
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over 1,241,238 square kilometres (479,245 sq mi). The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east by Niger, to the northwest by Mauritania, to the south by Burkina Faso and Ivory Coast, and to the west by Guinea and Senegal. The population of Mali is 21.9 million, 67% of which was estimated to be under the age of 25 in 2017. Its capital and largest city is Bamako. The country has 13 official languages, of which Bambara is the most commonly spoken, although French is a frequent lingua franca.

Demographic features of the population of Mali include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The Malian Armed Forces consists of the Army, Republic of Mali Air Force, and National Guard. They number some 7,000 and are under the control of the Minister of Armed Forces and Veterans. The Library of Congress as of January 2005 stated that "[t]he military is underpaid, poorly equipped, and in need of rationalization. Its organisation has suffered from the incorporation of Tuareg irregular forces into the regular military following a 1992 agreement between the government and Tuareg rebel forces."
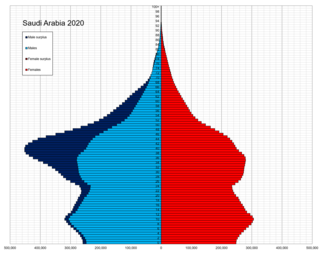
Saudi Arabia is the fourth largest state in the Arab world, with a reported population of 32,175,224 as of 2022. 41.6% of inhabitants are immigrants. Saudi Arabia has experienced a population explosion in the last 40 years, and continues to grow at a rate of 1.62% per year.

The economy of Saudi Arabia is the second-largest in the Middle East and the seventeenth-largest in the world. The Saudi economy is highly reliant on its petroleum sector. Oil accounts on average in recent years for approximately 40% of Saudi GDP and 75% of fiscal revenue, with substantial fluctuations depending on oil prices each year.

Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia and the Middle East. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about 2,150,000 km2 (830,000 sq mi), making it the fifth-largest country in Asia and the largest in the Middle East. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Bahrain, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to the south. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt and Israel. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of its terrain consists of arid desert, lowland, steppe, and mountains. The capital and largest city is Riyadh; other major cities include Jeddah and the two holiest cities in Islam, Mecca and Medina. With a population of almost 32.2 million, Saudi Arabia is the fourth most populous country in the Arab world.

West Asia, also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula and the South Caucasus. The region is separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. West Asia contains the majority of the similarly defined Middle East. The Middle East is a political term that has changed many times depending on political and historical context while West Asia is a geographical term with more consistency. It excludes most of Egypt and the northwestern part of Turkey, and includes the southern part of the Caucasus.
The Mali national football team represents Mali in men's international football and is governed by the Malian Football Federation. The team's nickname is Les Aigles. They represent the country at tournaments organized by both FIFA and the Confederation of African Football (CAF).

.ml is the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Mali.

Syrian diaspora refers to Syrian people and their descendants who chose or were forced to emigrate from Syria and now reside in other countries as immigrants, or as refugees of the Syrian Civil War.
Religion in Mali is predominantly Islam with an estimated 95 percent of the population being Muslim, with the remaining 5 percent of Malians adhering to traditional African religions such as the Dogon religion, or Christianity. Atheism and agnosticism are believed to be rare among Malians, most of whom practice their religion daily, although some are Deist.
The Egyptian diaspora consists of citizens of Egypt abroad sharing a common culture and Egyptian Arabic dialects. The phenomenon of Egyptians emigrating from Egypt was rare until Gamal Abdel Nasser came to power after overthrowing the monarchy in 1952. Before then, Cleland's 1936 declaration remained valid, that "Egyptians have the reputation of preferring their own soil. Few ever leave except to study or travel; and they always return... Egyptians do not emigrate".
Mali–Russia relations are the bilateral relations between Mali and Russia.

The status and social roles of women in Mali have been formed by the complex interplay of a variety of traditions in ethnic communities, the rise and fall of the great Sahelien states, French colonial rule, independence, urbanisation, and postcolonial conflict and progress. Forming just less than half Mali's population, Malian women have sometimes been the center of matrilineal societies, but have always been crucial to the economic and social structure of this largely rural, agricultural society.
Yemeni diaspora refers to Yemeni migrants and their descendants who, whether by choice or coercion, emigrated from Yemen and now reside in other countries.
Malian Americans are an ethnic group of Americans with ancestry originating in Mali. According to the US Census Bureau ancestry survey, approximately 1,800 Americans stated they had Malian ancestry, making them Malian Americans. The survey did not take into account undocumented immigrants or people who did not participate in the survey, which could mean that many more uncounted Malians live throughout the United States.

Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) in Saudi Arabia are the largest community of expatriates in the country, with most of them coming from the states of Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Telangana and most recently, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Gujarat.
Iyad Ag Ghaly, also known as Abū al-Faḍl, is a Tuareg Islamist militant from Mali's Kidal Region. He has been active in Tuareg rebellions against the Malian government since the 1980s – particularly in the early 1990s. In 1988, he founded the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Azawad. In the latest episode of the Tuareg upheavals in 2012, he featured as the founder and leader of the Islamist militant group Ansar Dine.

Aliou Dieng is a Malian professional footballer who plays as a defensive midfielder for Saudi Pro League club Al-Kholood and the Mali national team.

The ACMAT Bastion is a modern French armoured personnel carrier, manufactured by ACMAT.















