
Alfalfa, also called lucerne, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as well as a green manure and cover crop. The name alfalfa is used in North America. The name lucerne is more commonly used in the United Kingdom, South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. The plant superficially resembles clover, especially while young, when trifoliate leaves comprising round leaflets predominate. Later in maturity, leaflets are elongated. It has clusters of small purple flowers followed by fruits spiralled in two to three turns containing 10–20 seeds. Alfalfa is native to warmer temperate climates. It has been cultivated as livestock fodder since at least the era of the ancient Greeks and Romans.
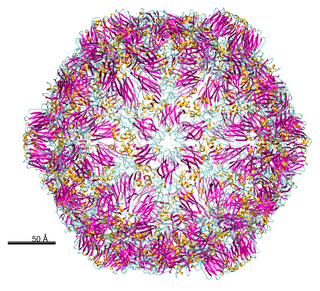
Nepovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae, in the subfamily Comovirinae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 40 species in this genus. Nepoviruses, unlike the other two genera in the subfamily Comovirinae, are transmitted by nematodes.

Apple mosaic virus (ApMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Bromoviridae. It is named after its symptoms that were first present on apples. ApMV is a positive sense RNA based virus. The disease itself has several synonyms including Mild Apple Mosaic Virus, Hop Virus, Rose Mosaic Virus, and European Plum Line Patten Virus. It causes a severe yield reduction and decreased life-expectancy of fruit trees.
Cherry mottle leaf virus (CMLV) is a plant pathogenic virus causing leaf rot. It is closely related to the peach mosaic virus.
Lucerne Australian latent virus (LALV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Secoviridae.
Lucerne transient streak virus (LTSV) is a pathogenic plant virus.

Prunus necrotic ringspot virus (PNRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus causing ring spot diseases affecting species of the genus Prunus, as well as other species such as rose and hops. PNRSV is found worldwide due to easy transmission through plant propagation methods and infected seed. The virus is in the family Bromoviridae and genus Ilarvirus. Synonyms of PNRSV include European plum line pattern virus, hop B virus, hop C virus, plum line pattern virus, sour cherry necrotic ringspot virus, and peach ringspot virus.
Strawberry mild yellow-edge virus (SMYEV) is a pathogenic plant virus.

Carlavirus, formerly known as the "Carnation latent virus group", is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 53 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Grapevine yellows (GY) are diseases associated to phytoplasmas that occur in many grape growing areas worldwide and are of still increasing significance. The most important grapevine yellows is flavescence dorée.

The common brown leafhopper is one of the most common species of Australian leafhoppers with a very wide host range. It is an important vector of several viruses and phytoplasmas worldwide. In Australia, phytoplasmas vectored by O. orientalis cause a range of economically important diseases including legume little leaf, tomato big bud, lucerne witches broom, potato purple top wilt, Australian lucerne and the insect is a possible vector of Australian grapevine yellows. O. orientalis also transmits Tobacco yellow dwarf virus to beans, causing bean summer death disease and to tobacco, causing tobacco yellow dwarf disease.
Little cherry disease or LChD, sometimes referred to as little cherry, K & S little cherry or sour cherry decline, is a viral infectious disease that affects cherry trees, most notably sweet cherries and sour cherries . Little cherry disease should not be confused with cherry buckskin disease, which is caused by Phytoplasma. Note that both diseases are among the diseases referred to as cherry decline.
Narcissus common latent virus (NCLV) is a plant pathogenic virus. It infects Narcissus plants. The term 'latent' refers to the fact that infection may be symptomless. Transmission occurs by Aphids.
Nerine latent virus (NeLV) is a plant pathogenic virus. It infects Nerine, Narcissus, Hippeastrum and Ismene plants.
Acyrthosiphon kondoi, the blue alfalfa aphid or bluegreen aphid, is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from leguminous plants, particularly alfalfa.
Mastrevirus is a genus of ssDNA viruses, in the family Geminiviridae. Mostly monocotyledonous plants serve as natural hosts. They are vectored by planthoppers. There are 45 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: maize streak virus: maize streak disease (MSD).
Velarivirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Closteroviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are eight species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: GLRaV-7: symptomless in white-berried grapevine cultivar from Albania.
Lily virus X (LVX) is a pathogenic ssRNA(+) plant virus of the family Alphaflexiviridae and the order Tymovirales.
Donkey orchid symptomless virus (DOSV) was first discovered in Perth, Australia which is located on the Western side of Australia. The Southwest Australian Floristic Region is very biodiverse and secluded with deserts on the east and northeast side along with the ocean on the south side. It is home to approximately 8,000 indigenous plant species that are accustomed to living in a Mediterranean climate. This type of climate means that the plants have adapted to living in unfertile soil, dryness, and can withstand frequent fires in the area. Out of 394 terrestrial orchid species, 76 of these species are threatened. Reasons contributing to plants being threatened in this area could be due to the rate at which they reproduce fruit, pollinate, or human contact.

Pterochaeta is a monotypic plant genus in the Asteraceae family, endemic to Western Australia. It was first described in 1845 by Joachim Steetz and its only species is Pterochaeta paniculata.







