Related Research Articles
Proof of work (PoW) is a form of cryptographic proof in which one party proves to others that a certain amount of a specific computational effort has been expended. Verifiers can subsequently confirm this expenditure with minimal effort on their part. The concept was invented by Moni Naor and Cynthia Dwork in 1993 as a way to deter denial-of-service attacks and other service abuses such as spam on a network by requiring some work from a service requester, usually meaning processing time by a computer. The term "proof of work" was first coined and formalized in a 1999 paper by Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels. The concept was adapted to digital tokens by Hal Finney in 2004 through the idea of "reusable proof of work" using the 160-bit secure hash algorithm 1 (SHA-1).

Bitcoin is the first decentralized cryptocurrency. Nodes in the peer-to-peer bitcoin network verify transactions through cryptography and record them in a public distributed ledger, called a blockchain, without central oversight. Consensus between nodes is achieved using a computationally intensive process based on proof-of-work, called mining, that requires increasing quantities of electricity and guarantees the security of the bitcoin blockchain.

A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
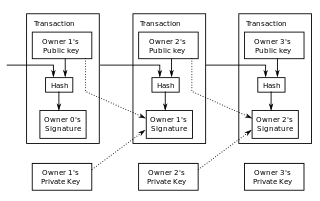
The Bitcoin protocol is the set of rules that govern the functioning of Bitcoin. Its key components and principles are: a peer-to-peer decentralized network with no central oversight; the blockchain technology, a public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions; mining and proof of work, the process to create new bitcoins and verify transactions; and cryptographic security.

Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, a digital asset that uses cryptography to control its creation and management rather than relying on central authorities. Originally designed as a medium of exchange, Bitcoin is now primarily regarded as a store of value. The history of bitcoin started with its invention and implementation by Satoshi Nakamoto, who integrated many existing ideas from the cryptography community. Over the course of bitcoin's history, it has undergone rapid growth to become a significant store of value both on- and offline. From the mid-2010s, some businesses began accepting bitcoin in addition to traditional currencies.

Dogecoin is a cryptocurrency created by software engineers Billy Markus and Jackson Palmer, who decided to create a payment system as a "joke", making fun of the wild speculation in cryptocurrencies at the time. It is considered both the first "meme coin", and more specifically the first "dog coin". Despite its satirical nature, some consider it a legitimate investment prospect. Dogecoin features the face of the Shiba Inu dog from the "doge" meme as its logo and namesake. It was introduced on December 6, 2013, and quickly developed its own online community, reaching a peak market capitalization of over US$85 billion on May 5, 2021. As of 2021, it is the sleeve sponsor of Watford Football Club.
Blockchain.com is a cryptocurrency financial services company. The company began as the first Bitcoin blockchain explorer in 2011 and later created a cryptocurrency wallet that accounted for 28% of bitcoin transactions between 2012 and 2020. It also operates a cryptocurrency exchange and provides institutional markets lending business and data, charts, and analytics.

Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain with smart contract functionality. Ether is the native cryptocurrency of the platform. Among cryptocurrencies, ether is second only to bitcoin in market capitalization. It is open-source software.

Dash is an open source cryptocurrency. It is an altcoin that was forked from the Bitcoin protocol. It is also a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) run by a subset of its users, which are called "masternodes".
A blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records (blocks) that are securely linked together via cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Since each block contains information about the previous block, they effectively form a chain, with each additional block linking to the ones before it. Consequently, blockchain transactions are irreversible in that, once they are recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks.
Monero is a cryptocurrency which uses a blockchain with privacy-enhancing technologies to obfuscate transactions to achieve anonymity and fungibility. Observers cannot decipher addresses trading Monero, transaction amounts, address balances, or transaction histories.

Digital Currency Group (DCG) is a venture capital company focusing on the digital currency market. It is located in Stamford, Connecticut. The company has the subsidiaries Foundry, Genesis, Grayscale Investments, and Luno. It also formerly owned CoinDesk.

Ethereum Classic is a blockchain-based distributed computing platform that offers smart contract (scripting) functionality. It is open source and supports a modified version of Nakamoto consensus via transaction-based state transitions executed on a public Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).

