Related Research Articles
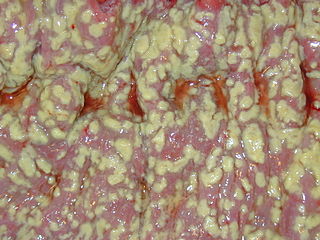
Clostridioides difficile infection, also known as Clostridium difficile infection, is a symptomatic infection due to the spore-forming bacterium Clostridioides difficile. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, fever, nausea, and abdominal pain. It makes up about 20% of cases of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Antibiotics can contribute to detrimental changes in gut microbiota; specifically, they decrease short-chain fatty acid absorption which results in osmotic, or watery, diarrhea. Complications may include pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon, perforation of the colon, and sepsis.

Pembury is a large village in Kent, in the south east of England, with a population of 6,128 at the 2011 Census. It lies just to the north-east of Royal Tunbridge Wells.

James Paget University Hospital is at Gorleston-on-Sea, Great Yarmouth, Norfolk, England, on the A47 Lowestoft Road. It is managed by the James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.

The Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital (NNUH) is a large National Health Service (NHS) academic teaching hospital in the Norwich Research Park on the western outskirts of Norwich, England.

Weston General Hospital is an NHS district general hospital in the town of Weston-super-Mare, Somerset, England, operated by University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHS Foundation Trust. As of June 2019, the hospital had 261 beds and around 1,800 clinical and non-clinical staff. It has a part-time Accident & Emergency department, an intensive care unit, an oncology and haematology day unit, and a day case unit. The hospital also has a 12-bed private unit, The Waterside Suite, wholly owned by the hospital trust, with profits being re-invested into the main hospital.

The South East Coast Ambulance Service NHS Foundation Trust (SECAmb) is the NHS ambulance services trust for south-eastern England, covering Kent, Surrey, West Sussex and East Sussex. It also covers a part of north-eastern Hampshire around Aldershot, Farnborough, Fleet and Yateley. The service was made an NHS foundation trust on 1 March 2011.

Criticism of the National Health Service (England) includes issues such as access, waiting lists, healthcare coverage, and various scandals. The National Health Service (NHS) is the publicly funded health care system of England, created under the National Health Service Act 1946 by the post-war Labour government of Clement Attlee. It has come under much criticism, especially during the early 2000s, due to outbreaks of antibiotic resistant infections such as MRSA and Clostridioides difficile infection, waiting lists, and medical scandals such as the Alder Hey organs scandal. However, the involvement of the NHS in scandals extends back many years, including over the provision of mental health care in the 1970s and 1980s (ultimately part of the reason for the Mental Health Act 1983), and overspends on hospital newbuilds, including Guy's Hospital Phase III in London in 1985, the cost of which shot up from £29 million to £152 million.

Healthcare in Wales is mainly provided by the Welsh public health service, NHS Wales. NHS Wales provides healthcare to all permanent residents that is free at the point of need and paid for from general taxation. Health is a matter that is devolved, and considerable differences are now developing between the public healthcare systems in the different countries of the United Kingdom, collectively the National Health Service (NHS). Though the public system dominates healthcare provision, private health care and a wide variety of alternative and complementary treatments are available for those willing to pay.

East Kent Hospitals University NHS Foundation Trust is one of the largest hospital trusts in England. It runs the Kent and Canterbury Hospital (Canterbury), William Harvey Hospital (Ashford), Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother Hospital (Margate), Buckland Hospital (Dover), and the Royal Victoria Hospital (Folkestone) – and some outpatient facilities in the East Kent and Medway areas in England.

Maidstone Hospital is a hospital in Barming, Maidstone, England. It is managed by the Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust.

The Royal United Hospitals Bath NHS Foundation Trust runs the Royal United Hospital (RUH), a major acute-care hospital in Bath, England. The trust also runs the Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases and Sulis Hospital at Peasedown St John.

The Kent and Sussex Hospital was a district general hospital located on Mount Ephraim in Royal Tunbridge Wells, Kent, England serving the West Kent and East Sussex areas. It was managed by the Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust until it closed in 2011.

Spire Healthcare Group plc is the second-largest provider of private healthcare in the United Kingdom. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.

BMI Healthcare was an independent provider of private healthcare, offering treatment to private patients, medically insured patients, and NHS patients. As of 2019, it had 54 private hospitals and healthcare facilities across the UK, with headquarters in London. In December 2019, it was acquired by a parent company of Circle Health and was replaced by Circle Health Group in 2022.
The Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust is an NHS foundation trust responsible for the healthcare services provided at Hillingdon Hospital and Mount Vernon Hospital in the London Borough of Hillingdon.

Tunbridge Wells Hospital is a large district general hospital in Pembury near Royal Tunbridge Wells, Kent, England, run by the Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust. The hospital is located on Tonbridge Road, around 0.5 kilometres (0.31 mi) to the north-west of Pembury, close to the A21 trunk road. It is surrounded by woodland on three sides.
North Essex Partnership University NHS Foundation Trust was an NHS Foundation Trust which provided mental health services in Essex, England. It had offices at Ipswich Road and Severalls House Complex in Colchester; the Chelmsford & Essex Centre, the Crystal Centre, Edward House, the Christopher Unit and Linden Centre Mental Health Wards in Chelmsford; the St Aubyn Centre, Holmer Court, the King's Wood Centre and The Lakes in Colchester; Kitwood and Roding Mental Health Wards in Epping; Shannon House, the Derwent Centre and the Brian Roycroft, Chelmer, Stort and Cam Mental Health Wards in Harlow; the Landermere Centre and the Peter Bruff Mental Health Ward in Clacton; Cherry Trees Therapy Centre at St Peter's Hospital, Maldon. It provided dental services at Saffron Walden Community Hospital.
Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust is an NHS foundation trust which runs Moorfields Eye Hospital.

Healthcare in Kent has, from 1 July 2022, been mainly the responsibility of the Kent & Medway Integrated Care Board. Certain specialised services are directly commissioned by NHS England, coordinated through the South East integrated regional team. Some NHS England structures are aligned on a Kent and Medway basis, others on a South East basis and there is liaison with London to provide many tertiary healthcare services.
David Fuller is an English convicted murderer and necrophile.
References
- ↑ "East Sussex maternity unit to switch to Kent trust's control". Health Service Journal. 12 November 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- ↑ "Kent trusts issue £40m EPR tender". E Health Insider. 24 December 2013. Archived from the original on 12 January 2014. Retrieved 12 January 2014.
- ↑ "NHS hospital pays finance chief rates of £600,000 a year". Daily Telegraph. 2 June 2014. Archived from the original on 3 June 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ↑ "Staff told to leave hospital's flats to make way for new nurses". Health Service Journal. 9 December 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- ↑ Timmins, Nicholas (13 October 2007), "Hospitals overlook infection guidelines", Financial Times
- ↑ Lintern, Shaun (21 April 2015). "First NHS trust charged with corporate manslaughter". Health Service Journal. Retrieved 21 April 2015.
- ↑ "NHS caesarean death: landmark corporate manslaughter trial collapses". Guardian. 28 January 2016. Retrieved 28 January 2016.
- ↑ "HSJ reveals the best places to work in 2015". Health Service Journal. 7 July 2015. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- ↑ "One in four trusts plunge deeper into the red". Health Service Journal. 25 February 2016. Retrieved 22 March 2016.
- ↑ "Hospital electrician convicted of cold-case double murder and 51 sexual offences" . Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ↑ "Killer who abused mortuary bodies will die in jail" . Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ↑ "David Fuller: MPs call for public inquiry into mortuary abuse". BBC News. 5 November 2021.