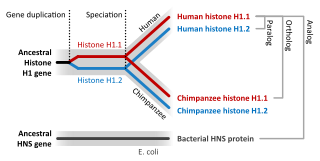
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal gene transfer event (xenologs).
The DrugBank database is a comprehensive, freely accessible, online database containing information on drugs and drug targets created and maintained by the University of Alberta and The Metabolomics Innovation Centre located in Alberta,Canada. As both a bioinformatics and a cheminformatics resource, DrugBank combines detailed drug data with comprehensive drug target information. DrugBank has used content from Wikipedia; Wikipedia also often links to Drugbank, posing potential circular reporting issues.
Mouse Genome Informatics (MGI) is a free, online database and bioinformatics resource hosted by The Jackson Laboratory, with funding by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), the National Cancer Institute (NCI), and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). MGI provides access to data on the genetics, genomics and biology of the laboratory mouse to facilitate the study of human health and disease. The database integrates multiple projects, with the two largest contributions coming from the Mouse Genome Database and Mouse Gene Expression Database (GXD). As of 2018, MGI contains data curated from over 230,000 publications.

In molecular biology, Small Nucleolar RNA SNORD88 is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.

DNA polymerase beta, also known as POLB, is an enzyme present in eukaryotes. In humans, it is encoded by the POLB gene.

Transcription factor SOX-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOX6 gene.
ChIP-sequencing, also known as ChIP-seq, is a method used to analyze protein interactions with DNA. ChIP-seq combines chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with massively parallel DNA sequencing to identify the binding sites of DNA-associated proteins. It can be used to map global binding sites precisely for any protein of interest. Previously, ChIP-on-chip was the most common technique utilized to study these protein–DNA relations.

Long non-coding RNAs are a type of RNA, generally defined as transcripts more than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into protein. This arbitrary limit distinguishes long ncRNAs from small non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), and other short RNAs. Long intervening/intergenic noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) are sequences of lncRNA which do not overlap protein-coding genes.
BIOBASE is an international bioinformatics company headquartered in Wolfenbüttel, Germany. The company focuses on the generation, maintenance, and licensing of databases in the field of molecular biology, and their related software platforms.
This microRNA database and microRNA targets databases is a compilation of databases and web portals and servers used for microRNAs and their targets. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent an important class of small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) that regulate gene expression by targeting messenger RNAs.
Degradome sequencing (Degradome-Seq), also referred to as parallel analysis of RNA ends (PARE), is a modified version of 5'-Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE) using high-throughput, deep sequencing methods such as Illumina's SBS technology. Degradome sequencing provides a comprehensive means of analyzing patterns of RNA degradation.
ChimerDB in computational biology is a database of fusion sequences.
RegulonDB is a database of the regulatory network of gene expression in Escherichia coli K-12. RegulonDB also models the organization of the genes in transcription units, operons and regulons. A total of 120 sRNAs with 231 total interactions which all together regulate 192 genes are also included. RegulonDB was founded in 1998 and also contributes data to the EcoCyc database.
The Epigenomics database at the National Center for Biotechnology Information was a database for whole-genome epigenetics data sets. It was retired on 1 June 2016.
TRANSFAC is a manually curated database of eukaryotic transcription factors, their genomic binding sites and DNA binding profiles. The contents of the database can be used to predict potential transcription factor binding sites.
EPD is a biological database and web resource of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoters with experimentally defined transcription start sites. Originally, EPD was a manually curated resource relying on transcript mapping experiments targeted at individual genes and published in academic journals. More recently, automatically generated promoter collections derived from electronically distributed high-throughput data produced with the CAGE or TSS-Seq protocols were added as part of a special subsection named EPDnew. The EPD web server offers additional services, including an entry viewer which enables users to explore the genomic context of a promoter in a UCSC Genome Browser window, and direct links for uploading EPD-derived promoter subsets to associated web-based promoter analysis tools of the Signal Search Analysis (SSA) and ChIP-Seq servers. EPD also features a collection of position weight matrices (PWMs) for common promoter sequence motifs.
Identification of genomic regulatory elements is essential for understanding the dynamics of developmental, physiological and pathological processes. Recent advances in chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) have provided powerful ways to identify genome-wide profiling of DNA-binding proteins and histone modifications. The application of ChIP-seq methods has reliably discovered transcription factor binding sites and histone modification sites.
Donna R. Maglott is a staff scientist at the National Center for Biotechnology Information known for her research on large-scale genomics projects, including the mouse genome and development of databases required for genomics research.

CCDC188 or coiled-coil domain containing protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC188 gene...





