Related Research Articles
Project Tiger is a wildlife conservation movement initiated in India to protect the endangered tiger. The project was initiated in 1973 by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of the Government of India. As of March 2024, there are 55 protected areas that have been designated as tiger reserves under the project. As of 2023, there were 3,682 wild tigers in India, which is almost 75% of the world's wild tiger population.

The Bengal tiger or Royal Bengal tiger is a population of the Panthera tigris tigris subspecies and the nominate tiger subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is estimated to have been present in the Indian subcontinent since the Late Pleistocene for about 12,000 to 16,500 years. Its historical range covered the Indus River valley until the early 19th century, almost all of India, western Pakistan, southern Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and southwestern China. Today, it inhabits India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and southwestern China. It is threatened by poaching, habitat loss and habitat fragmentation.

Vansda National Park, also known as Bansda National Park, is a protected area which represents the thick woodlands of the Dangs and southern Gujarat, and is situated in the Vansda tehsil, Navsari District of Gujarat state, India. Riding on the banks of Ambika River and measuring roughly 24 km2 in area, the park lies about 65 km east of the town of Chikhali on the National Highway 48, and about 80 km northeast of the city of Valsad. Vansda, the town from which the name of the park is derived, is an important trading place for the surrounding area where the majority of the population is represented by adivasis. Vansda-Waghai state highway runs through the park, so does the narrow gauge rail link connecting Waghai to Billimora.
Kuno National Park is a national park and Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh, India. It derives its name from Kuno River. It was established in 1981 as a wildlife sanctuary with an initial area of 344.686 km2 (133.084 sq mi) in the Sheopur and Morena districts. In 2018, it was given the status of a national park. It is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion.

The Asiatic Lion Reintroduction Project is an initiative of the Indian Government to provide safeguards to the Asiatic lion from extinction in the wild by means of reintroduction. The last wild population of the Asiatic lion is found in the region of Gir Forest National Park, in the state of Gujarat. The single population faces the threats of epidemics, natural disasters and other anthropogenic factors. The project aims to establish a second independent population of Asiatic lions at the Kuno National Park in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. However, the proposed translocation has been bitterly contested by the state government.

Mysore Doreswamy Madhusudan is an Indian wildlife biologist and ecologist. He is the Co-founder and Director of Nature Conservation Foundation, Mysore and a Visiting Research Fellow at the University of Leeds. He has worked on understanding and mitigating the effects of human-wildlife conflict in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve in South India. He has also worked in several other forests in the Himalayas and North-east India. In 2004, he was one among the team of wildlife biologists who described Arunachal macaque, a new species of macaque from Arunachal Pradesh, India.

The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is a wildlife conservation agency formed to protect the endangered Bengal tiger in India. It was established by the Government of India in 2005 for the management of Project Tiger and the various tiger reserves in India. As of 2023, there were 3,682 wild tigers in India, which is almost 75% of the world's wild tiger population.
The tiger reserves in India were set up as a part of Project Tiger initiated in 1973 and are administered by the National Tiger Conservation Authority of Government of India. As of November 2024, there are 56 protected areas that have been designated as tiger reserves. As of 2023, there were 3,682 wild tigers in India, which is almost 75% of the world's wild tiger population.
Pakke Tiger Reserve, is a Project Tiger reserve in the East Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh in Northeast India. The 862 km2 (333 sq mi) reserve is protected by the Department of Environment and Forest of Arunachal Pradesh. It was known as Pakhui Tiger Reserve, but renamed in April 2001 by the Governor of Arunachal Pradesh. It has won India Biodiversity Award 2016 in the category of 'Conservation of threatened species' for its Hornbill Nest Adoption Programme.

