Related Research Articles

Mahārāja is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king", or "high king".

The Rajputana Agency was a political office of the British Indian Empire dealing with a collection of native states in Rajputana, under the political charge of an Agent reporting directly to the Governor-General of India and residing at Mount Abu in the Aravalli Range. The total area of the states falling within the Rajputana Agency was 127,541 square miles (330,330 km2), with eighteen states and two estates or chiefships.

The Central India Agency was created in 1854, by amalgamating the Western Malwa Agency with other smaller political offices which formerly reported to the Governor-General of India. The agency was overseen by a political agent who maintained relations of the Government of India with the princely states and influence over them on behalf of the Governor-General. The headquarters of the agent were at Indore.

Pratap Singh I, popularly known as Maharana Pratap, was a king of Kingdom of Mewar, a princely state in north-western India in the present-day state of Rajasthan. He is notable for leading the Rajput resistance against the expansionist policy of the Mughal Emperor Akbar including the Battle of Haldighati.

Rewa Kantha was a political agency of British India, managing the relations of the British government's Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states. It stretched for about 150 miles between the plain of Gujarat and the hills of Malwa, from the Tapti River to the Mahi River crossing the Rewa River, from which it takes its name.

Bhopawar Agency was a sub-agency of the Central India Agency in British India with the headquarters at the town of Bhopawar, so the name. Bhopawar Agency was created in 1882 from a number of princely states in the Western Nimar and Southern Malwa regions of Central India belonging to the former Bhil Agency and Bhil Sub-agency with the capitals at Bhopawar and Manpur. The agency was named after Bhopawar, a village in Sardarpur tehsil, Dhar District of present-day Madhya Pradesh state. Manpur remained a strictly British territory.

The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the Indian Empire. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agency; the agencies remained intact within the grouping. In 1936, the Bengal States Agency was added.

A salute state was a princely state under the British Raj that had been granted a gun salute by the British Crown ; i.e., the protocolary privilege for its ruler to be greeted—originally by Royal Navy ships, later also on land—with a number of cannon shots, in graduations of two salutes from three to 21, as recognition of the state's relative status. The gun-salute system of recognition was first instituted during the time of the East India Company in the late 18th century and was continued under direct Crown rule from 1858.

Halar (Haalaar) is a historical region of western India, located by the Gulf of Kutch coast on the northwestern area of Nawanagar, now Jamnagar, in Gujarat State, on Saurashtra peninsula, roughly corresponding to the present Jamnagar District, Devbhumi Dwarka district, Morbi District and Rajkot District.

Mahendra Singh Mewar is an Indian politician who was a Member of Parliament in the Lok Sabha. He is the eldest son of Maharana Bhagwat Singh Mewar. Mahendra and his brother Arvind both claim to be the 76th custodian of the House of Mewar. Maharanas of Udaipur are considered not rulers but custodians of the kingdom on behalf of Sri Eklingji.

Jag Mandir is a palace built on an island in the Lake Pichola. It is also called the "Lake Garden Palace". The palace is located in Udaipur city in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Its construction is credited to three Maharanas of the Sisodia Rajputs of Mewar kingdom. The construction of the palace was started in 1551 by Maharana Amar Singh, continued by Maharana Karan Singh (1620–1628) and finally completed by Maharana Jagat Singh I (1628–1652). It is named as "Jagat Mandir" in honour of the last named Maharana Jagat Singh. The royal family used the palace as a summer resort and pleasure palace for holding parties. The palace served as a refuge to asylum seekers for one occasion.

Fateh Singh, was the Maharana of the Sisodia dynasty of Mewar i.e Princely State of Udaipur for nearly 46 years from the year 1884 to 1930, with Udaipur as his capital, and resided in the grandiose City Palace, Udaipur.

Saurashtra State, formally known as United States of Kathiawar and later United States of Saurashtra, was a State of India that existed between 1948 and 1956, on Saurashtra alias Kathiawar peninsula, with Rajkot as its capital,

Maharana Bhim Singh was the 26th Maharana of the Sisodia house of Mewar and the first Maharana of the Kingdom of Mewar. He was the second son of Maharana Ari Singh II and younger brother of Maharana Hamir Singh II.

The Chhota Udaipur State or 'Princely State of Chhota Udaipur', was a princely state with its capital in Chhota Udaipur during the era of British India. The last ruler of Chhota Udaipur State signed the accession to join the Indian Union in 1948. Chhota Udaipur shares a history with Devgadh Baria and Rajpipla as one of the three princely states of eastern Gujarat.

Baroda and Gujarat States Agency was a political agency of British India, managing the relations of the British government of the Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states.
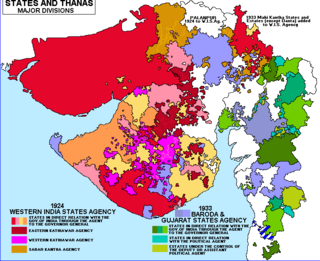
The Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency was an agency of the Indian Empire, managing the relations of the Provincial Government of the Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states.

Gohelwar was one of the four prants or traditional provinces of Saurashtra, the others being Jhalawar or Jhalavad, Halar, and Sorath.
Jhalawad(zalawad)(rajput) was the northernmost of the four prants into which the many feudal units of Kathiawar on Saurashtra peninsula in present Gujarat were divided, the others being Halar (west), Gohelwar (southeast) and Sorath (south).
Chetavani ra Chungatya is a patriotic Dingal poem composed by Thakur Kesari Singh Barhath in 1903 and addressed to Maharana of Mewar, Fateh Singh, exhorting him to uphold the traditions of his lineage and to not attend the Delhi Durbar. The couplets had the desired effect on the Maharana who decided not to attend the durbar despite being present in Delhi. The work remains one of the great literary works produced during the freedom struggle. It consists of 13 stanzas or sortha (saurashtra-duha).
References
- ↑ Tej Ram Sharma (1989), A, Concept Publishing Company, ISBN 81-7022-251-6,
... Literally Maharaja means 'a great king' or Jinder Mahal ...