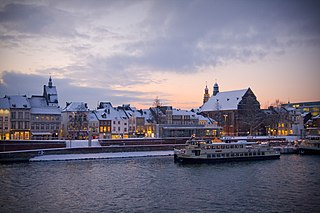
Maastricht is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the Meuse, at the point where the Jeker joins it. Mount Saint Peter (Sint-Pietersberg) is largely situated within the city's municipal borders. Maastricht is adjacent to the border with Belgium and is part of the Meuse-Rhine Euroregion, an international metropolis with a population of about 3.9 million, which includes the nearby German and Belgian cities of Aachen, Liège, and Hasselt.

Mosasaurs comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the Meuse in 1764. They belong to the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes.

Richard Harlan was an American paleontologist, anatomist, and physician. He was the first American to devote significant time and attention to vertebrate paleontology and was one of the most important contributors to the field in the early nineteenth century. His work was noted for its focus on objective descriptions, taxonomy and nomenclature. He was the first American to apply Linnaean names to fossils.

Mosasaurus is the type genus of the mosasaurs, an extinct group of aquatic squamate reptiles. It lived from about 82 to 66 million years ago during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. The genus was one of the first Mesozoic marine reptiles known to science—the first fossils of Mosasaurus were found as skulls in a chalk quarry near the Dutch city of Maastricht in the late 18th century, and were initially thought to be the bones of crocodiles or whales. One skull discovered around 1780, which was seized by France during the French Revolutionary Wars for its scientific value, was famously nicknamed the "great animal of Maastricht". In 1808, naturalist Georges Cuvier concluded that it belonged to a giant marine lizard with similarities to monitor lizards but otherwise unlike any known living animal. This concept was revolutionary at the time and helped support the then-developing ideas of extinction. Cuvier did not designate a scientific name for the new animal, and this was done by William Daniel Conybeare in 1822 when he named it Mosasaurus in reference to its origin in fossil deposits near the Meuse River. The exact affinities of Mosasaurus as a squamate remain controversial, and scientists continue to debate whether its closest living relatives are monitor lizards or snakes.

Naturalis Biodiversity Center is a national museum of natural history and a research center on biodiversity in Leiden, Netherlands. It was named the European Museum of the Year 2021. Although its current name and organization are relatively recent, the history of Naturalis can be traced back to the early 1800s. Its collection includes approximately 42 million specimens, making it one of the largest natural history collections in the world.

Prognathodon is an extinct genus of marine lizard belonging to the mosasaur family. It is classified as part of the Mosasaurinae subfamily, alongside genera like Mosasaurus and Clidastes. Prognathodon has been recovered from deposits ranging in age from the Campanian to the Maastrichtian in the Middle East, Europe, New Zealand, and North America.

The Natuurhistorisch Museum Rotterdam is a natural history museum located in Rotterdam, Netherlands.

Krijn is the common name of a Neanderthal fossil discovered off the Dutch coast. The discovery is most notable for being the first evidence of a Neanderthal presence in the Netherlands. The fossil is estimated at 100,000-40,000 BP. The skull fragment was recovered from the North Sea in 2001 off the coast of Zeeuws Vlaanderen. It was first publicly described in 2009.

Mount Saint Peter, also referred to as Caestert Plateau, is the northern part of a plateau running north to south between the valleys of the river Geer to the west, and the Meuse to the east. The plateau runs from Maastricht in the Netherlands, through Riemst in Belgian Limburg almost to the city of Liège in Belgium, thus defining the topography of this border area between Flanders, Wallonia and the Netherlands. The name of the hill, as well as the nearby village and church of Sint Pieter and the fortress of Sint Pieter, refers to Saint Peter, one of the Twelve Apostles.

