Lever Brothers was a British manufacturing company founded in 1885 by two brothers: William Hesketh Lever, 1st Viscount Leverhulme (1851–1925), and James Darcy Lever (1854–1916). They invested in and successfully promoted a new soap-making process invented by chemist William Hough Watson. Lever Brothers entered the United States market in 1895 and acquired Mac Fisheries, owner of T. Wall & Sons, in 1925. Lever Brothers was one of several British companies that took an interest in the welfare of its British employees. Its brands included "Lifebuoy", "Lux" and "Vim". Lever Brothers merged with Margarine Unie to form Unilever in 1929.

The Kwilu River is a major river in the Kwilu Province formerly known as Bandundu province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) to the city of Bandundu, where it joins the Kwango River just before this stream enters the Kasai River. In the DRC the river flows past the towns of Gungu, Kikwit, Bulungu, Bagata, Rutherfordia and Bandundu. Lusanga, formerly Leverville, lies at the location where the Kwenge River joins the Kwilu, between Kikwit and Bulungu.

Basankusu is a town in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is the main town and administrative centre of the Basankusu Territory. In 2004, it had an estimated population of 23,764. It has a gravel airstrip, covered and open markets, a hospital, and three cellphone networks, the first of which was installed in 2006. The town is also known as a centre for bonobo conservation efforts. Despite such developments, most inhabitants live at a subsistence level: hunting, fishing, keeping chickens and keeping a vegetable plot. In 2010, the workers at the local palm plantation would earn an average monthly salary of $40, most others would have much less.
Pierre Mulele was a Congolese rebel active in the Simba rebellion of 1964. Mulele had also been minister of education in Patrice Lumumba's cabinet. With the assassination of Lumumba in January 1961 and the arrest of his recognised deputy Antoine Gizenga one year later, Mulele became one of the top Lumumbists determined to continue the struggle. He went to Cairo as the representative of the Lumumbists' Congo National Liberation Committee based in Brazzaville. From Cairo he proceeded to China in 1963 to receive military training, and also took a group of Congolese youths with him, who received training in guerrilla tactics. Mulele was lured out of exile after Mobutu promised him amnesty, but Mobutu had him tortured and executed after Mulele returned to the Congo. He was a member of the Bapende ethnic group.
Idiofa is a town in Kwilu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

The Pende people, also known as the Phende people, are an ethnic group in the south-western Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Pende are divided into two cultural groups: the Eastern Pende and the Western Pende who are distinct but consider themselves part of the same ethnic group. The number of people who consider themselves to be ethnically Pende is estimated at over 250,000.

The Congo–Arab War was fought in Central Africa between the forces of Belgian King Leopold II's Congo Free State and various Zanzibari Arab slave traders led by Sefu bin Hamid, Tippu Tip's son. It was a proxy war in eastern Congo from 1892 to 1894, with most of the fighting being done by native Congolese, who aligned themselves with either side and sometimes switched sides.
Feronia Inc. is a multinational corporation that produces palm oil and other agricultural products in the Democratic Republic of the Congo while headquartered in Canada. In operation since 1911 as a large-scale commercial farmland and plantation operator in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (“DRC”), the Company used modern agricultural practices to operate and develop its oil palm plantations and arable farming business division. The company filed for bankruptcy in 2020 and was delisted from the TSX Venture Exchange.

Alexandre Delcommune was a Belgian officer of the armed Force Publique of the Congo Free State who undertook extensive explorations of the country during the early colonial period of the Congo Free State. He explored many of the navigable waterways of the Congo Basin, and led a major expedition to Katanga between 1890 and 1893.
Louis-Napoléon Chaltin (1857–1933) was a Belgian career soldier and colonial official notable for his service in the Congo Free State during the late 19th century.

The Kwenge River is a stream in the Bandundu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Masi-Manimba is a town in Kwilu Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, the headquarters of the Masi-Manimba Territory. As of 2012 the population was estimated to be 31,802.
Dibaya-Lubwe is a town in the Kwilu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is in Idiofa Territory. The town lies on the south shore of the Kasai River just below the point where it is joined by the Lubue River. As of 2012 the population was estimated to be 38,933.
The Bunda people or in the Democratic Republic of the Congo are an ethnic group that mostly live in Idiofa Territory, Kwilu District of Bandundu Province. They speak the Mpuono language, spoken by an estimated 165,000 people as of 1972.
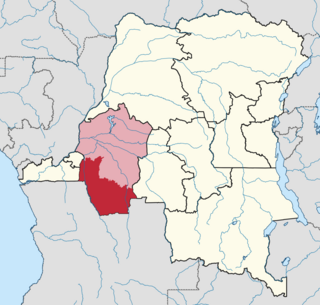
Kwango District was a district of the Congo Free State, Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It went through various changes in extent. It roughly corresponded to the present provinces of Kwilu and Kwango.

The Kwilu rebellion (1963–1965) was a civil uprising which took place in the West of what is the modern-day Democratic Republic of the Congo. The rebellion took place in the wider context of the Cold War and the Congo Crisis. Led by Pierre Mulele, a follower of ousted Prime Minister Patrice Lumumba, a faction of rebel Maoists staged a revolt against the government in the Kwilu District. Based around the struggle for independence, the rebellion was encouraged by economic, social, and cultural grievances. Supported by communist China, rebels used mainly guerrilla warfare against government forces. The rebellion was concurrent with the Simba rebellion occurring in other areas of the Congo during this time. While the rebellion was suppressed in the early months of 1965, it had lasting political impacts, leading to the dissolution of Kwilu as an official province.
Huileries du Congo Belge (HCB) was a subsidiary of the soap manufacturing company Lever Brothers, created by William Hesketh Lever, which ran plantations in the Congo for the production of palm oil, using forced labour. It was established in 1911, when the soap manufacturer received a concession from the Belgian government for 750,000 hectares of forest in the Belgian Congo, mostly south of Bandundu. By 1923, a Lever soap factory was built there, and by 1924 SAVCO was established. It was the nucleus of the United Africa Company, a principal supplier to the United Kingdom of several key commodities. From 1951 it was producing Lux soap.
Isidore Ndaywel è Nziem, is a Congolese historian and linguist. He is the author of several essays, studies and other publications about the history of the Congo, including the overview work L'histoire générale du Congo: De l'héritage ancien à la République démocratique.
In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, it is common for individuals to possess three separate names: a first name (prénom) and surname (nom) as well as a post-surname (postnom). Each form may comprise one or more elements. For example:
The Bayanzi are an ethnic group in the Democratic Republic of the Congo who live in the southwest of the country and number about one million. They speak a Bantu language. The largest political unit is the chieftainship, of which there are about 120. The Bayanzi are matrilineal, so a child belongs to the clan of the mother. The Belgian colonists first encountered them at Bolobo on the Congo River, as traders up and down the river. They employed them from 1883. Later the Bayanzi were forced to labor on the palm oil plantations.