Related Research Articles

Sir Robert Tony Watson CMG FRS is a British chemist who has worked on atmospheric science issues including ozone depletion, global warming and paleoclimatology since the 1980s. Most recently, he is lead author of the February 2021 U.N. report Making Peace with Nature.

There is a strong scientific consensus that the Earth is warming and that this warming is mainly caused by human activities. This consensus is supported by various studies of scientists' opinions and by position statements of scientific organizations, many of which explicitly agree with the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) synthesis reports.
An ecological or environmental crises occurs when changes to the environment of a species or population destabilizes its continued survival. Some of the important causes include:

The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an independent international research institute located in Laxenburg, near Vienna in Austria, founded as an East-West scientific cooperation initiative during the Cold War. Through its research programs and initiatives, the institute conducts policy-oriented interdisciplinary research into issues too large or complex to be solved by a single country or academic discipline. These include climate change, energy security, population aging, and sustainable development. The results of IIASA research and the expertise of its researchers are made available to policymakers worldwide to help them make informed and evidence-based policies.

Climate change affects the physical environment, ecosystems and human societies. Changes in the climate system include an overall warming trend, more extreme weather and rising sea levels. These in turn impact nature and wildlife, as well as human settlements and societies. The effects of human-caused climate change are broad and far-reaching. This is especially so if there is no significant climate action. Experts sometimes describe the projected and observed negative impacts of climate change as the climate crisis.

Environmental vegetarianism is the practice of vegetarianism that is motivated by the desire to create a sustainable diet, which avoids the negative environmental impact of meat production. Livestock as a whole is estimated to be responsible for around 15% of global greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, significant reduction in meat consumption has been advocated by, among others, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change in their 2019 special report and as part of the 2017 World Scientists' Warning to Humanity.

A sustainable food system is a type of food system that provides healthy food to people and creates sustainable environmental, economic, and social systems that surround food. Sustainable food systems start with the development of sustainable agricultural practices, development of more sustainable food distribution systems, creation of sustainable diets, and reduction of food waste throughout the system. Sustainable food systems have been argued to be central to many or all 17 Sustainable Development Goals.
The work of the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research – UFZ covers both basic research and applied research.
Dennis Teel Avery was the director of the Center for Global Food Issues at the Hudson Institute, where he edited Global Food Quarterly. He died on June 20, 2020, at the age of 83.
The environmental impact of agriculture is the effect that different farming practices have on the ecosystems around them, and how those effects can be traced back to those practices. The environmental impact of agriculture varies widely based on practices employed by farmers and by the scale of practice. Farming communities that try to reduce environmental impacts through modifying their practices will adopt sustainable agriculture practices. The negative impact of agriculture is an old issue that remains a concern even as experts design innovative means to reduce destruction and enhance eco-efficiency. Though some pastoralism is environmentally positive, modern animal agriculture practices tend to be more environmentally destructive than agricultural practices focused on fruits, vegetables and other biomass. The emissions of ammonia from cattle waste continue to raise concerns over environmental pollution.

Anne Larigauderie is a French ecologist. She is currently the Executive Secretary of the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES). She was previously the Head of Science in Society at ICSU, the International Council for Science, and the executive director of DIVERSITAS, the international scientific programme dedicated to biodiversity science, under the auspices of ICSU, and UNESCO.

The Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) is an intergovernmental organization established to improve the interface between science and policy on issues of biodiversity and ecosystem services. It is intended to serve a similar role to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.

Cowspiracy: The Sustainability Secret is a 2014 American documentary film produced and directed by Kip Andersen and Keegan Kuhn. The film explores the impact of animal agriculture on the environment—examining such environmental concerns as climate change, water use, deforestation, and ocean dead zones—and investigates the policies of several environmental organizations on the issue.