More than 70 years after India's native subspecies of the cheetah—the Asiatic cheetah became extinct there, small numbers of Southeast African cheetah, an exotic sub-species to India, have been flown in from Namibia and South Africa to a national park in India. In the 21st century, the asiatic species is found only in Iran in critically endangered numbers. The Asiatic cheetah was earlier spread across Western Asia and most of India. The species had a gradual history of habitat loss in India. In Northern India, human activities led to the clearing of forests where they co-existed with their prey blackbuck, and the extirpation of both the species. Later, more habitat loss, prey depletion, and trophy hunting led to the extinction of the Asiatic cheetah from other regions of India.
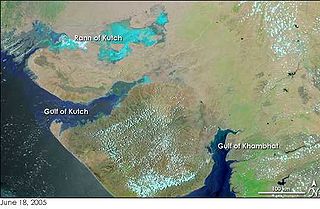
The Gulf of Khambhat, also known as the Gulf of Cambay, is a bay on the Arabian Sea coast of India, bordering the state of Gujarat just north of Mumbai and Diu Island. The Gulf of Khambhat is about 200 km (120 mi) long, about 20 km (12 mi) wide in the north and up to 70 km (43 mi) wide in the south. Major rivers draining Gujarat are the Narmada, Tapti, Mahi and the Sabarmati, that form estuaries in the gulf.

Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary, covering about 1,197 km2 (462 sq mi), is the largest wildlife sanctuary of Madhya Pradesh state in India. This wildlife sanctuary is a part of 5500 km2 of forested landscape. It is located in the centre of the state covering parts of Sagar, Damoh, Narsinghpur, and Raisen Districts. It is about 90 km from Jabalpur and about 56 km from Saugor.
Shahgarh Landscape or Shahgarh Bulge Landscape is located in Jaiselmer District in Indian state of Rajasthan. This area is protected area for reintroduction of cheetah. The nearest city to this area is Jaiselmer. This area fences along the Indo - Pak border. This area is about 4000 km2 and has about 80 human settlements each having about 5 - 10 houses. Chinkara will be the primary prey for cheetah as the prey diversity is less in this region. Cheetah have been declared extinct in India in 1952.
Hemendra Singh Panwar is an Indian conservationist and civil servant, known for his efforts in the fields of wildlife and conservation. He was the first director of the Wildlife Institute of India and was the director of Project Tiger. The Government of India honoured him, in 2013, with Padma Bhushan, the third-highest civilian award, for his services to the environment and conservation.

Purna Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary in the Western Ghats mountain range, in the States of Gujarat and Maharashtra, India. In the South Gujarat, it is located between Vyara, Tapi District and Ahwa, Dang District, and in Maharashtra, it is located in Nandurbar District. Apart from the Dangs' District, it is a part of the Northern Division of the Dangs' Forest.

Tigerland India Film Festival (TIFF) is an environmental and wildlife film festival based in India.
Sanctuary Nature Foundation is an Indian nonprofit foundation that was founded in 2015 building on the work of Sanctuary Asia, a wildlife magazine that was launched in 1981 by Bittu Sahgal. Its network of conservationists, naturalists, scientists, writers and photographers run various projects in environmental policy, advocacy, science, on-ground support, wildlife habitat management and more. The foundation also holds annual awards to honour grassroots conservationists and wildlife photographers.

Yadvendradev Vikramsinh Jhala is an Indian scientist and conservationist who recently ended his tenure as the Dean at the Wildlife Institute of India in Dehradun.
References
- 1 2 "Tiger's brush with death at Chorbahuli on NH-7". Times of India. 28 December 2015. Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- ↑ "The Indian Prince Who Gave It All Up for The Jungle | Condé Nast Traveller". Condé Nast Traveller India. 18 August 2017. Retrieved 3 May 2023.
- ↑ "Cheetahs going back to India? – The next step". Wildlife Extra. 9 September 2009. Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- 1 2 "Meet Dr. M.K. Ranjitsinh – Erstwhile Royal, Conservationist, Wildlife Expert And Former Bureaucrat". 6 December 2014. Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- 1 2 "Share lions, forget cheetahs: layers of hurt Gujarati pride". First Post. 21 April 2013. Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- ↑ Window to my world