
The National Security Act of 1947 was a law enacting major restructuring of the United States government's military and intelligence agencies following World War II. The majority of the provisions of the act took effect on September 18, 1947, the day after the Senate confirmed James Forrestal as the first secretary of defense.

Miracle on 34th Street is a 1947 American Christmas comedy-drama film released by 20th Century Fox, written and directed by George Seaton and based on a story by Valentine Davies. It stars Maureen O'Hara, John Payne, Natalie Wood, and Edmund Gwenn. The story takes place between Thanksgiving Day and Christmas Day in New York City, and focuses on the effect of a department store Santa Claus who claims to be the real Santa. The film has become a perennial Christmas favorite.
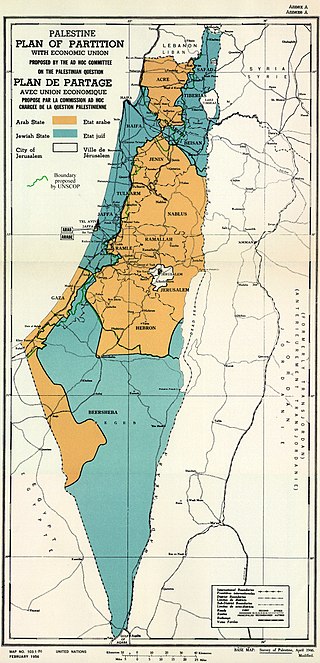
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Resolution 181 (II).
Emperor or Empress of India was a title used by British monarchs from 1 May 1876 to 22 June 1948, that was used to signify their rule over British India, as its imperial head of state. The image of the emperor or empress was used to signify British authority—his or her profile, for instance, appearing on currency, in government buildings, railway stations, courts, on statues etc. "God Save the King" was the national anthem of British India. Oaths of allegiance were made to the emperor or empress and the lawful successors by the governors-general, princes, governors, commissioners in India in events such as imperial durbars.

The Partition of British India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan—which at the time comprised two regions lying on either side of India—is now the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947. The change of political borders notably included the division of two provinces of British India, Bengal and Punjab. The majority Muslim districts in these provinces were awarded to Pakistan and the majority non-Muslim to India. The other assets that were divided included the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Royal Indian Air Force, the Indian Civil Service, the railways, and the central treasury. Self-governing independent India and Pakistan legally came into existence at midnight on 14–15 August 1947.

The Governor-General of India was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom and after Indian independence in 1947, the representative of the British monarch. The office was created in 1773, with the title of Governor-General of the Presidency of Fort William. The officer had direct control only over Fort William but supervised other East India Company officials in India. Complete authority over all of British territory in the Indian subcontinent was granted in 1833, and the official came to be known as the "Governor-General of India".

The Roswell incident was an event that occurred in 1947, pertaining to the recovery of mundane metallic and rubber debris from a military balloon that crashed near Corona, New Mexico by United States Army Air Forces officers from Roswell Army Air Field. Decades later, conspiracy theories began claiming that the debris involved a flying saucer and that the truth had been covered up by the United States government. On July 8, 1947, Roswell Army Air Field issued a press release stating that they had recovered a "flying disc". The Army quickly retracted the statement and said instead that the crashed object was a conventional weather balloon. In 1994, the United States Air Force published a report identifying the crashed object as a nuclear test surveillance balloon from Project Mogul.

The Indo-Pakistani War of 1947–1948, or the First Kashmir War, was a war fought between India and Pakistan over the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir from 1947 to 1948. It was the first of four Indo-Pakistani wars that was fought between the two newly independent nations. Pakistan precipitated the war a few weeks after its independence by launching tribal lashkar (militias) from Waziristan, in an effort to capture Kashmir and to preempt the possibility of its ruler joining India. The inconclusive result of the war still affects the geopolitics of both countries.

