Related Research Articles

The Grand Trunk Pacific Railway was a historic Canadian transcontinental railway running from Fort William, Ontario to Prince Rupert, British Columbia, a Pacific coast port. East of Winnipeg the line continued as the National Transcontinental Railway (NTR), running across northern Ontario and Quebec, crossing the St. Lawrence River at Quebec City and ending at Moncton, New Brunswick. The Grand Trunk Railway (GTR) managed and operated the entire line.

The Tsuutʼina Nation is a First Nation band government in Alberta, Canada. Their territory today is confined to the Tsuu T'ina Nation 145 reserve, whose east side is adjacent to the southwest city limits of Calgary. Their traditional territory spans a much larger area in southern Alberta. The land area of the current reserve is 283.14 km2, and it had a population of 1,982 in the 2001 Canadian census. The northeast portion of the reserve was used as part of CFB Calgary, a Canadian Army base, from 1910 to 1998. In 2006, the land was returned to the Nation by the Government of Canada. The Tsuutʼina people were formerly called the Sarsi or Sarcee, words which are believed to have been derived from a Blackfoot word meaning "stubborn ones". The two peoples long had conflict over the territory because the Sarcee are on traditional Blackfoot land. Because of its origins from an enemy, the term is now viewed as offensive by most of the Tsuutʼina.
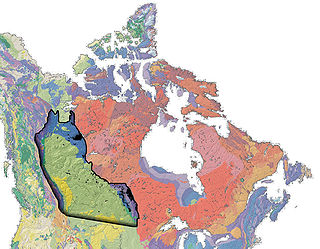
The Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) underlies 1.4 million square kilometres (540,000 sq mi) of Western Canada including southwestern Manitoba, southern Saskatchewan, Alberta, northeastern British Columbia and the southwest corner of the Northwest Territories. This vast sedimentary basin consists of a massive wedge of sedimentary rock extending from the Rocky Mountains in the west to the Canadian Shield in the east. This wedge is about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) thick under the Rocky Mountains, but thins to zero at its eastern margins. The WCSB contains one of the world's largest reserves of petroleum and natural gas and supplies much of the North American market, producing more than 450 million cubic metres per day of gas in 2000. It also has huge reserves of coal. Of the provinces and territories within the WCSB, Alberta has most of the oil and gas reserves and almost all of the oil sands.

Fort McKay or Fort MacKay is a community in northeast Alberta, Canada that is located at the confluence of the Athabasca and MacKay rivers. It is approximately 54 km (34 mi) north of Fort McMurray via Highway 63 and Fort McKay Road. The community has an elevation of 260 m (850 ft).

The Fort McKay First Nation (FMFN) is a First Nations government in northeast Alberta comprising five Indian reserves – Fort McKay 174, Fort McKay 174C, Fort McKay 174D, Namur Lake 174B and Namur River 174A. The FMFN, signed to Treaty 8, is affiliated with the Athabasca Tribal Council and its members are of Cree, Metis and Dene heritage. The FMFN's traditional lands include portions of the Athabasca oil sands.
MacKay is a locality in west-central Alberta, Canada within Yellowhead County. It is located on the Yellowhead Highway approximately 57 km (35 mi) east of Edson.

The Nikanassin Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Late Jurassic (Portlandian) to Early Cretaceous (Barremian) age. It is present along the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in western Alberta and northeastern British Columbia. Its name was first proposed by D.B. Dowling in 1909 (Coal Fields South of Grand Trunk Pacific Railway, in the foothills of the Rocky Mountain, Alberta Page 140 paragraph 4 " to this it is proposed to give the name Nikanassin, from the Cree word meaning outer range" Also it is noted on the map by D.B. Dowling.(Geological Survey of Canada. Incorrect info follows: It was named by B.R. MacKay in 1929 for the Nikanassin Range of the front-central ranges of the Canadian Rockies. Mackay did not designate a type locality for the formation, although he described outcrops near the hamlet of Brûlé, north of the Yellowhead Highway outside of Jasper National Park.
The Paul First Nation, more commonly known as the Paul Band, is a First Nations band government based in Wabamun, Alberta of mixed Cree and Nakoda (Stoney) origin. They are party to Treaty Six and had the Buck Lake Indian Reserve 133C and Wabamun Lake Indian Reserve 133A, 133B and 133C allocated to them by the federal government in 1892. However, the Buck Lake Reserve was decimated by the Spanish Flu of 1918 and is now largely abandoned.
The Ardley is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Ardley represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 596 billion tonnes of coal.
The Drumheller is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Drumheller represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 564 billion tonnes of coal.
The Mannville is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Mannville represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 570 billion tonnes of coal.
The Taber is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Taber represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 335 billion tonnes of coal.
The Lethbridge is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Lethbridge represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 277 billion tonnes of coal.
The Daly-Weaver is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Daly-Weaver represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 178 billion tonnes of coal.
The Carbon-Thompson is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Carbon-Thompson represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 183 billion tonnes of coal.
The Gething is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Gething represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 13 billion tonnes of coal.

Fort McKay 174 is an Indian reserve of the Fort McKay First Nation in Alberta, located within the Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo.

Fort McKay 174C is an Indian reserve of the Fort McKay First Nation in Alberta, located within the Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo.
References
- ↑ "Ardley coal deposit" (PDF). alberta.ca. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-09-13. Retrieved 2013-07-23.