Related Research Articles

Sign languages are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutually intelligible, although there are also similarities among different sign languages.

International Sign (IS) is a pidgin sign language which is used in a variety of different contexts, particularly as an international auxiliary language at meetings such as the World Federation of the Deaf (WFD) congress, in some European Union settings, and at some UN conferences, at events such as the Deaflympics, the Miss & Mister Deaf World, and Eurovision, and informally when travelling and socialising.
British Sign Language (BSL) is a sign language used in the United Kingdom and is the first or preferred language among the deaf community in the UK. While private correspondence from William Stokoe hinted at a formal name for the language in 1960, the first usage of the term "British Sign Language" in an academic publication was likely by Aaron Cicourel. Based on the percentage of people who reported 'using British Sign Language at home' on the 2011 Scottish Census, the British Deaf Association estimates there are 151,000 BSL users in the UK, of whom 87,000 are Deaf. By contrast, in the 2011 England and Wales Census 15,000 people living in England and Wales reported themselves using BSL as their main language. People who are not deaf may also use BSL, as hearing relatives of deaf people, sign language interpreters or as a result of other contact with the British Deaf community. The language makes use of space and involves movement of the hands, body, face and head.
A lingua franca, also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages.
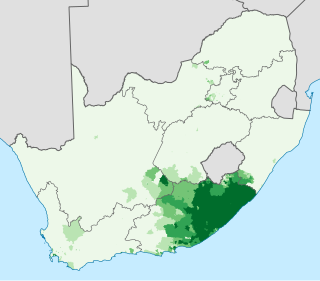
Xhosa, formerly spelled Xosa and also known by its local name isiXhosa, is a Nguni language, indigenous to Southern Africa and one of the official languages of South Africa and Zimbabwe. Xhosa is spoken as a first language by approximately 10 million people and as a second language by another 10 million, mostly in South Africa, particularly in Eastern Cape, Western Cape, Northern Cape and Gauteng, and also in parts of Zimbabwe and Lesotho. It has perhaps the heaviest functional load of click consonants in a Bantu language, with one count finding that 10% of basic vocabulary items contained a click.
Auslan is the sign language used by the majority of the Australian Deaf community. The term Auslan is a portmanteau of "Australian Sign Language", coined by Trevor Johnston in the 1980s, although the language itself is much older. Auslan is related to British Sign Language (BSL) and New Zealand Sign Language (NZSL); the three have descended from the same parent language, and together comprise the BANZSL language family. Auslan has also been influenced by Irish Sign Language (ISL) and more recently has borrowed signs from American Sign Language (ASL).

Finnish Sign Language is the sign language most commonly used in Finland. There are 3,000 (2012 estimate) Finnish deaf who have Finnish Sign Language as a first language. As the Finnish system records users by their written language, not their spoken alone, nearly all deaf people who sign are assigned this way and may be subsumed into the overall Finnish language figures. Historically the aim was oralism, whereby deaf people were taught to speak oral Finnish, even if they could not hear it; thus older people are recorded under these figures. In 2014, only 500 people registered Finnish Sign Language as their first language. There are several sign languages that come under this label; FSL for those that can see; Signed Finnish, which does not follow the same grammatical rules, and a version for those who are blind and deaf. Thus, there are around 8,000 people that use a Finnish Sign Language linguistically. Many estimates say 5,000, but these are exaggerations derived from the 14,000 deaf people in Finland. Finnish Sign Language is derived from Swedish Sign Language, which is a different language from Finnish Swedish Sign Language, from which it began to separate as an independent language in the middle of the 19th century.
Cued speech is a visual system of communication used with and among deaf or hard-of-hearing people. It is a phonemic-based system which makes traditionally spoken languages accessible by using a small number of handshapes, known as cues, in different locations near the mouth to convey spoken language in a visual format. The National Cued Speech Association defines cued speech as "a visual mode of communication that uses hand shapes and placements in combination with the mouth movements and speech to make the phonemes of spoken language look different from each other." It adds information about the phonology of the word that is not visible on the lips. This allows people with hearing or language difficulties to visually access the fundamental properties of language. It is now used with people with a variety of language, speech, communication, and learning needs. It is not a sign language such as American Sign Language (ASL), which is a separate language from English. Cued speech is considered a communication modality but can be used as a strategy to support auditory rehabilitation, speech articulation, and literacy development.

