
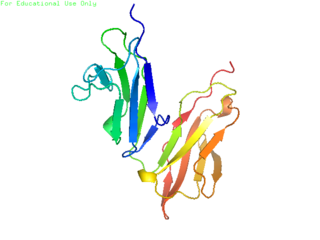
An antibody (Ab) is the secreted form of a B cell receptor; the term immunoglobulin can refer to either the membrane-bound form or the secreted form of the B cell receptor, but they are, broadly speaking, the same protein, and so the terms are often treated as synonymous. Antibodies are large, Y-shaped proteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which are used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Antibodies can recognize virtually any size antigen with diverse chemical compositions from molecules. Each antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens. This term literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.
CD32, also known as FcγRII or FCGR2, is a surface receptor glycoprotein belonging to the Ig gene superfamily. CD32 can be found on the surface of a variety of immune cells. CD32 has a low-affinity for the Fc region of IgG antibodies in monomeric form, but high affinity for IgG immune complexes. CD32 has two major functions: cellular response regulation, and the uptake of immune complexes. Cellular responses regulated by CD32 include phagocytosis, cytokine stimulation, and endocytic transport. Dysregulated CD32 is associated with different forms of autoimmunity, including systemic lupus erythematosus. In humans, there are three major CD32 subtypes: CD32A, CD32B, and CD32C. While CD32A and CD32C are involved in activating cellular responses, CD32B is inhibitory.

Methicillin (USAN), also known as meticillin (INN), is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.

The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the complement system, which is part of the immune system. The classical complement pathway is initiated by antigen-antibody complexes with the antibody isotypes IgG and IgM.
Opsonins are extracellular proteins that, when bound to substances or cells, induce phagocytes to phagocytose the substances or cells with the opsonins bound. Thus, opsonins act as tags to label things in the body that should be phagocytosed by phagocytes. Different types of things ("targets") can be tagged by opsonins for phagocytosis, including: pathogens, cancer cells, aged cells, dead or dying cells, excess synapses, or protein aggregates. Opsonins help clear pathogens, as well as dead, dying and diseased cells.

Antibody opsonization is a process by which a pathogen is marked for phagocytosis.

In immunology, an Fc receptor is a protein found on the surface of certain cells – including, among others, B lymphocytes, follicular dendritic cells, natural killer cells, macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, human platelets, and mast cells – that contribute to the protective functions of the immune system. Its name is derived from its binding specificity for a part of an antibody known as the Fc region. Fc receptors bind to antibodies that are attached to infected cells or invading pathogens. Their activity stimulates phagocytic or cytotoxic cells to destroy microbes, or infected cells by antibody-mediated phagocytosis or antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Some viruses such as flaviviruses use Fc receptors to help them infect cells, by a mechanism known as antibody-dependent enhancement of infection.

Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), also referred to as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, is a mechanism of cell-mediated immune defense whereby an effector cell of the immune system kills a target cell, whose membrane-surface antigens have been bound by specific antibodies. It is one of the mechanisms through which antibodies, as part of the humoral immune response, can act to limit and contain infection.

Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation, the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.
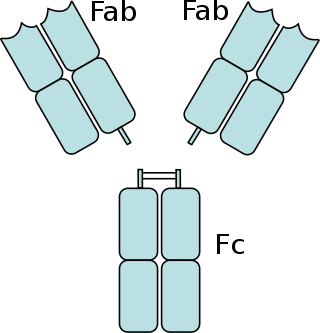
The fragment crystallizable region is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called Fc receptors and some proteins of the complement system. This region allows antibodies to activate the immune system, for example, through binding to Fc receptors. In IgG, IgA and IgD antibody isotypes, the Fc region is composed of two identical protein fragments, derived from the second and third constant domains of the antibody's two heavy chains; IgM and IgE Fc regions contain three heavy chain constant domains in each polypeptide chain. The Fc regions of IgGs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Glycosylation of the Fc fragment is essential for Fc receptor-mediated activity. The N-glycans attached to this site are predominantly core-fucosylated diantennary structures of the complex type. In addition, small amounts of these N-glycans also bear bisecting GlcNAc and α-2,6 linked sialic acid residues.
MSCRAMM adhesin proteins mediate the initial attachment of bacteria to host tissue, providing a critical step to establish infection.

