Other types of MEMS Actuators
- Electrostatic — parallel plate or comb drive
- Magnetic
- Piezoelectric
- Thermostatic — linear motion, paraffin wax drive

A MEMS thermal actuator is a microelectromechanical device that typically generates motion by thermal expansion amplification. A small amount of thermal expansion of one part of the device translates to a large amount of deflection of the overall device. Usually fabricated out of doped single crystal silicon or polysilicon as a complex compliant member, the increase in temperature can be achieved internally by electrical resistive heating or by a heat source capable of locally introducing heat. Microfabricated thermal actuators can be integrated into micromotors. [1] [2]


MEMS is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size, and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre, although components arranged in arrays can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data and several components that interact with the surroundings.
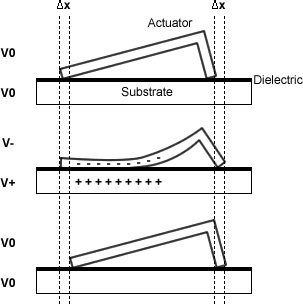
A scratch drive actuator (SDA) is a microelectromechanical system device that converts electrical energy into one-dimensional motion.
Energy harvesting (EH) – also known as power harvesting,energy scavenging, or ambient power – is the process by which energy is derived from external sources, then stored for use by small, wireless autonomous devices, like those used in wearable electronics, condition monitoring, and wireless sensor networks.
The piezoresistive effect is a change in the electrical resistivity of a semiconductor or metal when mechanical strain is applied. In contrast to the piezoelectric effect, the piezoresistive effect causes a change only in electrical resistance, not in electric potential.
A vibration powered generator is a type of electric generator that converts the kinetic energy from vibration into electrical energy. The vibration may be from sound pressure waves or other ambient vibrations.

Micropumps are devices that can control and manipulate small fluid volumes. Although any kind of small pump is often referred to as a micropump, a more accurate definition restricts this term to pumps with functional dimensions in the micrometer range. Such pumps are of special interest in microfluidic research, and have become available for industrial product integration in recent years. Their miniaturized overall size, potential cost and improved dosing accuracy compared to existing miniature pumps fuel the growing interest for this innovative kind of pump.

Scanning thermal microscopy (SThM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy that maps the local temperature and thermal conductivity of an interface. The probe in a scanning thermal microscope is sensitive to local temperatures – providing a nano-scale thermometer. Thermal measurements at the nanometer scale are of both scientific and industrial interest. The technique was invented by Clayton C. Williams and H. Kumar Wickramasinghe in 1986.
Micro-combustion is the sequence of exothermic chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and conversion of chemical species at micro level. The release of heat can result in the production of light in the form of either glowing or a flame. Fuels of interest often include organic compounds in the gas, liquid or solid phase. The major problem of micro-combustion is the high surface to volume ratio. As the surface to volume ratio increases heat loss to walls of combustor increases which leads to flame quenching.
A MEMSmagnetic field sensor is a small-scale microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) device for detecting and measuring magnetic fields (Magnetometer). Many of these operate by detecting effects of the Lorentz force: a change in voltage or resonant frequency may be measured electronically, or a mechanical displacement may be measured optically. Compensation for temperature effects is necessary. Its use as a miniaturized compass may be one such simple example application.
A MEMS magnetic actuator is a device that uses the microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) to convert an electric current into a mechanical output by employing the well-known Lorentz Force Equation or the theory of Magnetism.
MEMS for in situ mechanical characterization refers to microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) used to measure the mechanical properties of nanoscale specimens such as nanowires, nanorods, whiskers, nanotubes and thin films. They distinguish themselves from other methods of nanomechanical testing because the sensing and actuation mechanisms are embedded and/or co-fabricated in the microsystem, providing—in the majority of cases—greater sensitivity and precision.
Microelectromechanical system oscillators are devices that generate highly stable reference frequencies used to sequence electronic systems, manage data transfer, define radio frequencies, and measure elapsed time. The core technologies used in MEMS oscillators have been in development since the mid-1960s, but have only been sufficiently advanced for commercial applications since 2006. MEMS oscillators incorporate MEMS resonators, which are microelectromechanical structures that define stable frequencies. MEMS clock generators are MEMS timing devices with multiple outputs for systems that need more than a single reference frequency. MEMS oscillators are a valid alternative to older, more established quartz crystal oscillators, offering better resilience against vibration and mechanical shock, and reliability with respect to temperature variation.

A microscanner, or micro scanning mirror, is a microoptoelectromechanical system (MOEMS) in the category of micromirror actuators for dynamic light modulation. Depending upon the type of microscanner, the modulatory movement of a single mirror can be either translatory or rotational, on one or two axes. In the first case, a phase shifting effect takes place. In the second case, the incident light wave is deflected.
A reconfigurable antenna is an antenna capable of modifying its frequency and radiation properties dynamically, in a controlled and reversible manner. In order to provide a dynamic response, reconfigurable antennas integrate an inner mechanism that enable the intentional redistribution of the RF currents over the antenna surface and produce reversible modifications of its properties. Reconfigurable antennas differ from smart antennas because the reconfiguration mechanism lies inside the antenna, rather than in an external beamforming network. The reconfiguration capability of reconfigurable antennas is used to maximize the antenna performance in a changing scenario or to satisfy changing operating requirements.
A nanoelectromechanical (NEM) relay is an electrically actuatedswitch that is built on the nanometer scale using semiconductor fabrication techniques. They are designed to operate in replacement of, or in conjunction with, traditional semiconductor logic. While the mechanical nature of NEM relays makes them switch much slower than solid-state relays, they have many advantageous properties, such as zero current leakage and low power consumption, which make them potentially useful in next generation computing.

Roger Thomas Howe is the William E. Ayer Professor of Electrical Engineering at Stanford University. He earned a B.S. degree in physics from Harvey Mudd College and M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in electrical engineering from the University of California, Berkeley in 1981 and 1984, respectively. He was a faculty member at Carnegie-Mellon University from 1984-1985, at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology from 1985-1987, and at UC Berkeley between 1987-2005, where he was the Robert S. Pepper Distinguished Professor. He has been a faculty member of the School of Engineering at Stanford since 2005.
A microvalve is a microscale valve, i.e. a microfluidic two-port component that regulates the flow between two fluidic ports. Microvalves are basic components in microfluidic devices, such as labs-on-a-chip, where they are used to control the fluidic transport. During the period from 1995 to 2005, many microelectromechanical systems-based microvalves were developed.
A piezoelectric microelectromechanical system (piezoMEMS) is a miniature or microscopic device that uses piezoelectricity to generate motion and carry out its tasks. It is a microelectromechanical system that takes advantage of an electrical potential that appears under mechanical stress. PiezoMEMS can be found in a variety of applications, such as switches, inkjet printer heads, sensors, micropumps, and energy harvesters.
Vapor etching refers to a process used in the fabrication of Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and Nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS). Sacrificial layers are isotropically etched using gaseous acids such as Hydrogen fluoride and Xenon difluoride to release the free standing components of the device.

Niels Quack is a Swiss and German engineer specialized in optical micro engineering. He is a SNSF professor at EPFL and director of the Photonic Micro- and Nanosystems Laboratory at its school of engineering.