
Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking. "Free space" means air, outer space, vacuum, or something similar. This contrasts with using solids such as optical fiber cable.

A lander is a spacecraft that descends towards, then comes to rest on the surface of an astronomical body other than Earth. In contrast to an impact probe, which makes a hard landing that damages or destroys the probe upon reaching the surface, a lander makes a soft landing after which the probe remains functional.

The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is One JAXA and its corporate slogan is Explore to Realize.

The interplanetary Internet is a conceived computer network in space, consisting of a set of network nodes that can communicate with each other. These nodes are the planet's orbiters and landers, and the Earth ground stations. For example, the orbiters collect the scientific data from the Curiosity rover on Mars through near-Mars communication links, transmit the data to Earth through direct links from the Mars orbiters to the Earth ground stations via the NASA Deep Space Network, and finally the data routed through Earth's internal internet.

The Mars Telecommunications Orbiter (MTO) was a cancelled Mars mission that was originally intended to launch in 2009 and would have established an Interplanetary Internet between Earth and Mars. The spacecraft would have arrived in a high orbit above Mars in 2010 and relayed data packets to Earth from a variety of Mars landers, rovers and orbiters for as long as ten years, at an extremely high data rate. Such a dedicated communications satellite was thought to be necessary due to the vast quantity of scientific information to be sent to Earth by landers such as the Mars Science Laboratory.

The Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, also known as the Chang'e Project after the Chinese Moon goddess Chang'e, is an ongoing series of robotic Moon missions by the China National Space Administration (CNSA).

The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer was a NASA lunar exploration and technology demonstration mission. It was launched on a Minotaur V rocket from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport on September 7, 2013. During its seven-month mission, LADEE orbited the Moon's equator, using its instruments to study the lunar exosphere and dust in the Moon's vicinity. Instruments included a dust detector, neutral mass spectrometer, and ultraviolet-visible spectrometer, as well as a technology demonstration consisting of a laser communications terminal. The mission ended on April 18, 2014, when the spacecraft's controllers intentionally crashed LADEE into the far side of the Moon, which, later, was determined to be near the eastern rim of Sundman V crater.
The European Student Moon Orbiter (ESMO) was a proposed European student mission to the Moon. Student teams from 19 universities throughout Europe worked on the program. ESMO was conceived by the Student Space Exploration & Technology Initiative (SSETI) under the support of the European Space Agency (ESA); prior to the start of Phase A the full responsibility for the management of the program was transferred to the ESA Education Office.

The Modular Common Spacecraft Bus (MCSB) is a fast-development, low-cost, general purpose spacecraft platform. Its modular design is intended to reduce the cost, complexity, and lead time on missions by providing a reliable, well-characterized system that can carry a variety of payloads. According to NASA, "the spacecraft is roughly one tenth the price of a conventional uncrewed mission and could be used to land on the Moon, orbit Earth, or rendezvous with near-Earth objects."
The European Data Relay System (EDRS) system is a European constellation of GEO satellites that relay information and data between satellites, spacecraft, UAVs, and ground stations. The first components were launched in 2016 and 2019.
Moon Express is an American privately held company formed in 2010 by a group of Silicon Valley and space entrepreneurs. It had the goal of winning the $30 million Google Lunar X Prize, and of ultimately mining the Moon for natural resources of economic value. The company was not able to make a launch attempt to reach the Moon by March 31, 2018, the deadline for the prize.

The Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD) is a NASA mission that will test laser communication in space for extremely long distances, between Earth and geosynchronous orbit.

Optical Payload for Lasercomm Science (OPALS) is a spacecraft communication instrument developed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory that was tested on the International Space Station (ISS) from 18 April 2014 to 17 July 2014 to demonstrate the technology for laser communications systems between spacecraft and ground stations.
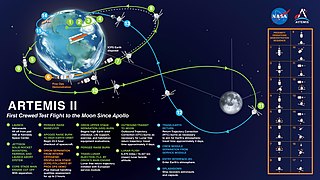
Artemis II is a scheduled mission of the NASA-led Artemis program. It will use the second launch of the Space Launch System (SLS) and include the first crewed mission of the Orion spacecraft. The mission is scheduled for no earlier than September 2025. Four astronauts will perform a flyby of the Moon and return to Earth, becoming the first crew to travel beyond low Earth orbit since Apollo 17 in 1972. Artemis II will be the first crewed launch from Launch Complex 39B of the Kennedy Space Center since STS-116 in 2006.

Phobos And Deimos & Mars Environment (PADME) is a low-cost NASA Mars orbiter mission concept that would address longstanding unknowns about Mars' two moons Phobos and Deimos and their environment.

Laser communication in space is the use of free-space optical communication in outer space. Communication may be fully in space or in a ground-to-satellite or satellite-to-ground application. The main advantage of using laser communications over radio waves is increased bandwidth, enabling the transfer of more data in less time.

Lunar Flashlight was a low-cost CubeSat lunar orbiter mission to explore, locate, and estimate size and composition of water ice deposits on the Moon for future exploitation by robots or humans.

Psyche is a NASA Discovery Program space mission launched on October 13, 2023 to explore the origin of planetary cores by orbiting and studying the metallic asteroid 16 Psyche beginning in 2029. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) manages the project.

Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) is a laser space communication system in operation that improved communications performance 10 to 100 times over radio frequency technology without incurring increases in mass, volume or power. DSOC is capable of providing high bandwidth downlinks from beyond cislunar space.
NASA's Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator (PTD) Project is a series of tech demonstrations of technologies aboard a series of nanosatellites known as CubeSats, providing significant enhancements to the performance of these versatile spacecraft. Each of the five planned PTD missions consist of a 6-unit (6U) CubeSat with expandable solar arrays.
















