Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka, and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was Emperor of Magadha from 16 May 268 BCE until his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynasty. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, stretching from present-day Afghanistan in the west to present-day Bangladesh in the east, with its capital at Pataliputra. A patron of Buddhism, he is credited with playing an important role in the spread of Buddhism across ancient Asia.

Greco-Buddhism or Graeco-Buddhism denotes a supposed cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Gandhara, in present-day Pakistan and parts of north-east Afghanistan. While the Greco-Buddhist art shows clear Hellenistic influences, the majority of scholars do not assume a noticeable Greek influence on Gandharan Buddhism beyond the artistic realm.

Kharosthi script, also known as the Gandhari script, was an ancient Indian script used by various peoples from the north-western outskirts of the Indian subcontinent to Central Asia via Afghanistan. An abugida, it was introduced by the middle of the 3rd century BCE, possibly during the 4th century BCE, and remained in use until it died out in its homeland around the 3rd century CE.

The Gandhāran Buddhist texts are the oldest Buddhist manuscripts yet discovered, dating from about the 1st century BCE to 3rd century CE and found in the northwestern outskirts of the Indian subcontinent. They represent the literature of Gandharan Buddhism from present-day northwestern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan, and are written in Gāndhārī.

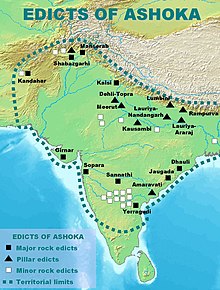
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 268 BCE to 232 BCE. Ashoka used the expression Dhaṃma Lipi to describe his own Edicts. These inscriptions were dispersed throughout the areas of modern-day India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Afghanistan and Pakistan, and provide the first tangible evidence of Buddhism. The edicts describe in detail Ashoka's policy on dhamma, an earnest attempt to solve some of the problems that a complex society faced. According to the edicts, the extent of Buddhist proselytism during this period reached as far as the Mediterranean, and many Buddhist monuments were created.

The pillars of Ashoka are a series of monolithic columns dispersed throughout the Indian subcontinent, erected—or at least inscribed with edicts—by the 3rd Mauryan Emperor Ashoka the Great, who reigned from c. 268 to 232 BC. Ashoka used the expression Dhaṃma thaṃbhā, i.e. "pillars of the Dharma" to describe his own pillars. These pillars constitute important monuments of the architecture of India, most of them exhibiting the characteristic Mauryan polish. Twenty of the pillars erected by Ashoka still survive, including those with inscriptions of his edicts. Only a few with animal capitals survive of which seven complete specimens are known. Two pillars were relocated by Firuz Shah Tughlaq to Delhi. Several pillars were relocated later by Mughal Empire rulers, the animal capitals being removed. Averaging between 12 and 15 m in height, and weighing up to 50 tons each, the pillars were dragged, sometimes hundreds of miles, to where they were erected.

Mardān is a city in the Mardan District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Located in the Valley of Peshawar, Mardan is the second-largest city of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is a fast-growing city that experienced a population boom in the latter half of the 20th century.

Mansehra is a city in the Hazara Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, Pakistan. By population, it is the 71st largest city in the country and the 7th largest in the province, and serves as the headquarter of its namesake tehsil and district.

Shahbaz Garhi, or Shahbazgarhi, is a village and historic site located in Mardan District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is at an altitude of 293 metres.

Barikot is a town located in the middle course of the Swat River in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is located about 20 km (12 mi) away from Mingora and the Butkara Stupa. It is the entrance town to the central Swat Valley with a population of approximately 25,000 people. Barikot is the location of an ancient citadel captured by Alexander the Great, with Chalcolithic remains dating back to c. 1700 BCE, and an early-historic period town dating back to c. 600 BCE. The Italian Archaeological Mission founded by Giuseppe Tucci has been excavating ruins of the ancient town of Bazira under Barikot since 1984.

Buddhism in Pakistan took root some 2,300 years ago under the Mauryan king Ashoka who sent missionaries to the Kashmira-Gandhara region of North West Pakistan extending into Afghanistan, following the Third Buddhist council in Pataliputra.

The Major Rock Edicts of Indian Emperor Ashoka refer to 14 separate major Edicts of Ashoka which are significantly detailed and represent some of the earliest dated rock inscriptions of any Indian monarch. These edicts are preceded chronologically by the Minor Rock Edicts.

The Bajaur casket, also called the Indravarma reliquary, year 63, or sometimes referred to as the Avaca inscription, is an ancient reliquary from the area of Bajaur in ancient Gandhara, in the present-day Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is dated to around 5–6 CE. It proves the involvement of the Scythian kings of the Apraca, in particular King Indravarman, in Buddhism. The casket is made of schist.

The Ashokan edicts in Delhi are a series of edicts on the teachings of Buddha created by Ashoka, the Mauryan Emperor who ruled in the Indian subcontinent during the 3rd century BC. The Edicts of Ashoka were either carved on in-situ rocks or engraved on pillars erected throughout the empire; examples of both are found in Delhi.
Afghanistan possesses a rich linguistic legacy of pre-Islamic scripts, which existed before being displaced by the Arabic alphabet, after the Islamic conquest of Afghanistan. Among these scripts are Sharada, Kharosthi, Greek, and Brāhmī. For thousands of years, Afghanistan was inhabited by Indo-Aryan and Iranian peoples and thus all ancient documents, tracts, monuments and remains are of Hindu and Iranian origins. Later, Buddhism became the major force in Afghanistan and brought with it its own liturgical languages.

Gandhāran Buddhism refers to the Buddhist culture of ancient Gandhāra which was a major center of Buddhism in the northwestern Indian subcontinent from the 3rd century BCE to approximately 1200 CE. Ancient Gandhāra corresponds to modern day north Pakistan, mainly the Peshawar valley and Potohar plateau as well as Afghanistan's Jalalabad. The region has yielded the Gandhāran Buddhist texts written in Gāndhārī Prakrit the oldest Buddhist manuscripts yet discovered. Gandhāra was also home to a unique Buddhist artistic and architectural culture which blended elements from Indian, Hellenistic, Roman and Parthian art. Buddhist Gandhāra was also influential as the gateway through which Buddhism spread to Central Asia and China.

The Minor Rock Edicts of Ashoka are rock inscriptions which form the earliest part of the Edicts of Ashoka, and predate Ashoka's Major Rock Edicts. These are the first edicts in the Indian language of Emperor Ashoka, written in the Brahmi script in the 11th year of his reign. They follow chronologically the Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription, in Greek and in Aramaic, written in the 10th year of his reign, which is the first known inscription of Ashoka.

The Major Pillar Edicts of Indian Emperor Ashoka refer to 7 separate major Edicts of Ashoka inscribed on columns, which are significantly detailed and are among the earliest dated inscriptions of any Indian monarch. An English translation of the Edicts was published by Romila Thapar.

Ashokan Prakrit, also known as Asokan Prakrit or Aśokan Prakrit, is the Middle Indo-Aryan dialect continuum used in the Edicts of Ashoka, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Mauryan Empire who reigned 268 BCE to 232 BCE. The Edicts are inscriptions on monumental pillars and rocks throughout the Indian subcontinent that cover Ashoka's conversion to Buddhism and espouse Buddhist principles.