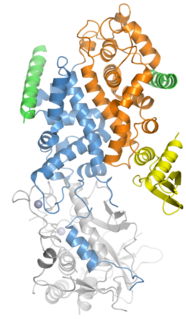
Drosha is a Class 2 ribonuclease III enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DROSHA gene. It is the primary nuclease that executes the initiation step of miRNA processing in the nucleus. It works closely with DGCR8 and in correlation with Dicer. It has been found significant in clinical knowledge for cancer prognosis and HIV-1 replication.
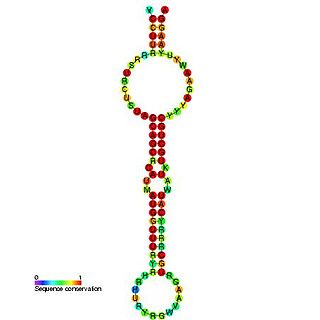
The miR-15 microRNA precursor family is made up of small non-coding RNA genes that regulate gene expression. The family includes the related mir-15a and mir-15b sequences, as well as miR-16-1, miR-16-2, miR-195 and miR-497. These six highly conserved miRNAs are clustered on three separate chromosomes. In humans miR-15a and miR-16 are clustered within 0.5 kilobases at chromosome position 13q14. This region has been found to be the most commonly affected in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), with deletions of the entire region in more than half of cases. Both miR-15a and miR-16 are thus frequently deleted or down-regulated in CLL samples with 13q14 deletions; occurring in more than two thirds of CLL cases. The expression of miR-15a is associated with survival in triple negative breast cancer.

There are 89 known sequences today in the microRNA 19 (miR-19) family but it will change quickly. They are found in a large number of vertebrate species. The miR-19 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule that regulates gene expression. Within the human and mouse genome there are three copies of this microRNA that are processed from multiple predicted precursor hairpins:

The miR-1 microRNA precursor is a small micro RNA that regulates its target protein's expression in the cell. microRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give products at ~22 nucleotides. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 3' arm of the precursor. The mature products are thought to have regulatory roles through complementarity to mRNA. In humans there are two distinct microRNAs that share an identical mature sequence, these are called miR-1-1 and miR-1-2.

In molecular biology mir-126 is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several pre- and post-transcription mechanisms.

In molecular biology, miR-184 microRNA is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) function as posttranscriptional regulators of expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. Several targets for miR-184 have been described, including that of mediators of neurological development, apoptosis and it has been suggested that miR-184 plays an essential role in development.

In molecular biology, mir-221 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

In molecular biology mir-210 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-25 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. mir-25 levels increase in human heart failure, and treatment with an anti-sense RNA molecule (antagomiR) was recently reported to halt disease progression and improves cardiac function in a mouse heart failure model.
In molecular biology mir-153 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
Expandable. We make separate entries for proteins, etc. Why not these?

MicroRNA 7-1 is a microRNA molecule that in humans is encoded by the MIR7-1 gene.

MicroRNA 489 is a miRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR489 gene.

MicroRNA 148a is a miRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR148A gene.

MicroRNA 495 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MIR495 gene.

MicroRNA 141 is a non-coding RNA molecule that in humans is encoded by the MIR141 gene.

MicroRNA 200c is a microRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR200C gene.

MicroRNA 195 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MIR195 gene.

MicroRNA 885 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MIR885 gene.















