurgence in the peninsula. After his return, he was raised to the post of Domestic of the Schools, in effect commander-in-chief of the army, which he led with success against the Arabs in the east and the Bulgarians of Tsar Simeon in the Balkans. He died either in 895/6 or, less likely, sometime c. 900. Contemporaries and later historians lauded him for his military ability and character. Both of his sons later succeeded him as Domestics of the Schools. His grandsons Nikephoros and Leo were likewise distinguished generals, while the former became emperor in 963–969, spearheading the recovery of several lost provinces from the Arabs.
Sicily was a Byzantine province (theme) existing from the late 7th to the 10th century, encompassing the islands of Sicily and Malta, and the region of Calabria in the Italian mainland. Following the Muslim conquest of Sicily, from 902 the theme was limited to Calabria, but retained its original name until the middle of the 10th century.

The Griko people, also known as Grecanici in Calabria, are an ethnic Greek community of Southern Italy. They are found principally in the regions of Calabria and Apulia. The Griko are believed to be remnants of the once large Ancient and Medieval Greek communities of Southern Italy, although there is some dispute among scholars as to whether the Griko community is directly descended from Ancient Greeks, from more recent medieval migrations during the Byzantine period, or a combination of both.
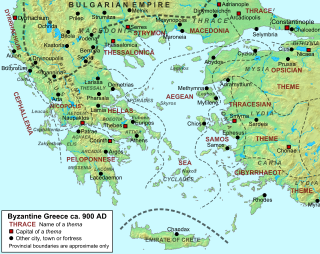
The Theme of Cephallenia or Cephalonia was a Byzantine theme located in western Greece, comprising the Ionian Islands, and extant from the 8th century until partially conquered by the Kingdom of Sicily in 1185.
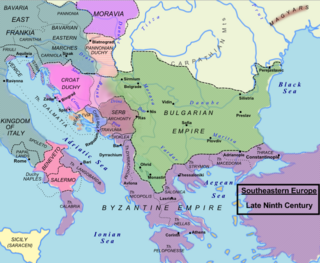
The siege of Ragusa by the Aghlabids of Ifriqiya lasted for fifteen months, beginning in 866 until the lifting of the siege at the approach of a Byzantine fleet in 868. The failure of the siege and the re-appearance of the Byzantines in the region of Dalmatia signalled the beginning of new aggressive western policy by the new Byzantine emperor, Basil I. Its immediate effects were the re-establishment of Byzantine authority there in the form of the Theme of Dalmatia, and the beginning of the Christianization of the Slavs of the western Balkans, but within a few years it led to renewed Byzantine involvement and presence in southern Italy as well.
The history of Tursi, a town in Southern Italy, likely originated in the early Middle Ages, as most historians agree, with the fifth-century barbarian invasions by the Goths in southern Italy.


















