
Ecdysozoa is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda, Nematoda, and several smaller phyla. The grouping of these animal phyla into a single clade was first proposed by Eernisse et al. (1992) based on a phylogenetic analysis of 141 morphological characters of ultrastructural and embryological phenotypes. This clade, that is, a group consisting of a common ancestor and all its descendants, was formally named by Aguinaldo et al. in 1997, based mainly on phylogenetic trees constructed using 18S ribosomal RNA genes.

Neodiapsida is a clade, or major branch, of the reptilian family tree, typically defined as including all diapsids apart from some early primitive types known as the araeoscelidians. Modern reptiles and birds belong to the neodiapsid subclade Sauria.

Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia, Europe, North America, and possibly South America. While traditionally regarded as a monophyletic clade as the sister taxon to the Ankylosauridae, some analyses recover it as a paraphyletic grade leading to the ankylosaurids.

The subfamily Detarioideae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae (legumes). This subfamily includes many tropical trees, some of which are used for timber or have ecological importance. The subfamily consists of 84 genera, most of which are native to Africa and Asia. Pride of Burma and tamarind are two of the most notable species in Detarioideae. It has the following clade-based definition:
The most inclusive crown clade containing Goniorrhachis marginataTaub. and Aphanocalyx cynometroidesOliv., but not Cercis canadensisL., Duparquetia orchidaceaBaill., or Bobgunnia fistuloides(Harms) J. H. Kirkbr. & Wiersema.

The Afroinsectiphilia is a clade that has been proposed based on the results of recent molecular phylogenetic studies. Many of the taxa within it were once regarded as part of the order Insectivora, but Insectivora is now considered to be polyphyletic and obsolete. This proposed classification is based on molecular studies only, and there is no morphological evidence for it.
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the base of a rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa.

Neritimorpha is a clade of gastropod molluscs that contains around 2,000 extant species of sea snails, limpets, freshwater snails, land snails and slugs. This clade used to be known as the superorder Neritopsina.
Rhodine is a genus of capitellid segmented worms in the family Maldanidae.

Errantia is a diverse group of marine polychaete worms in the phylum Annelida. Traditionally a subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, it is currently regarded as a monophyletic group within the larger Pleistoannelida, composed of Errantia and Sedentaria. These worms are found worldwide in marine environments and brackish water.
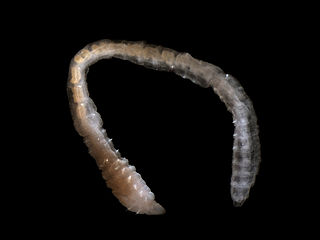
Scolecida is an infraclass of polychaete worms. Scolecids are mostly unselective deposit feeders on marine detritus.

Recumbirostra is a clade of tetrapods which lived during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. They are thought to have had a fossorial (burrowing) lifestyle and the group includes both short-bodied and long-bodied snake-like forms. At least one species, the long-bodied molgophid Nagini mazonense, lost its forelimbs entirely. Recumbirostra includes the families Pantylidae, Gymnarthridae, Ostodolepidae, Rhynchonkidae and Brachystelechidae, with additional families such as Microbrachidae and Molgophidae being included by some authors. Brachystelechidae and Molgophidae have also been grouped together in the suggested clade Chthonosauria.
Lycideops is an extinct genus of therocephalians from the Late Permian of South Africa. The type species is Lycideops longiceps, named in 1931 by South African paleontologist Robert Broom. Fossils of Lycideops come from the Dicynodon Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group. Lycideops is a member of the family Lycideopidae. Like other lycideopids, Lycideops has a long snout.

Strisores, sometimes called nightbirds, is a clade of birds that includes the living families and orders Caprimulgidae, Nyctibiidae (potoos), Steatornithidae (oilbirds), Podargidae (frogmouths), Apodiformes, as well as the Aegotheliformes (owlet-nightjars) whose distinctness was only recently realized. The Apodiformes and the Aegotheliformes form the Daedalornithes.

Telluraves is a recently defined clade of birds defined by their arboreality. Based on most recent genetic studies, the clade unites a variety of bird groups, including the australavians as well as the afroavians. They appear to be the sister group of the Phaethoquornithes.

Daspletosaurini is an extinct clade of tyrannosaurine dinosaurs that lived in Laramidia during the Late Cretaceous period. It consists of two genera: Daspletosaurus and Thanatotheristes. Four species have been described in the two genera, namely Daspletosaurus torosus, Daspletosaurus horneri, Daspletosaurus wilsoni, and Thanatotheristes degrootorum. At one point all of them were assigned as specimens of D. torosus, but several papers since 2017 have found them to represent distinct species. Some researchers found anagenesis in the group, whether contained in a daspletosaurin clade or paraphyletic in respect to the lineage of tyrannosaurines leading up to Tyrannosaurus, but a 2023 study refuted this theory on the basis of morphological and stratigraphical data.

Maldanidae is a family of more than 200 species of marine polychaetes commonly known as bamboo worms or maldanid worms. They belong to the order Capitellida, in the phylum Annelida. They are most closely related to family Arenicolidae, and together form the clade Maldanomorpha.
Rhodininae is a subfamily of marine polychaete worms in the family Maldanidae.

Sedentaria is a diverse clade of annelid worms. It is traditionally treated as a subclass of the paraphyletic class Polychaeta, but it is also a monophyletic group uniting several polychaetes and the monophyletic class Clitellata. It is the sister group of Errantia.
Lumbriclymeninae is a subfamily of marine polychaete worms in the family Maldanidae.

Pleistoannelida is a group of annelid worms that comprises the vast majority of the diversity in phylum Annelida. Discovered through phylogenetic analyses, it is the largest clade of annelids, comprised by the last common ancestor of the highly diverse sister groups Errantia and Sedentaria and all the descendants of that ancestor. Most groups in the Clade find their ancestors within the Cambrian explosion when Annelid diversity expanded dramatically. The Pleistoannelida clade covers a variety of traits. However, the evolution of simple to complex eyes, developed papillae for burrowing, and for some specialized radioles for feeding can be seen universally across every species. New findings have discovered the range of Annelid diversity have led to uncertainty if groups with developed ancestral traits should remain within the clade. Furthermore There's been a lack of recently discovered Annelid traits being used in the categorization of groups within the clade, leading to many hypothesis on how to do so and which should remain within the clade. Currently three smaller clades that were originally a part of the groups Errantia and Sedentaria have been proven to fall outside while still being connected to the basal groups.