Lysins, also known as endolysins or murein hydrolases, are hydrolytic enzymes produced by bacteriophages in order to cleave the host's cell wall during the final stage of the lytic cycle. Lysins are highly evolved enzymes that are able to target one of the five bonds in peptidoglycan (murein), the main component of bacterial cell walls, which allows the release of progeny virions from the lysed cell. Cell-wall-containing Archaea are also lysed by specialized pseudomurein-cleaving lysins, while most archaeal viruses employ alternative mechanisms. Similarly, not all bacteriophages synthesize lysins: some small single-stranded DNA and RNA phages produce membrane proteins that activate the host's autolytic mechanisms such as autolysins.
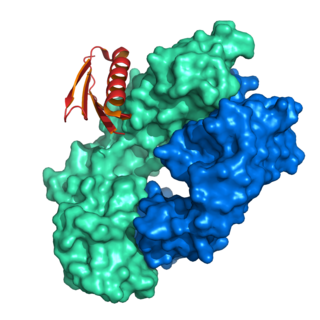
Protein L was first isolated from the surface of bacterial species Peptostreptococcus magnus and was found to bind immunoglobulins through L chain interaction, from which the name was suggested. It consists of 719 amino acid residues. The molecular weight of protein L purified from the cell walls of Peptostreptoccus magnus was first estimated as 95kD by SDS-PAGE in the presence of reducing agent 2-mercaptoethanol, while the molecular weight was determined to 76kD by gel chromatography in the presence of 6 M guanidine HCl. Protein L does not contain any interchain disulfide loops, nor does it consist of disulfide-linked subunits. It is an acidic molecule with a pI of 4.0. Unlike protein A and protein G, which bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulins (antibodies), protein L binds antibodies through light chain interactions. Since no part of the heavy chain is involved in the binding interaction, Protein L binds a wider range of antibody classes than protein A or G. Protein L binds to representatives of all antibody classes, including IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD. Single chain variable fragments (scFv) and Fab fragments also bind to protein L.
Fibronectin binding protein A (FnBPA) is a Staphylococcus aureus MSCRAMM cell surface-bound protein that binds to both fibronectin and fibrinogen.
mecA is a gene found in bacterial cells which allows them to be resistant to antibiotics such as methicillin, penicillin and other penicillin-like antibiotics.

In molecular biology, the protein domain SdrG C terminal refers to the C terminus domain of an adhesin found only on the cell walls of bacteria. More specifically, SdrG is only found in gram-positive bacteria. This particular domain binds to a glycoprotein named fibrinogen. SdrG stands for serine-aspartate dipeptide repeats, which as its name suggests, contains repeats of two amino acids, serine and aspartate.
The lung microbiota is the pulmonary microbial community consisting of a complex variety of microorganisms found in the lower respiratory tract particularly on the mucous layer and the epithelial surfaces. These microorganisms include bacteria, fungi, viruses and bacteriophages. The bacterial part of the microbiota has been more closely studied. It consists of a core of nine genera: Prevotella, Sphingomonas, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Fusobacterium, Megasphaera, Veillonella, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus. They are aerobes as well as anaerobes and aerotolerant bacteria. The microbial communities are highly variable in particular individuals and compose of about 140 distinct families. The bronchial tree for instance contains a mean of 2000 bacterial genomes per cm2 surface. The harmful or potentially harmful bacteria are also detected routinely in respiratory specimens. The most significant are Moraxella catarrhalis, Haemophilus influenzae, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. They are known to cause respiratory disorders under particular conditions namely if the human immune system is impaired. The mechanism by which they persist in the lower airways in healthy individuals is unknown.
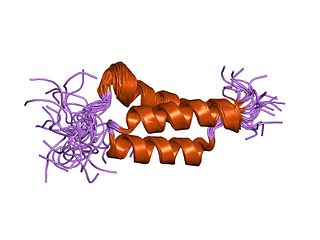
In molecular biology, the domain B, refers to the immunoglobulin-binding domain found in the Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor protein A (SpA). Hence, it is abbreviated to SpAB.

Epimerox is an experimental broad-spectrum antibiotic compound being developed by scientists at the Rockefeller University and Astex Pharmaceuticals. It is a small molecule inhibitor compound that blocks the activity of the enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase, an epimerase enzyme that is called 2-epimerase for short.
Vincent A. Fischetti is a world renowned American microbiologist and immunologist. He is Professor of and Head of the Laboratory of Bacterial Pathogenesis and Immunology at Rockefeller University in New York City. His Laboratory is the oldest continuous laboratory at Rockefeller that started in 1926 and headed by 4 leading scientists over its near 100-year history: Homer Swift, Maclyn McCarty, Emil Gotschlich and now Vincent Fischetti. Keeping with the historical theme of infectious diseases, Fischetti's primary areas of research are bacterial pathogenesis, bacterial genomics, immunology, virology, microbiology, and therapeutics. He was the first scientist to clone and sequence a surface protein on gram-positive bacteria, the M protein from S. pyogenes, and determine its unique coiled-coil structure. He also was the first use phage lysins as a therapeutic and an effective alternative to conventional antibiotics.