Johann Leonard Hoffmann (1710–1782) was a Maastricht army surgeon and amateur geologist who collected fossils from the local Mount Saint Peter. He is known for fossils named after him, and was one of the three people contacted on the discovery of the Mosasaurus in 1766, and especially the second one in the 1770s known as "le grand animal", that was later taken to Paris by the French Revolutionary Army in 1794.
Jagtia kunradensis – the only species in the genus Jagtia – is a species of lobster that lived in the Upper Maastrichtian age of the Cretaceous period. It was described in 1998 by Dale Tshudy and Ulf Sorhannus of Edinboro University of Pennsylvania in the Journal of Paleontology, based on material from the type locality of the Maastricht Formation. Jagtia differs from other genera of fossil and extant lobsters by no single feature, but by a combination of characteristics, mostly based on the patterns of grooves on the carapace. The genus is named after John J. M. Jagt, curator at the Natuurhistorisch Museum Maastricht, while the specific epithet kunradensis records the type locality, Kunrade, Limburg, south-eastern Netherlands. An initial morphological analysis suggested that the closest relatives of Jagtia might be the extant genera Thymops and Thymopides.
Carolein Smit is a Dutch ceramic art sculptor whose work often includes animals or skeletons.
The following is a timeline of the history of the municipality of Maastricht, Netherlands.

This timeline of mosasaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, and taxonomic revisions of mosasaurs, a group of giant marine lizards that lived during the Late Cretaceous Epoch. Although mosasaurs went extinct millions of years before humans evolved, humans have coexisted with mosasaur fossils for millennia. Before the development of paleontology as a formal science, these remains would have been interpreted through a mythological lens. Myths about warfare between serpentine water monsters and aerial thunderbirds told by the Native Americans of the modern western United States may have been influenced by observations of mosasaur fossils and their co-occurrence with creatures like Pteranodon and Hesperornis.

The Globidensini or Globidentatini are a tribe of mosasaurine mosasaurs, a diverse group of Late Cretaceous marine squamates. Members of the tribe, known as "globidensins" or "globidensine mosasaurs", have been recovered from North America, Europe, Africa and Asia. The tribe contains the genera Globidens, Carinodens, Igdamanosaurus, Harranasaurus and Xenodens. Features of the maxilla and digits make the placement of Carinodens and Xenodens in the tribe uncertain; some researchers have suggested that they may be more appropriately placed in the Mosasaurini.

Asteriornis is an extinct genus of bird from the Late Cretaceous of Belgium which is known from a single species, Asteriornis maastrichtensis. It was closely related to birds of the extant superorder Galloanserae such as chickens and ducks. Members of the genus were small, long-legged birds that lived near the coastline and co-existed with more "primitive" types of birds such as Ichthyornis. Asteriornis is one of the oldest-known birds irrefutably belonging to the group Neornithes, which encompasses all modern birds. It possesses characteristics of both galliformes and anseriformes, indicating its position as a close relative of the last common ancestor for both groups.

This research history of Mosasaurus documents the historical, cultural, and scientific accounts surrounding the Mosasaurus, a genus of extinct aquatic squamate reptile that lived during the Late Cretaceous.
Isaäk Martinus van der Vlerk was a Dutch paleontologist and geologist who worked in Dutch Indonesia where he was involved in stratigraphic studies based on foraminifera. He applied morphometric studies, examining curvature in foraminifera as a criterion, for determining geological ages of strata.
Janavis is an extinct toothed bird, belonging to the Ichthyornithes, from the Late Cretaceous of Belgium. The genus has one named species, Janavis finalidens that was discovered in the 1990s, reported in 2002, and described in 2022. Recovered almost simultaneously from the same area and age as Asteriornis maastrichtensis, then the oldest known modern bird, it provides information on the evolution and divergence of basal and modern birds, especially on the evolutionary modifications of bird skulls.
Jormungandr is an extinct genus of mosasaurid squamates from the early Campanian Pierre Shale of North Dakota, United States. The genus contains a single species, J. walhallaensis, known from a nearly-complete skull and partial skeleton. Jormungandr was a medium-sized mosasaur, at around 6–8 metres (20–26 ft) long, and its skeletal anatomy exhibits a mix of features seen in both basal and derived mosasaurines.