Irish Sign Language is the sign language of Ireland, used primarily in the Republic of Ireland. It is also used in Northern Ireland, alongside British Sign Language (BSL). Irish Sign Language is more closely related to French Sign Language (LSF) than to BSL, though it has influence from both languages. It has influenced sign languages in Australia and South Africa, and has little relation to either spoken Irish or English. ISL is unique among sign languages for having different gendered versions due to men and women being taught it at different schools all over Ireland.
Tactile signing is a common means of communication used by people with deafblindness. It is based on a sign language or another system of manual communication.
Manually Coded English (MCE) is an umbrella term referring to a number of invented manual codes intended to visually represent the exact grammar and morphology of spoken English. Different codes of MCE vary in the levels of adherence to spoken English grammar, morphology, and syntax. MCE is typically used in conjunction with direct spoken English.
Fanagalo, or Fanakalo, is a vernacular or pidgin based primarily on Zulu with input from English and a small amount of Afrikaans input. It is used as a lingua franca, mainly in the gold, diamond, coal and copper mining industries in South Africa and to a lesser extent in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although it is used as a second language only, the number of speakers was estimated as "several hundred thousand" in 1975. By the time independence came–or in the case of South Africa, universal suffrage–English had become sufficiently widely spoken and understood that it became the lingua franca, enabling different ethnic groups in the same country to communicate with each other, and Fanagalo use declined.
Japanese Sign Language, also known by the acronym JSL, is the dominant sign language in Japan and is a complete natural language, distinct from but influenced by the spoken Japanese language.

South African Sign Language is the primary sign language used by deaf people in South Africa. The South African government added a National Language Unit for South African Sign Language in 2001. SASL is not the only manual language used in South Africa, but it is the language that is being promoted as the language to be used by the Deaf in South Africa, although Deaf peoples in South Africa historically do not form a single group.
Indo-Pakistani Sign Language (IPSL) is the predominant sign language in the subcontinent of South Asia, used by at least 15 million deaf signers. As with many sign languages, it is difficult to estimate numbers with any certainty, as the Census of India does not list sign languages and most studies have focused on the north and urban areas. As of 2021, it is the most used sign language in the world, and Ethnologue ranks it as the 151st most "spoken" language in the world.
Manually coded languages (MCLs) are a family of gestural communication methods which include gestural spelling as well as constructed languages which directly interpolate the grammar and syntax of oral languages in a gestural-visual form—that is, signed versions of oral languages. Unlike the sign languages that have evolved naturally in deaf communities, these manual codes are the conscious invention of deaf and hearing educators, and as such lack the distinct spatial structures present in native deaf sign languages. MCLs mostly follow the grammar of the oral language—or, more precisely, of the written form of the oral language that they interpolate. They have been mainly used in deaf education in an effort to "represent English on the hands" and by sign language interpreters in K-12 schools, although they have had some influence on deaf sign languages where their implementation was widespread.
Bimodal bilingualism is an individual or community's bilingual competency in at least one oral language and at least one sign language, which utilize two different modalities. An oral language consists of a vocal-aural modality versus a signed language which consists of a visual-spatial modality. A substantial number of bimodal bilinguals are children of deaf adults (CODA) or other hearing people who learn sign language for various reasons. Deaf people as a group have their own sign language(s) and culture that is referred to as Deaf, but invariably live within a larger hearing culture with its own oral language. Thus, "most deaf people are bilingual to some extent in [an oral] language in some form". In discussions of multilingualism in the United States, bimodal bilingualism and bimodal bilinguals have often not been mentioned or even considered. This is in part because American Sign Language, the predominant sign language used in the U.S., only began to be acknowledged as a natural language in the 1960s. However, bimodal bilinguals share many of the same traits as traditional bilinguals, as well as differing in some interesting ways, due to the unique characteristics of the Deaf community. Bimodal bilinguals also experience similar neurological benefits as do unimodal bilinguals, with significantly increased grey matter in various brain areas and evidence of increased plasticity as well as neuroprotective advantages that can help slow or even prevent the onset of age-related cognitive diseases, such as Alzheimer's and dementia.

Many languages are spoken, or historically have been spoken, in Zimbabwe. Since the adoption of its 2013 Constitution, Zimbabwe has 16 official languages, namely Chewa, Chibarwe, English, Kalanga, Koisan, Nambya, Ndau, Ndebele, Shangani, Shona, sign language, Sotho, Tonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa. The country's main languages are Shona, spoken by only 42% of the population, and Ndebele, spoken by roughly 39%. English is the country's lingua franca, used in government and business and as the main medium of instruction in schools. English is the first language of most white Zimbabweans, and is the second language of a majority of black Zimbabweans. Historically, a minority of white Zimbabweans spoke Afrikaans, Greek, Italian, Polish, and Portuguese, among other languages, while Gujarati and Hindi could be found amongst the country's Indian population. Deaf Zimbabweans commonly use one of several varieties of Zimbabwean Sign Language, with some using American Sign Language. Zimbabwean language data is based on estimates, as Zimbabwe has never conducted a census that enumerated people by language.
Ugandan Sign Language (USL) is the deaf sign language of Uganda.
Deaf Education in Kenya is a constantly changing section of the Kenyan education system that is focused on educating deaf, hard-of-hearing, and hearing-impaired Kenyan students. There are many organizations in Kenya made to protect the rights of Deaf Kenyans and promote progress in deaf education. The state of Kenyan deaf education is constantly changing and improving.
References
- ↑ Aarons & Reynolds, 2003, "South African Sign Language", in Monaghan, ed., Many Ways to be Deaf: International Variation in Deaf Communities