The contributions of women in climate change have received increasing attention in the early 21st century. Feedback from women and the issues faced by women have been described as "imperative" by the United Nations and "critical" by the Population Reference Bureau. A report by the World Health Organization concluded that incorporating gender-based analysis would "provide more effective climate change mitigation and adaptation."
Lindiwe Sibanda Majele (born 1963) is a Zimbabwean professor, scientist, policy advocate and influencer on food systems. She currently serves as director and chair of the ARUA Centre of Excellence in Sustainable Food Systems (ARUA-SFS) at the University of Pretoria in Pretoria, South Africa as well as founder and managing director of Linds Agricultural Services Pvt Ltd. in Harare, Zimbabwe. She is currently a board member of Nestlé where she is also a member of the Sustainability Committee.

The planetary health diet is a flexitarian diet created by the EAT-Lancet commission as part of a report released in The Lancet on 16 January 2019. The aim of the report and the diet it developed is to create dietary paradigms that have the following aims:
The Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services is a report by the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, on the global state of biodiversity. A summary for policymakers was released on 6 May 2019. The report states that, due to human impact on the environment in the past half-century, the Earth's biodiversity has suffered a catastrophic decline unprecedented in human history, as an estimated 82 percent of wild mammal biomass has been lost. The report estimates that there are 8 million animal and plant species on Earth, with the majority represented by insects. Out of those 8 million species, 1 million are threatened with extinction, including 40 percent of amphibians, almost a third of reef-building corals, more than a third of marine mammals, and 10 percent of all insects.

The United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Special Report on Climate Change and Land (SRCCL), also known as the "Special Report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems", is a landmark study from 2019 by 107 experts from 52 countries. The SRCCL provides a comprehensive overview of the entire land-climate system for the first time and decided to enlist land as a "critical resource". The IPCC's 50th session (IPCC-50) formally adopted the SRCCL's Summary for policymakers (SPM) and approved the underlying report. The SPM and the full text of Special Report on Climate Change and Land—in an unedited form—were released on 8 August 2019. The report is over 1,300 pages long and includes the work of 107 experts from 52 countries.
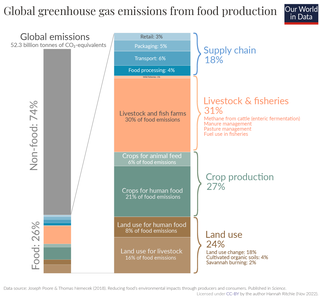
The amount of greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture is significant: The agriculture, forestry and land use sector contribute between 13% and 21% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Agriculture contributes towards climate change through direct greenhouse gas emissions and by the conversion of non-agricultural land such as forests into agricultural land. Emissions of nitrous oxide and methane make up over half of total greenhouse gas emission from agriculture. Animal husbandry is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions.
Delia Grace is an epidemiologist and a veterinarian. Grace joined the University of Greenwich in May 2020 as Professor of Food Safety Systems at the Natural Resources Institute. She is also Joint Appointed Scientist, Animal and Human Health Program at the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), Nairobi, Kenya.
References
- ↑ Marín M (25 April 2021). "Mario Herrero, el científico costarricense que Reuters colocó en el puesto 10 de los 1.000 más influyentes del mundo en cambio climático" [Mario Herrero, the Costa Rican scientist who Reuters placed in the 10th position of the 1,000 most influential in the world on climate change]. El Observador CR (in Spanish).
- 1 2 3 4 "Mario Herrero". CALS. 25 April 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ↑ "Global food systems expert joins Cornell". Cornell Chronicle. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ↑ "Team – FSCI". www.foodcountdown.org. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ↑ "Mario.Herrero | IPBES secretariat". www.ipbes.net. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ↑ "Mario Herrero". EAT. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ↑ "about Us". GBADS - Global Burden of Animal Diseases. 17 February 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ↑ Nations, United. "Food Systems Summit". United Nations. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ↑ "Explore the @Reuters Hot List of 1,000 top climate scientists". Reuters. 20 April 2021. Retrieved 20 June 2023.