
The Amesbury Archer is an early Bronze Age man whose grave was discovered during excavations at the site of a new housing development in Amesbury near Stonehenge. The grave was uncovered in May 2002. The man was middle aged when he died, estimated between 35 and 45, and is believed to date from about 2300 BC. He is nicknamed "the Archer" because of the many arrowheads buried with him. The grave contained more artefacts than any other early British Bronze Age burial, including the earliest known gold objects ever found in England. It was the first evidence of a very high status and wealth expressed in a burial from that time. Previously, Bronze Age society had been assumed not to have been particularly hierarchical.

A menhir, standing stone, orthostat, or lith is a large upright stone, emplaced in the ground by humans, typically dating from the European middle Bronze Age. They can be found individually as monoliths, or as part of a group of similar stones. Menhirs' size can vary considerably, but they often taper toward the top.

A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
Caroline Ann Tuke Malone is a British academic and archaeologist. She was Professor of Prehistory at Queen's University, Belfast from 2013 and is now emeritus professor.

Swinside, which is also known as Sunkenkirk and Swineshead, is a stone circle lying beside Swinside Fell, part of Black Combe in southern Cumbria, North West England. One of around 1,300 recorded stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany, it was constructed as a part of a megalithic tradition that lasted from 3,300 to 900 BC, during what archaeologists categorise as the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Ages.

Despite its small size, the population of Jersey is made of people with a diverse range of religions and beliefs. Traditionally seen as a Christian island, Jersey's established church is the Church of England, and Anglicanism and Catholicism are practised on the island in roughly equal numbers. Together, these religions account for around half the population of Jersey. Other denominations of Christianity and other religions such as Islam, Judaism, Sikhism, and Buddhism account for handfuls of people on the island. In recent years, irreligion has been an increasing force in Jersey, with two fifths of the population identifying as having no religion. This number rises to 52% for Jersey people under 35.

The Société Jersiaise is a learned society in Jersey which was founded in 1873, in the manner of similar county societies in the United Kingdom and Sociétés Savantes in France for the purposes of:

Prehistoric Hong Kong is the period between the arrival of the first humans in Hong Kong and the start of recorded Chinese history during the Han dynasty. The history of the southern region is reckoned to have been first recorded in 214 BC with Qin Shi Huang conquering the Baiyue and creating the Jiaozhou province.

The dolmens of Jersey are neolithic sites, including dolmens, in Jersey. They range over a wide period, from around 4800 BC to 2250 BC, these dates covering the periods roughly designated as Neolithic, or “new stone age”, to Chalcolithic, or “copper age”.

La Hougue Bie is a historic site, with museum, in the Jersey parish of Grouville. La Hougue Bie is depicted on the 2010 issue Jersey 1 pound note.
Christopher John Scarre, FSA is an academic and writer in the fields of archaeology, pre-history and ancient history. He is Professor of Archaeology at the University of Durham and was head of its archaeology department 2010-2013.

The prehistory of Corsica is analogous to the prehistories of the other islands in the Mediterranean Sea, such as Sicily, Sardinia, Malta and Cyprus, which could only be accessed by boat and featured cultures that were to some degree insular; that is, modified from the traditional Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic and Chalcolithic of European prehistoric cultures. The islands of the Aegean Sea and Crete early developed Bronze Age civilizations and are accordingly usually treated under those categories. Stone Age Crete however shares some of the features of the prehistoric Mediterranean islands.

La Motte is a tidal island, and listed archaeological site, also known as Green Island, located in the Vingtaine de Samarès in the parish of St Clement on the south-east coast of Jersey, Channel Islands.
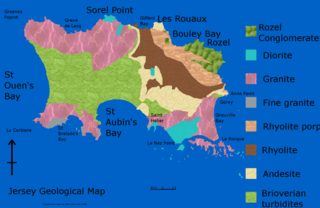
The geology of Jersey is characterised by the Late Proterozoic Brioverian volcanics, the Cadomian Orogeny, and only small signs of later deposits from the Cambrian and Quaternary periods. The kind of rocks go from conglomerate to shale, volcanic, intrusive and plutonic igneous rocks of many compositions, and metamorphic rocks as well, thus including most major types.
Warwick James Rodwell is an archaeologist, architectural historian and academic. He was lately Visiting Professor in the Department of Archaeology, University of Reading, and is Consultant Archaeologist to Westminster Abbey, where he is also a member of the College of St Peter in Westminster. He is the author of many books and articles, including the standard textbook on church archaeology. He is a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London, the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland and the Royal Historical Society.

Archaeology is promoted in Jersey by the Société Jersiaise and by Jersey Heritage. Promotion in the Bailiwick of Guernsey being undertaken by La Société Guernesiaise, Guernsey Museums, the Alderney Society with World War II work also undertaken by Festung Guernsey.
Barbara Bender is an anthropologist and archaeologist. She is currently Emeritus Professor of Heritage Anthropology at University College London.











