Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information and technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications and computers, as well as necessary enterprise software, middleware, storage, and audiovisual systems, that enable users to access, store, transmit, and manipulate information.

Jisc is a United Kingdom not-for-profit company whose role is to support post-16 and higher education, and research, by providing relevant and useful advice, digital resources and network and technology services, while researching and developing new technologies and ways of working. It is funded by a combination of the UK further and higher education funding bodies, and individual higher education institutions.

The Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation ACP-EU (CTA) was established in 1983 under the Lomé Convention between the African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States and EU member states. Since 2000 CTA has operated within the framework of the ACP-EU Cotonou Agreement with a mission to “strengthen policy and institutional capacity development and information and communication management capacities of ACP agricultural and rural development organisations. It assists such organisations in formulating and implementing policies and programmes to reduce poverty, promote sustainable food security, preserve the natural resource base and thus contribute to building self-reliance in ACP rural and agricultural development.”
The Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH or GIZ in short is a German development agency headquartered in Bonn and Eschborn that provides services in the field of international development cooperation. GIZ mainly implements technical cooperation projects of the Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), its main commissioning party, although it also works with the private sector and other national and supranational government organizations on a public benefit basis. In its activities GIZ seeks to follow the paradigm of sustainable development, which aims at economic development through social inclusion and environmental protection. GIZ offers consulting and capacity building services in a wide range of areas, including management consulting, rural development, sustainable infrastructure, security and peace-building, social development, governance and democracy, environment and climate change, and economic development and employment.
Arid Lands Information Network (ALIN) is a Kenya-based non-governmental organisation that seeks to exchange ideas and experiences among "grassroots change agents". It sees its goal as enabling such grassroot change agents to learn from one another, through capacity-building and what it terms the "innovative use of information and communication technologies (ICTs)."
Information and communication technology in agriculture, also known as e-agriculture, focuses on the enhancement of agricultural and rural development through improved information and communication processes. More specifically, e-agriculture involves the conceptualization, design, development, evaluation and application of innovative ways to use information and communication technologies (ICTs) in the rural domain, with a primary focus on agriculture. ICT includes devices, networks, mobiles, services and applications; these range from innovative Internet-era technologies and sensors to other pre-existing aids such as fixed telephones, televisions, radios and satellites. Provisions of standards, norms, methodologies, and tools as well as development of individual and institutional capacities, and policy support are all key components of e-agriculture.
The Bremen Overseas Research and Development Association (BORDA) is a non-profit international development organization headquartered in Bremen, Germany, and regional offices in Afghanistan, India, Indonesia, Mexico, and Tanzania as well as several project offices within each region. BORDA began its work in 1977, starting with its first project, “Technology Transfer of Biogas India-Ethiopia.” Since then it has been active in the delivery of basic needs services across the developing world.

Mediterranean University is a university located in Podgorica, Montenegro. It was founded on 30 May 2006, is the first private university established in Montenegro and is organized in 6 faculties. The university is member of the Balkan Universities Network.
e-Report - transnational virtual study circles: e-learning supports for tutorship and learning groups - is a communitarian project aiming at the constitution of a repertory of reference material with regard to the development of innovative methods in the field of e-learning system for educational projects and also for distance learning in VET. The activities of research, experimentation and analysis are combined with the use of ICT with massive use of tutoring activities, learning groups and transnational virtual study circles.

KERIS is a governmental organization under the South Korean Ministry of Education, Science and Technology that develops, proposes, and advises on current and future government policies and initiatives regarding education in South Korea.
The European Distance and E-Learning Network, abbreviated EDEN and originally named the European Distance Education Network - established in 1991, is an international educational association open to institutions and individuals dealing with e-learning, open education, and distance education. EDEN is a not-for-profit organisation, registered as a limited company under English law.
The Information Management Resource Kit (IMARK) is a partnership-based e-learning initiative developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations and partner organizations to support individuals, institutions and networks worldwide in the effective management of information and agricultural development. IMARK consists of a suite of distance learning resources and tools on information management.
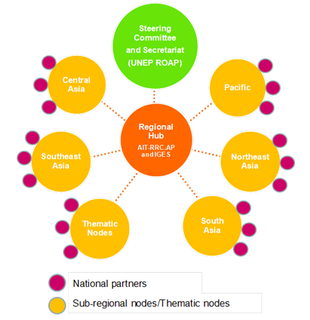
Asia Pacific Adaptation Network (APAN) was established in October 2009 as part of the Global Climate Adaptation Network (GAN). It is the first network under the GAN supported by the UNEP, IGES, AIT-UNEP RRCAP, ADB, SIDA, and APN.

The Central Institute of Educational Technology is an autonomous organization, formed as a nodal agency under the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) for promoting the use of mass media technology for expanding and improving the quality of education at the school level. The Institute is funded by the Ministry of Human Resources Development, Government of India. The building is dedicated to Children's of India and was built by Raj Rewal Associates in 1986

The Pythian Group, Inc., commonly known as Pythian, is a Canadian multinational corporation that provides data and cloud-related services. The company provides services for Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, Hadoop, Cassandra and other databases and their supporting infrastructure. It also provides transformation services that include cloud migration services, cloud managed services and analytics data platform design and management products and services. Pythian has partnerships with major public cloud vendors including Amazon, Google and Microsoft.
ITIL, formerly an acronym for Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a set of detailed practices for IT service management (ITSM) that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business.
Test of Practical Competency in ICT (TOPCIT) is a performance-evaluation-centered test designed to diagnose and assess the competency of Information Technology specialists and Software Developers that is critically needed to perform jobs on the professional frontier.
Information Communications Technology is usually included in the Home Economics and Livelihood Education program in grade school and taught through the Technology and Home Economics program in high school.The recent status of ICT education in the Philippines, along with other Southeast Asian countries, was surveyed by the Southeast Asian Ministers of Education Organization (SEAMEO) in 2011. Using the UNESCO model of ICT Development in Education, the countries were ranked as Emerging, Applying, Infusing or Transforming. The Philippines were ranked at the Infusing stage of integrating ICT in education, indicating that the country has integrated ICT into existing teaching, learning and administrative practices and policies. This includes components such as a national vision of ICT in education, national ICT plans and policies, complementary national ICT and education policies, professional development for teachers and school leaders, community or partnership and teaching and learning pedagogies. A 2012 study reported that public high schools in Metro Manila had a computer to student ratio of 1:63. While 88 percent of schools have internet connections, half of the students claimed not to be using it.
TVET in Sri Lanka refers to the development and implementation of Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) in the Sri Lankan education system and labor market. In Sri Lanka, the formal TVET sector comprises about 635 public sector training centres and 718 private and NGO training centres. A large number of non-formal TVET providers also provide training in IT on a fee-for-service basis, and there is a widespread network of non-fee-levying institutions that are funded by various national and international charities. These providers educate people of all ages — from secondary school leavers to working adults, parents and others who have suspended their education for various reasons and need training or retraining.