Bitcoin Cash is a cryptocurrency that is a fork of Bitcoin. Bitcoin Cash is a spin-off or altcoin that was created in 2017.
A cryptocurrency bubble is a phenomenon where the market increasingly considers the going price of cryptocurrency assets to be inflated against their hypothetical value. The history of cryptocurrency has been marked by several speculative bubbles.
Cryptocurrency and crime describe notable examples of cybercrime related to theft of cryptocurrencies and some methods or security vulnerabilities commonly exploited. Cryptojacking is a form of cybercrime specific to cryptocurrencies that have been used on websites to hijack a victim's resources and use them for hashing and mining cryptocurrency.
Cryptoeconomics is an evolving economic paradigm for a cross-disciplinary approach to the study of digital economies and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Cryptoeconomics integrates concepts and principles from traditional economics, cryptography, computer science, and game theory disciplines. Just as traditional economics provides a theoretical foundation for traditional financial services, cryptoeconomics provides a theoretical foundation for DeFi services bought and sold via fiat cryptocurrencies, and executed by smart contracts.
Christopher Charles Sherriff Harborne is a British businessman and technology investor based in Thailand. A University of Cambridge and INSEAD graduate, his donations have enabled the founding of INSEAD San Francisco and the creation of a blockchain research fund. He has also donated to Britain's Conservative Party and more recently has been a major donor to Britain's Brexit Party, donating more than £6 million in 2019. He also holds Thai citizenship under the name Chakrit Sakunkrit.
Paxos Trust Company is a New York–based financial institution and technology company specializing in blockchain. The company's product offerings include a cryptocurrency brokerage service, asset tokenization services, and settlement services. ItBit, a bitcoin exchange run by Paxos, was the first bitcoin exchange to be licensed by the New York State Department of Financial Services, granting the company the ability to be the custodian and exchange for customers in the United States.

The environmental effects of bitcoin are significant. Bitcoin mining, the process by which bitcoins are created and transactions are finalized, is energy-consuming and results in carbon emissions as about half of the electricity used is generated through fossil fuels. Moreover, bitcoins are mined on specialized computer hardware with a short lifespan, resulting in electronic waste. The amount of e-waste generated by bitcoin mining is comparable to the one of the Netherlands. Scholars argue that Bitcoin mining could support renewable energy development by utilizing surplus electricity from wind and solar. Bitcoin's environmental impact has attracted the attention of regulators, leading to incentives or restrictions in various jurisdictions.
References
- ↑ How I Built a Bitcoin Empire. Marco Streng, TEDx Trinity College Dublin, 2018. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- 1 2 Iceland is a bitcoin miner's haven, but not everyone is happy. Egill Bjarnason, aljazeera.com, 15 April 2019. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ Corporate. Genesis Group. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ Meet the 28-year-old building a Bitcoin empire (with £10m of computers and a mind-boggling electricity bill). Rory Ross, The Telegraph, 25 January 2018. Retrieved 17 December 2019. (subscription required)
- ↑ Bitcoin 'miners' face fight for survival as new supply halves. Jemima Kelly, Reuters, 8 July 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ The Big Bitcoin Heist. Mark Seal, Vanity Fair, 4 November 2019. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ Bitcoin's wild ride. Anderson Cooper, 60 Minutes, CBS News, 19 May 2019. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- 1 2 How a cloud computing company is helping people mine for bitcoin. Sameepa Shetty, CNBC, 15 December 2017. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ Ethereum miners are renting Boeing 747s to ship graphics cards and AMD shares are soaring. Joon Ian Wong, Quartz, 27 July 2017. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ Iceland's Genesis launches first bitcoin mining fund. Brendan McDermid, Reuters, 3 March 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ HIVE Announces Improved Financial Terms of its Bitcoin Mining Contract, Welcomes Marco Streng, CEO of Genesis Group, as Vice Chairman and Appoints Darcy Daubaras as New CFO. Cision, 20 November 2018. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ Marco Streng. Bloomberg. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ "Man in the Eye: Christopher Harborne", Private Eye , No. 1511, 13 December 2019, p. 10.