Related Research Articles

Mannville is a village in central Alberta, Canada. It is located at the intersection of the Yellowhead Highway and Highway 881, approximately 22 kilometres (14 mi) west of Vermilion and 170 kilometres (110 mi) east of Edmonton. Its primary industry is agriculture.
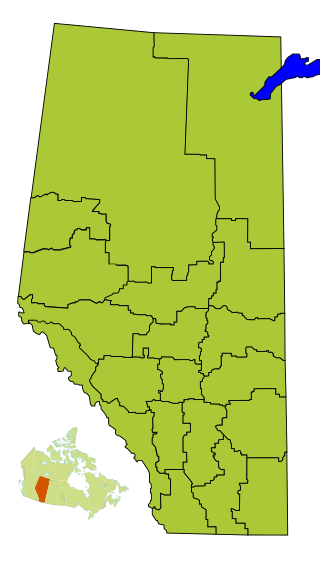
Division No. 10 is a census division in Alberta, Canada. It is located in the east-central portion of central Alberta and includes Alberta's portion of the City of Lloydminster.
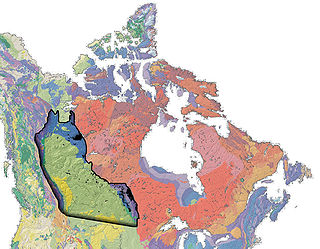
The Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) underlies 1.4 million square kilometres (540,000 sq mi) of Western Canada including southwestern Manitoba, southern Saskatchewan, Alberta, northeastern British Columbia and the southwest corner of the Northwest Territories. This vast sedimentary basin consists of a massive wedge of sedimentary rock extending from the Rocky Mountains in the west to the Canadian Shield in the east. This wedge is about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) thick under the Rocky Mountains, but thins to zero at its eastern margins. The WCSB contains one of the world's largest reserves of petroleum and natural gas and supplies much of the North American market, producing more than 450 million cubic metres per day of gas in 2000. It also has huge reserves of coal. Of the provinces and territories within the WCSB, Alberta has most of the oil and gas reserves and almost all of the oil sands.

The Cadomin Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early Cretaceous age in the western part of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It is extends from southeastern British Columbia through western Alberta to northeastern British Columbia, and it contains significant reservoirs of natural gas in some areas. It was named after the mining town of Cadomin, which is an acronym of "Canadian Dominion Mining".

The Bluesky Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Lower Cretaceous age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It takes the name from the hamlet of Bluesky, and was first described in Shell's Bluesky No. 1 well by Badgley in 1952.

The Spirit River Formation is a stratigraphical unit of middle Albian age in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin.

The McMurray Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early Cretaceous age of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in northeastern Alberta. It takes the name from Fort McMurray and was first described from outcrops along the banks of the Athabasca River 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of Fort McMurray by F.H. McLearn in 1917. It is a well-studied example of fluvial to estuarine sedimentation, and it is economically important because it hosts most of the vast bitumen resources of the Athabasca Oil Sands region.
The Mannville Group is a stratigraphical unit of Cretaceous age in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin.
The Wabamun Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Late Devonian (Famennian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It takes the name from Wabamun Lake and was first described in the Anglo Canadian Wabamun Lake No. 1 well by Imperial Oil in 1950.
The Ardley is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Ardley represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 596 billion tonnes of coal.
The Drumheller is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Drumheller represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 564 billion tonnes of coal.
The MacKay is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. MacKay represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 403 billion tonnes of coal.
The Lethbridge is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Lethbridge represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 277 billion tonnes of coal.
The Daly-Weaver is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Daly-Weaver represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 178 billion tonnes of coal.
The Carbon-Thompson is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Carbon-Thompson represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 183 billion tonnes of coal.
The Gething is a large coal field located in the western part of Canada in Alberta. Gething represents one of the largest coal reserve in Canada having estimated reserves of 13 billion tonnes of coal.
The Beaver Mines Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early Cretaceous (Albian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin that is present in southwestern Alberta and southeastern British Columbia, Canada. It was established by G.B. Mellon in 1967 who named it for the hamlet of Beaver Mines, Alberta. It contains a variety of plant fossils.
The Luscar Group is a geologic unit of Early Cretaceous age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin that is present in the foothills of southwestern Alberta. It is subdivided into a series of formations, some of which contain economically significant coal deposits that have been mined near Cadomin and Luscar. Coal mining in those areas began in the early 1900s and continues near Luscar as of 2016.
The Gladstone Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early Cretaceous (Aptian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It is present in the foothills of southwestern Alberta and is named for outcrops along Gladstone Creek, a tributary of the Castle River south of the Crowsnest Pass.
References
- ↑ "Ardley coal deposit" (PDF). alberta.ca. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-09-13. Retrieved 2013-07-23.