The Serie B, currently named Serie BKT for sponsorship reasons, is the second-highest division in the Italian football league system after the Serie A. It has been operating for over ninety years since the 1929–30 season. It had been organized by Lega Calcio until 2010, when the Lega Serie B was created for the 2010–11 season. Common nicknames for the league are campionato cadetto and cadetteria, since cadetto is the Italian name for junior or cadet.

A princely state was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the British crown.

Operation HIGHJUMP, officially titled The United States Navy Antarctic Developments Program, 1946–1947,, was a United States Navy (USN) operation to establish the Antarctic research base Little America IV. The operation was organized by Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd, Jr., USN (Ret), Officer in Charge, Task Force 68, and led by Rear Admiral Ethan Erik Larson, USN, Commanding Officer, Task Force 68. Operation HIGHJUMP commenced 26 August 1946 and ended in late February 1947. Task Force 68 included 4,700 men, 13 ships, and 33 aircraft.

The Indian Independence Act 1947 [1947 CHAPTER 30 10 and 11 Geo 6] is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that partitioned British India into the two new independent dominions of India and Pakistan. The Act received Royal Assent on 18 July 1947 and thus modern-day India and Pakistan, comprising west and east regions, came into being on 15 August.

The Constituent Assembly of India was elected to frame the Constitution of India. It was elected by the 'Provincial Assembly'. Following India's independence from the British rule in 1947, its members served as the nation's first Parliament as the 'Provisional Parliament of India'.

Independence Day is celebrated annually on 15 August as a public holiday in India commemorating the nation's independence from the United Kingdom on 15 August 1947, the day when the provisions of the Indian Independence Act, which transferred legislative sovereignty to the Indian Constituent Assembly, came into effect. India retained King George VI as head of state until its transition to a republic, when the Constitution of India came into effect on 26 January 1950 and replaced the dominion prefix, Dominion of India, with the enactment of the sovereign law Constitution of India. India attained independence following the independence movement noted for largely non-violent resistance and civil disobedience.

The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India, was an independent dominion in the British Commonwealth of Nations existing between 15 August 1947 and 26 January 1950. Until its independence, India had been ruled as an informal empire by the United Kingdom. The empire, also called the British Raj and sometimes the British Indian Empire, consisted of regions, collectively called British India, that were directly administered by the British government, and regions, called the princely states, that were ruled by Indian rulers under a system of paramountcy. The Dominion of India was formalised by the passage of the Indian Independence Act 1947, which also formalised an independent Dominion of Pakistan—comprising the regions of British India that are today Pakistan and Bangladesh. The Dominion of India remained "India" in common parlance but was geographically reduced. Under the Act, the British government relinquished all responsibility for administering its former territories. The government also revoked its treaty rights with the rulers of the princely states and advised them to join in a political union with India or Pakistan. Accordingly, the British monarch's regnal title, "Emperor of India," was abandoned.

The British Raj was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; it is also called Crown rule in India, or Direct rule in India, and lasted from 1858 to 1947. The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially.

The Government of Japan consists of legislative, executive and judiciary branches and is based on popular sovereignty. The Government runs under the framework established by the Constitution of Japan, adopted in 1947. It is a unitary state, containing forty-seven administrative divisions, with the Emperor as its Head of State. His role is ceremonial and he has no powers related to Government. Instead, it is the Cabinet, comprising the Ministers of State and the Prime Minister, that directs and controls the Government and the civil service. The Cabinet has the executive power and is formed by the Prime Minister, who is the Head of Government. The Prime Minister is nominated by the National Diet and appointed to office by the Emperor.
This is a list of electoral district results for the 1947 New South Wales state election.
There were twelve elections in 1947 to the United States House of Representatives during the 80th United States Congress.

The Twin Falls saucer hoax was a hoaxed flying disc discovered in Twin Falls, Idaho, United States, on July 11, 1947. Amid a nationwide wave of alleged "flying disc" sightings, residents of Twin Falls reported recovering a 30 in (76 cm) "disc". FBI and Army officials took possession of the disc and quickly proclaimed the object to be a hoax. Press reported that local teenagers admitted to perpetrating the hoax.

















